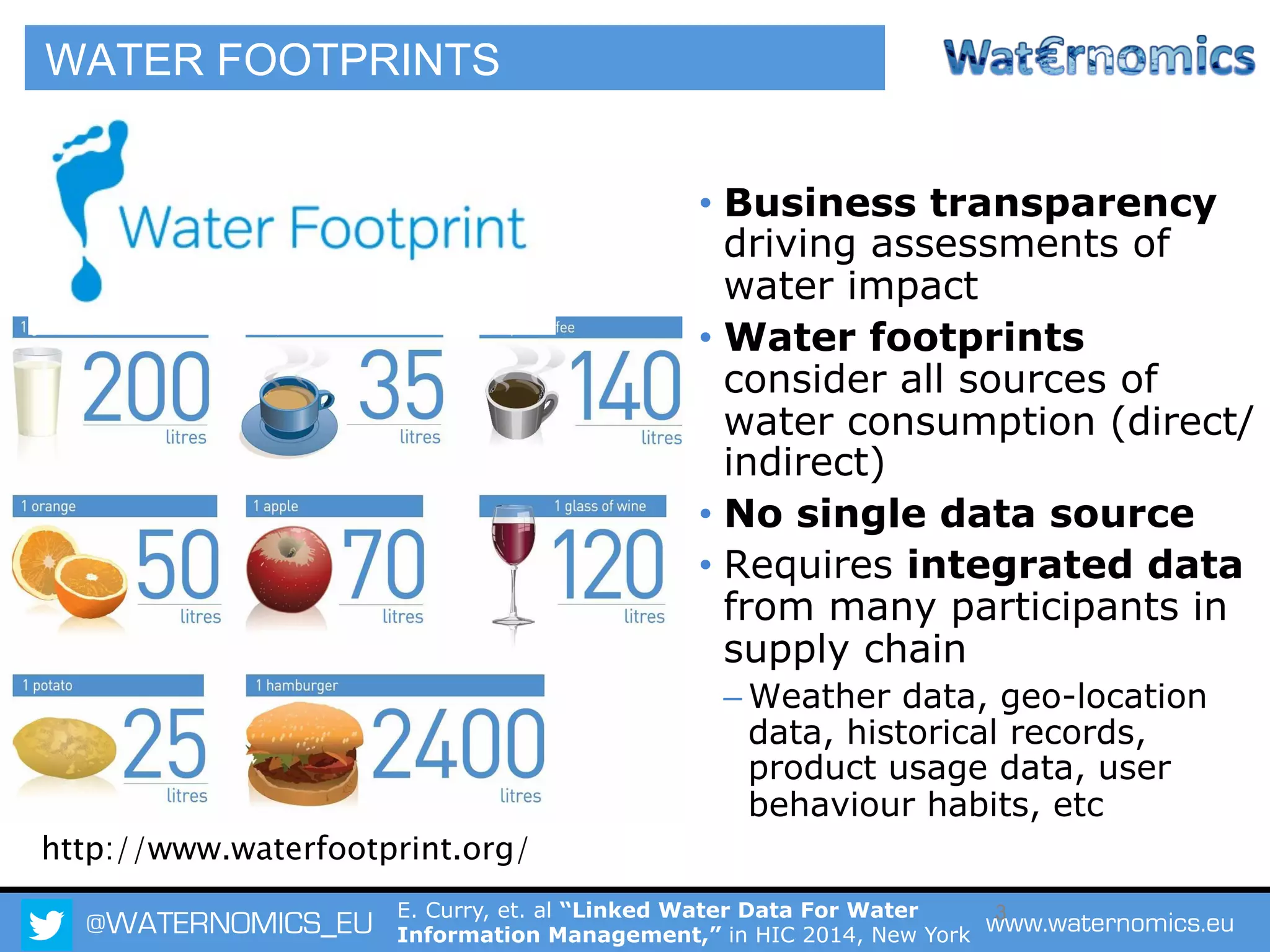
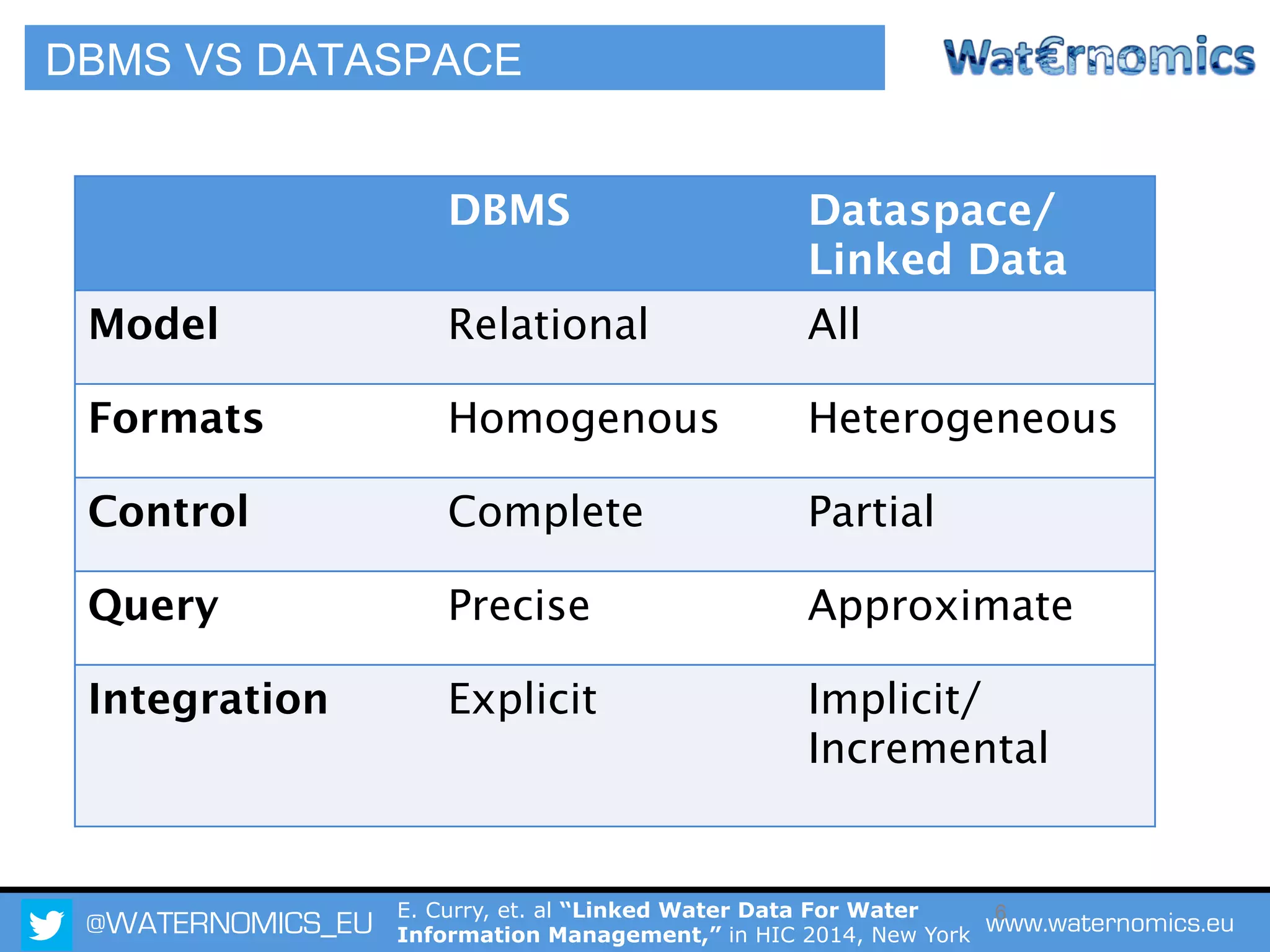
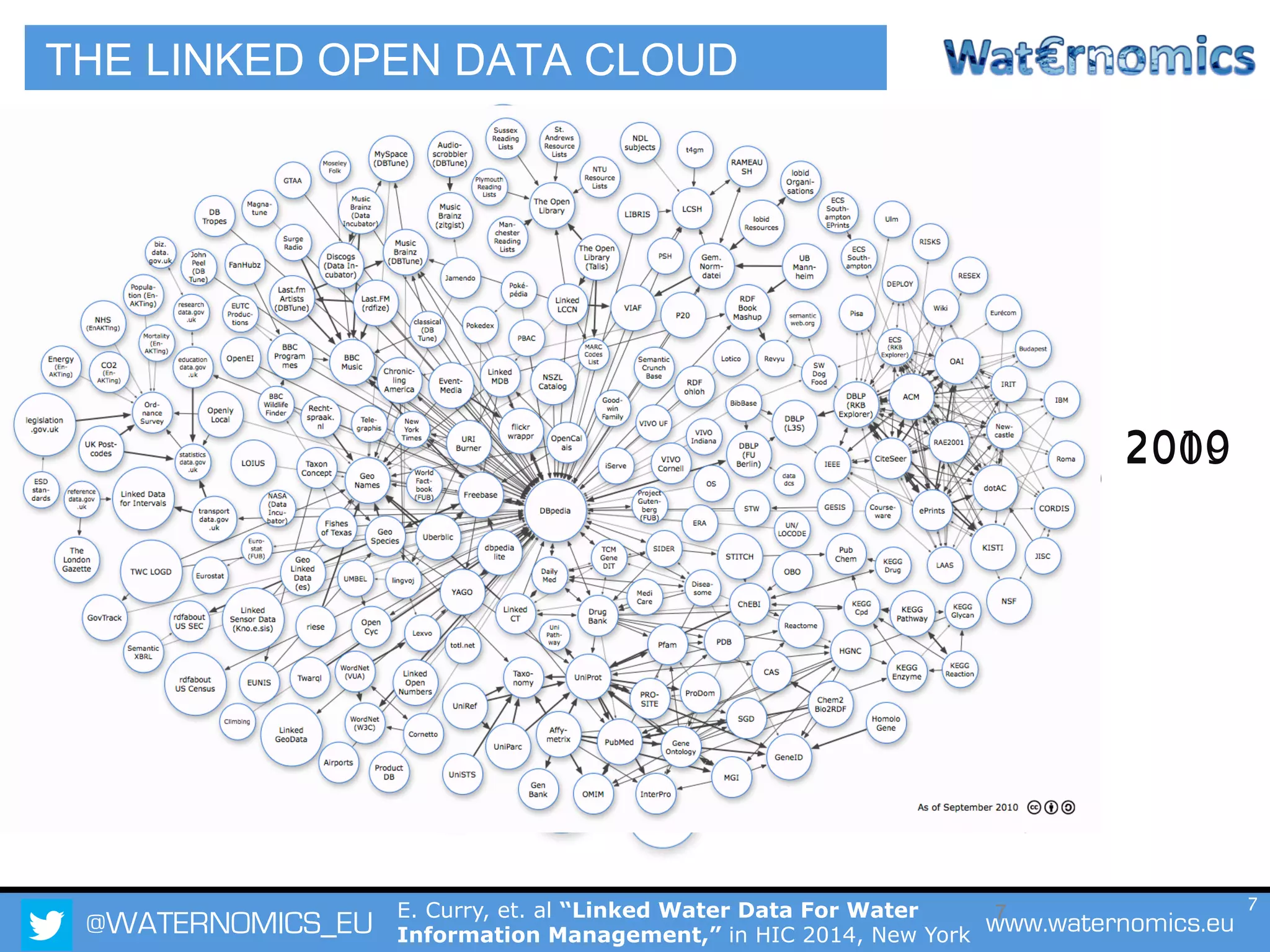
