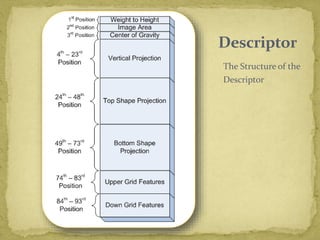
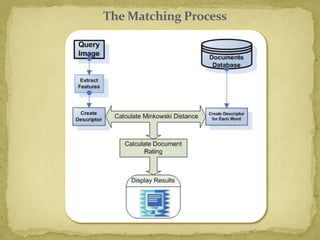
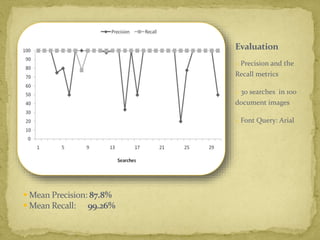
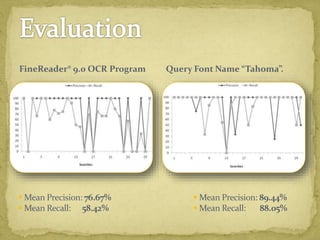
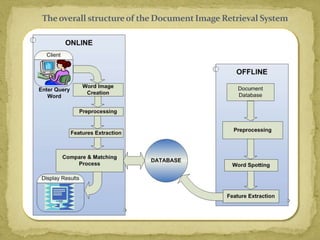
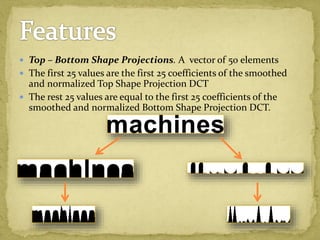
The document discusses advancements in document image retrieval systems, focusing on the challenges posed by the rapid increase in multimedia data. It outlines a method for processing document images using techniques like binarization, connected components analysis, and feature extraction, resulting in high precision and recall rates. The proposed system outperforms existing OCR solutions by effectively suppressing noise and variations across different fonts.







![[0,0,0,1195 ,0,0,0,0,0,0]
[0,0,0,1 ,0,0,0,0,0,0]
[0,0,0,0 ,0,0,0, 598 , 50 , 33 ]
[0,0,0,0 ,0,0,0,1,1,0]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/developingdocumentimageretrievalsystem-101024115518-phpapp01/85/Developing-Document-Image-Retrieval-System-10-320.jpg)