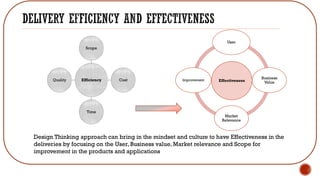
The presentation discusses how design thinking can improve delivery effectiveness and efficiency. It outlines the typical design thinking model and how various roles can use it. It also discusses perceptions of design thinking and challenges teams face in adopting it. The document provides details on how design thinking focuses on the user, business value, market relevance, and improvement opportunities. It provides guidance on identifying user personas, understanding needs, ideating solutions, and validating ideas through quick prototypes and user testing.