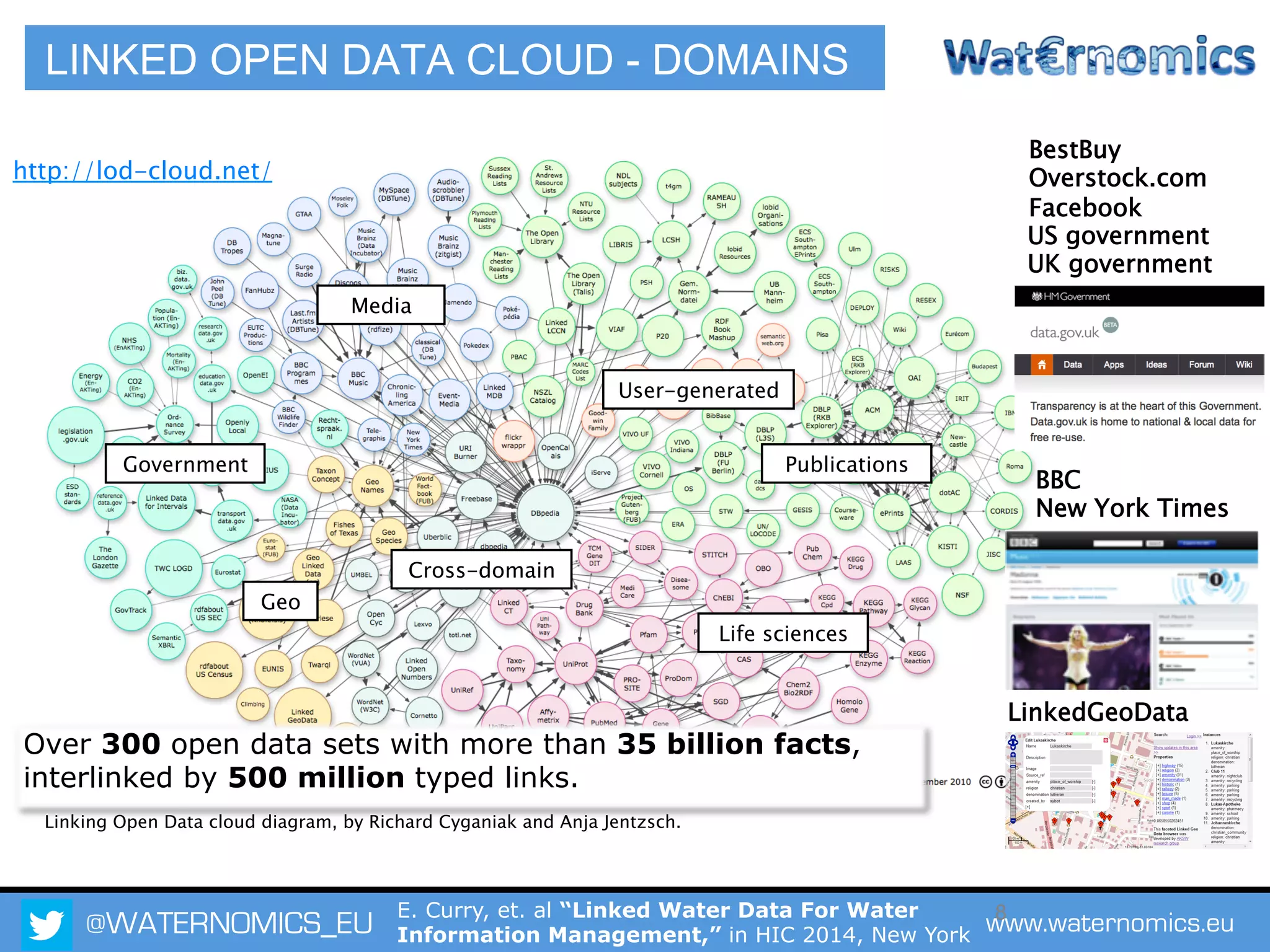
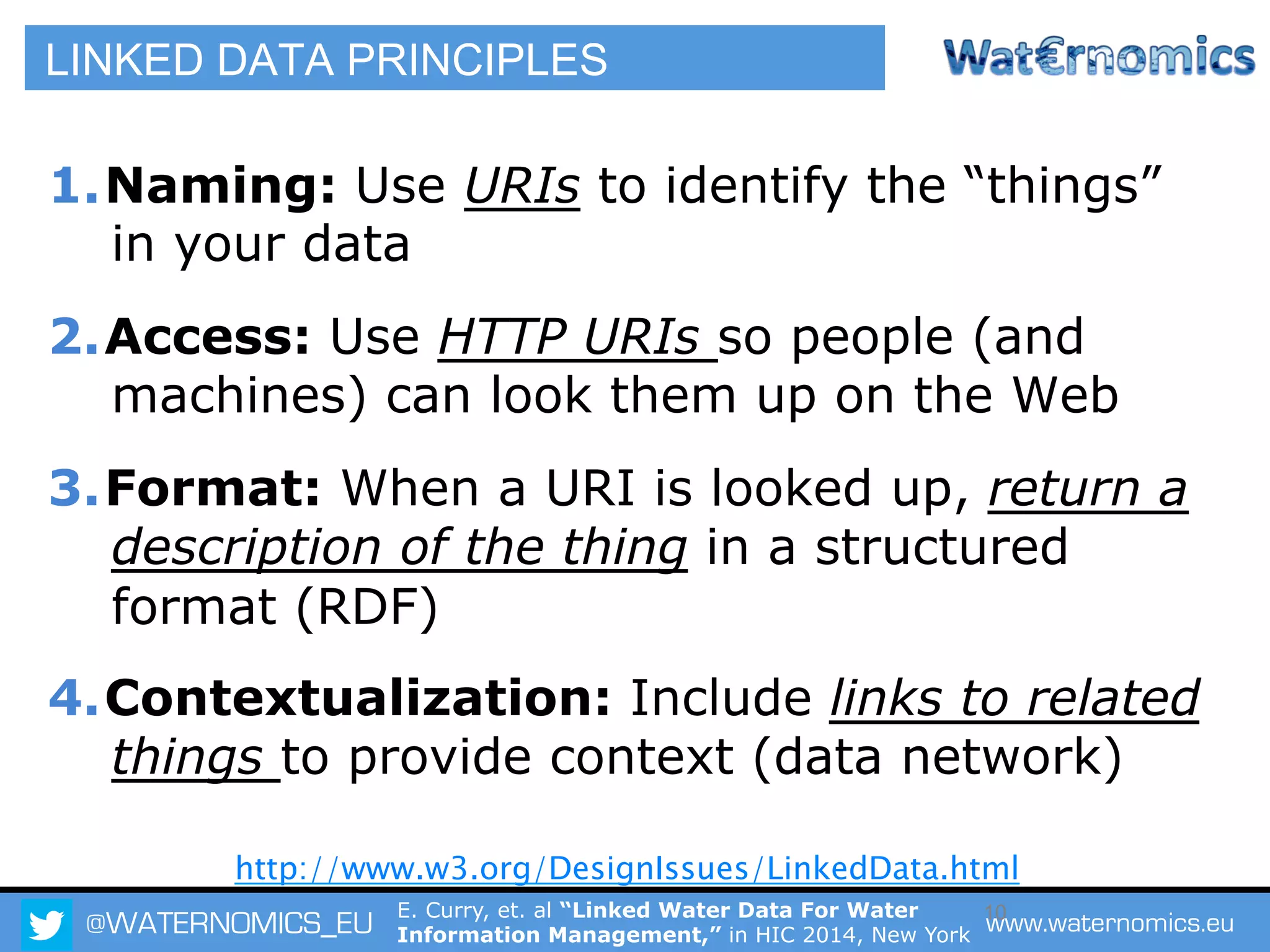
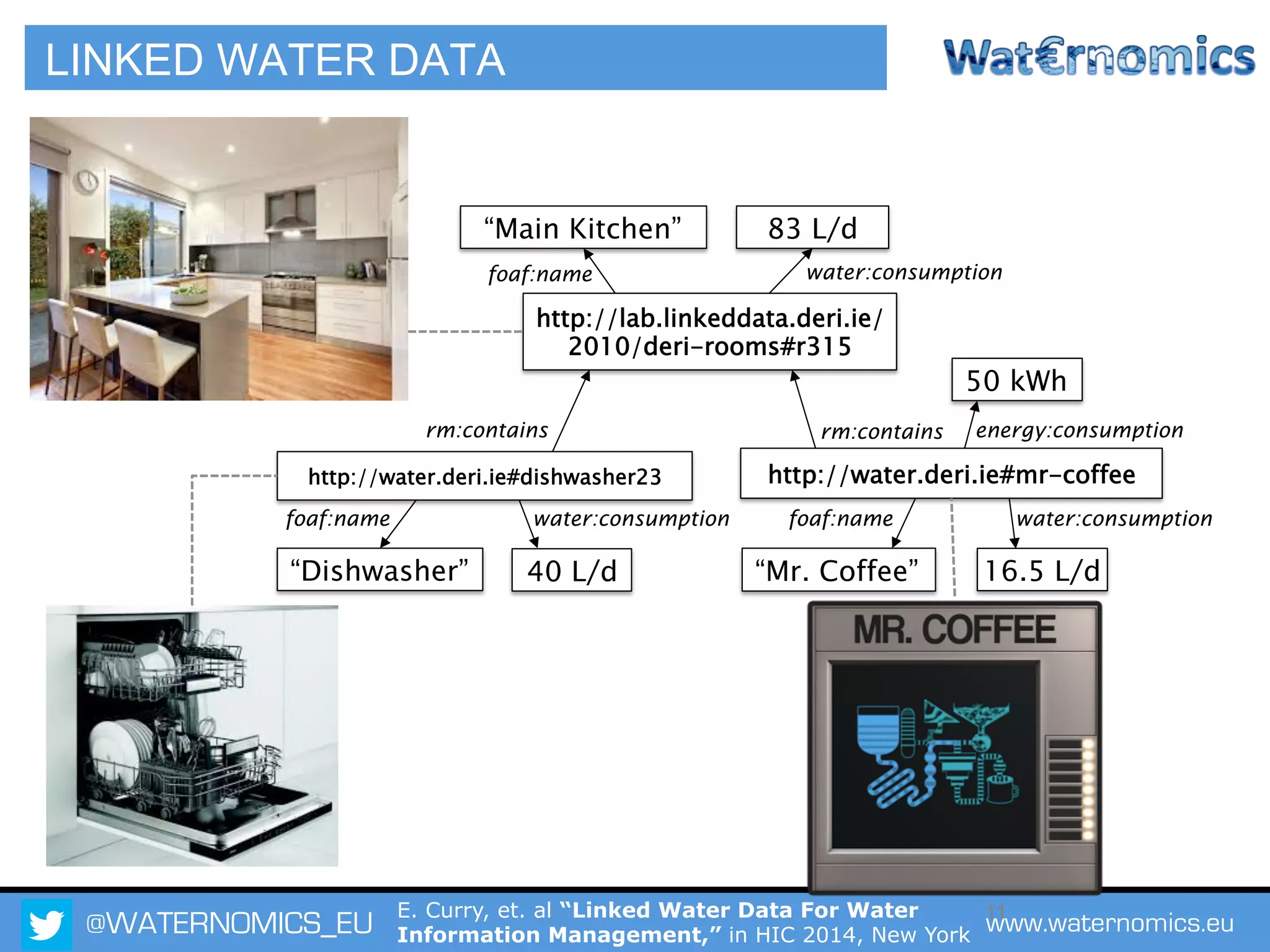
