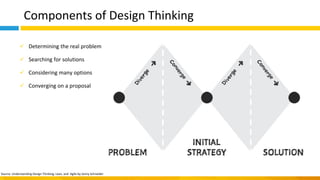
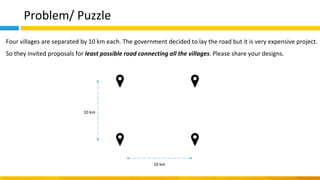
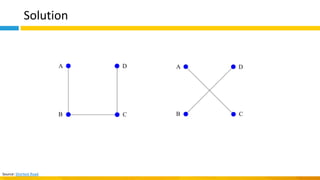
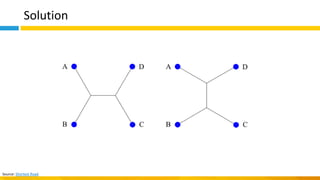
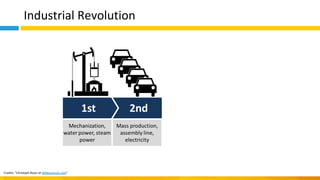
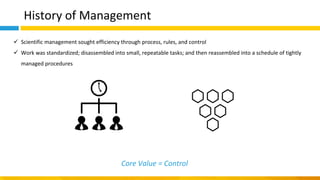
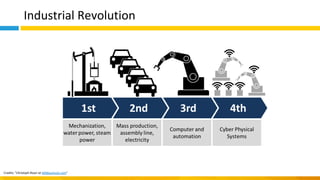
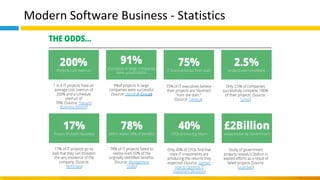
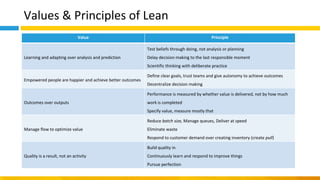
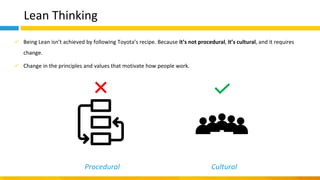
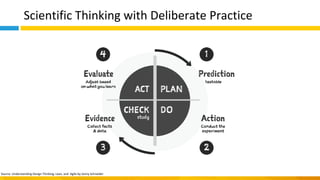
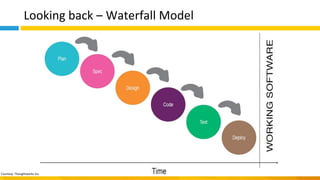
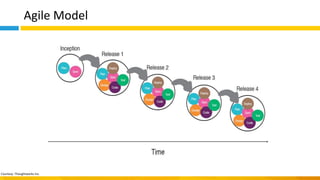
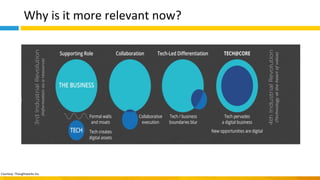
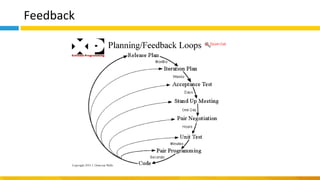
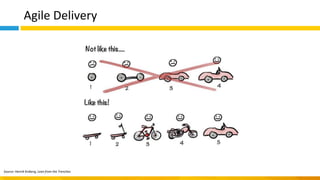
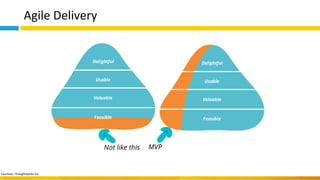
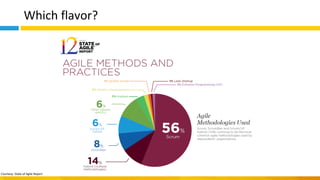
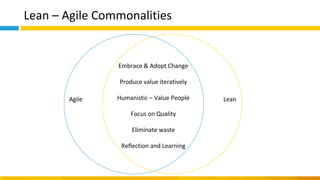
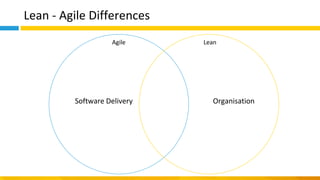
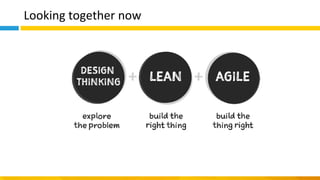
This document discusses principles of design thinking, lean, and agile thinking. It provides an overview of each approach including definitions, histories, key aspects, and differences. Design thinking focuses on exploring problems and finding innovative solutions through techniques like determining real problems and considering many options. Lean emphasizes continuous improvement, reducing waste, and respecting people. Agile thinking values planning for and assuming change through practices like regular feedback and iterative delivery. The document argues that adopting a combination of these approaches through principles like embracing change and focusing on quality is most effective.