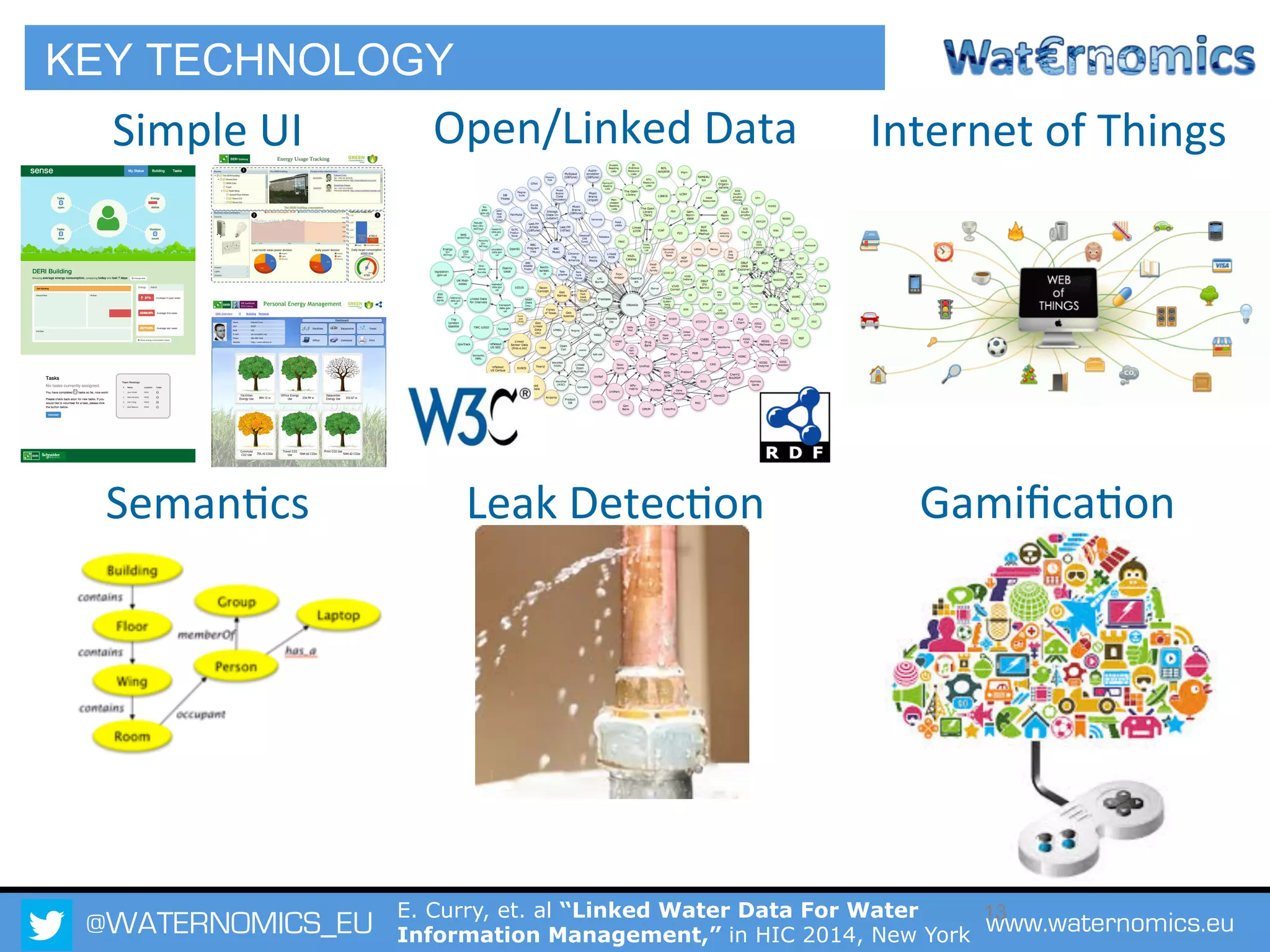
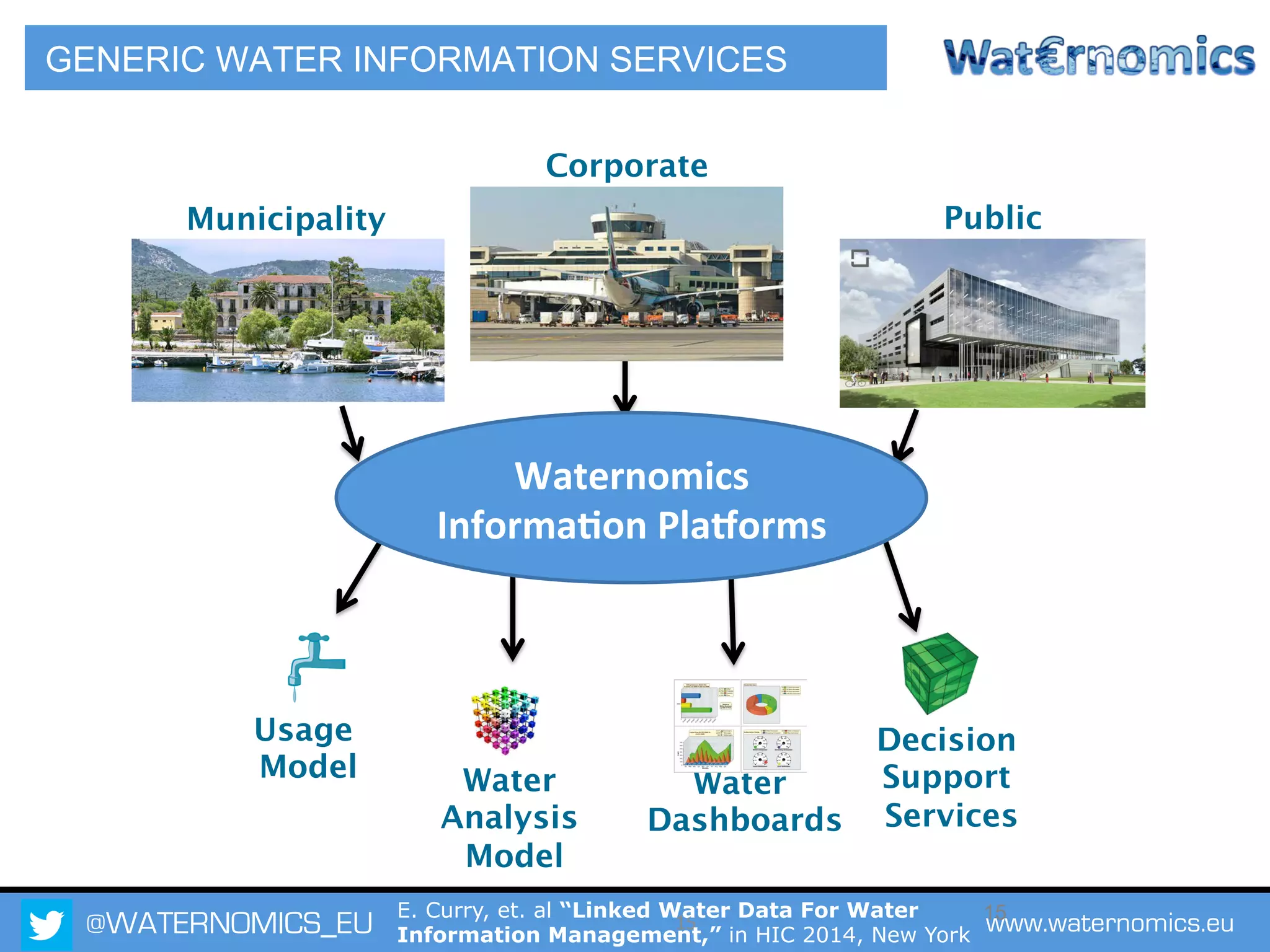
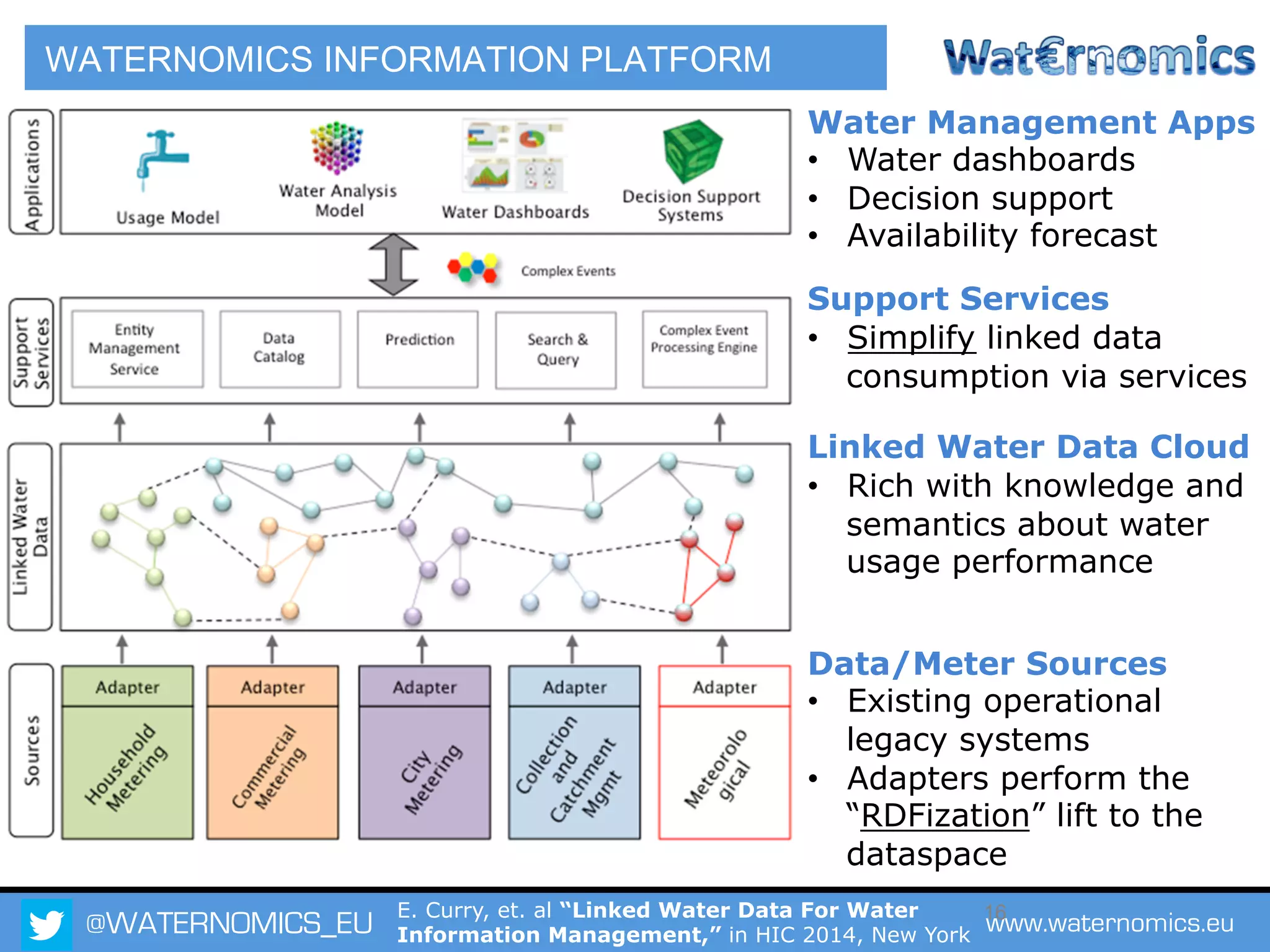
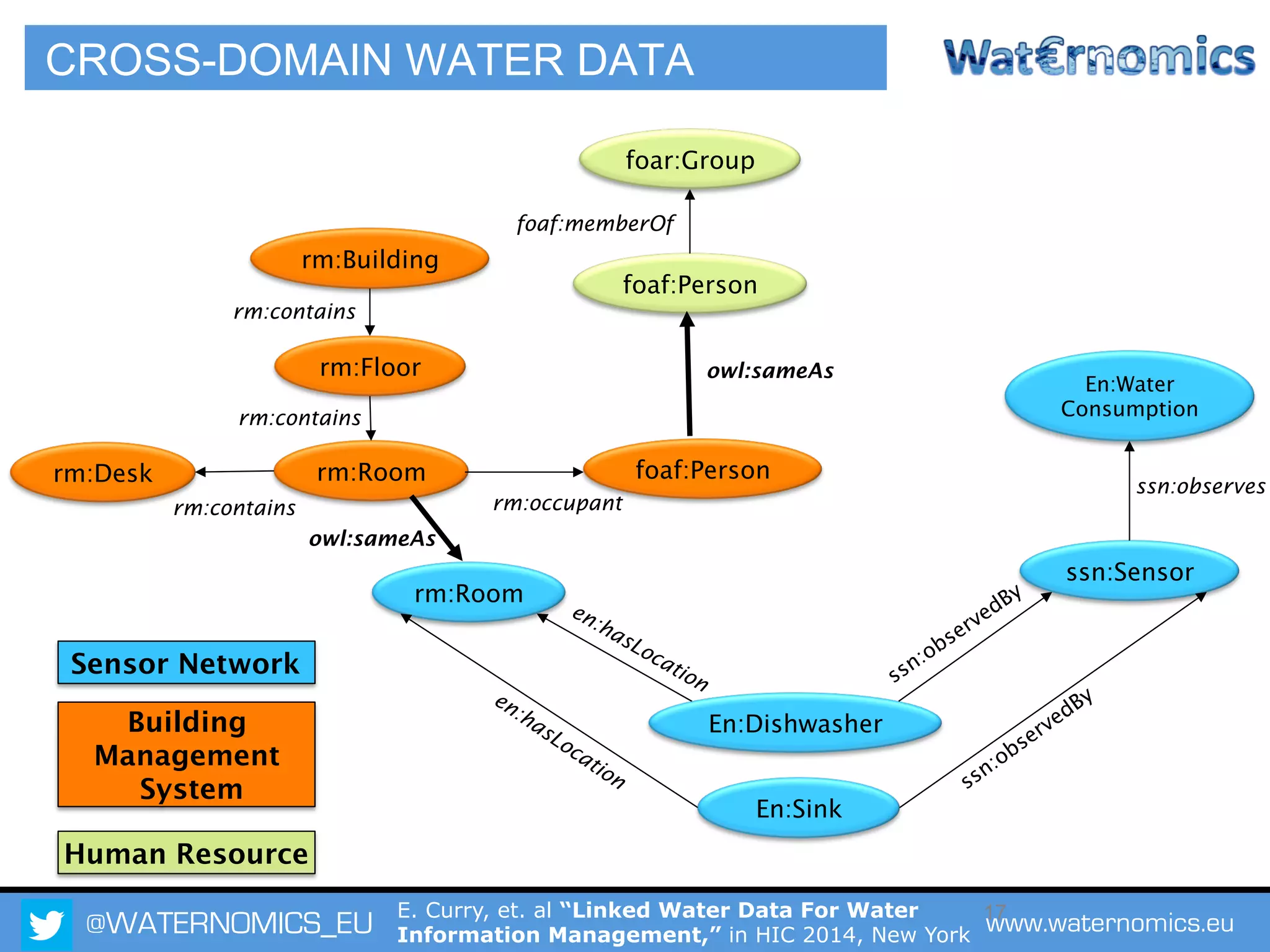
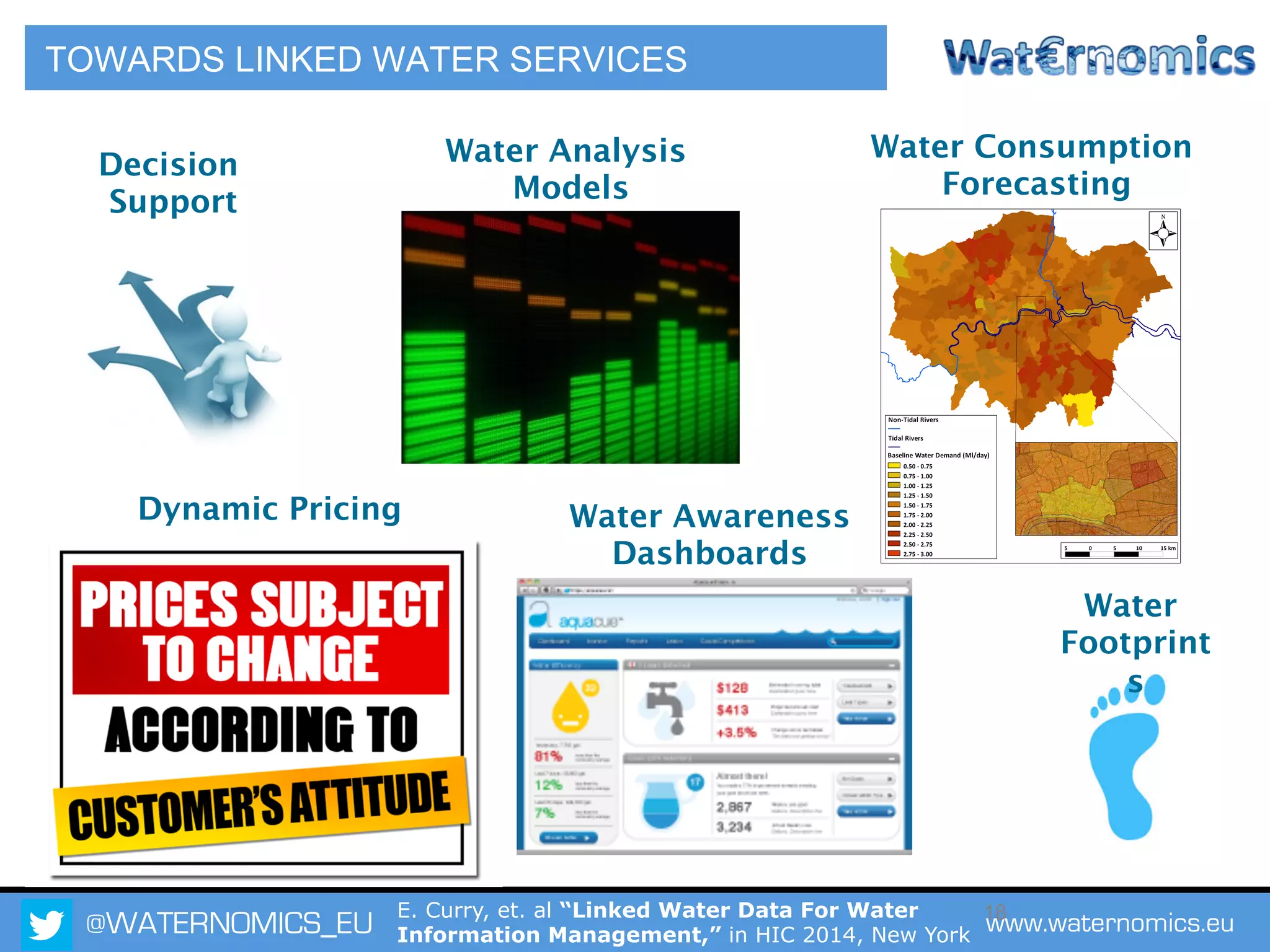
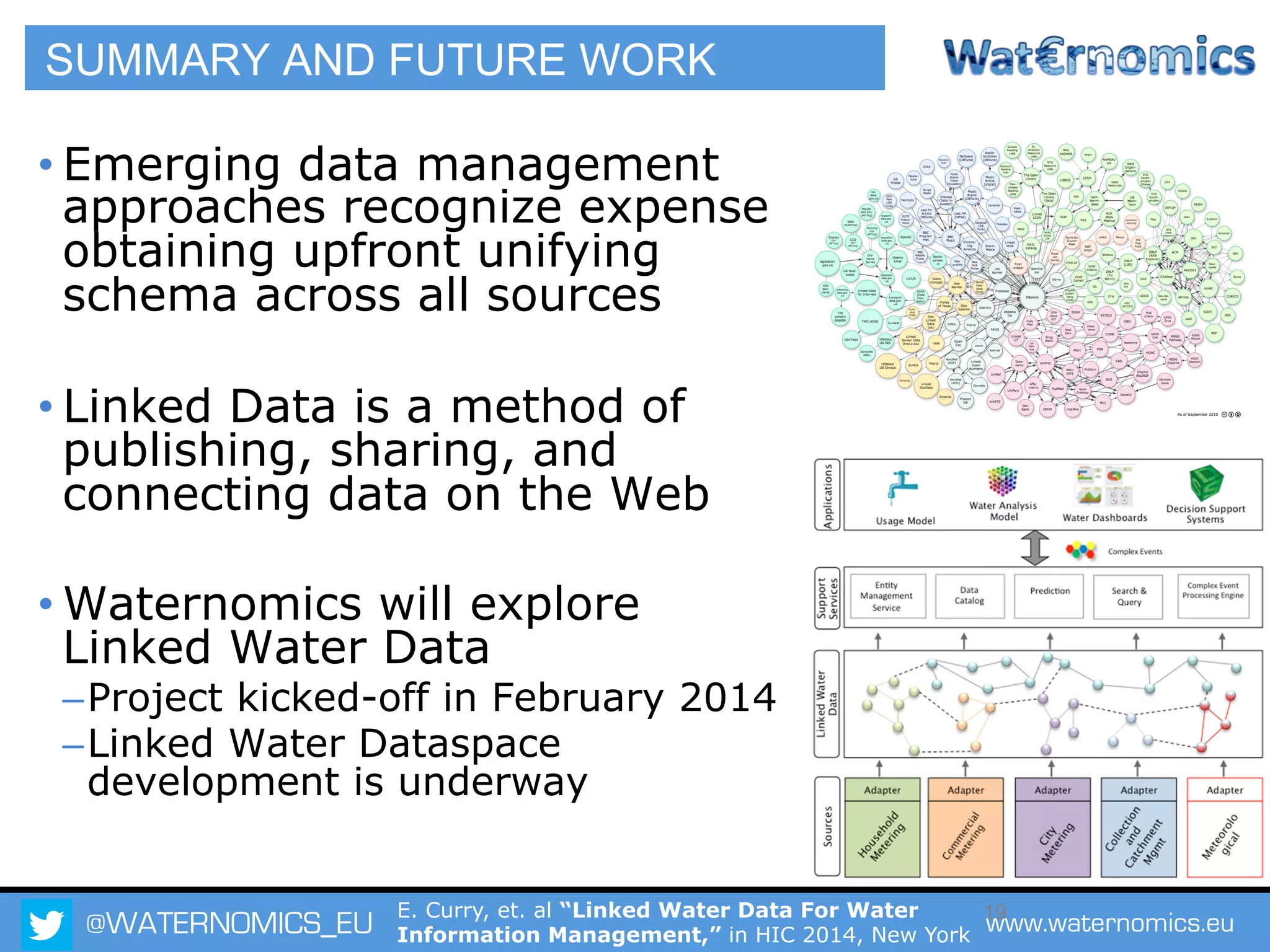
The Waternomics project aims to enhance water management through the integration and sharing of linked water data, utilizing new technologies and methodologies. It seeks to empower consumers and corporations with personalized water information, promoting efficient water usage and informed decision-making. The project will demonstrate its impact through pilot programs across various end-users, including domestic households and corporate entities.