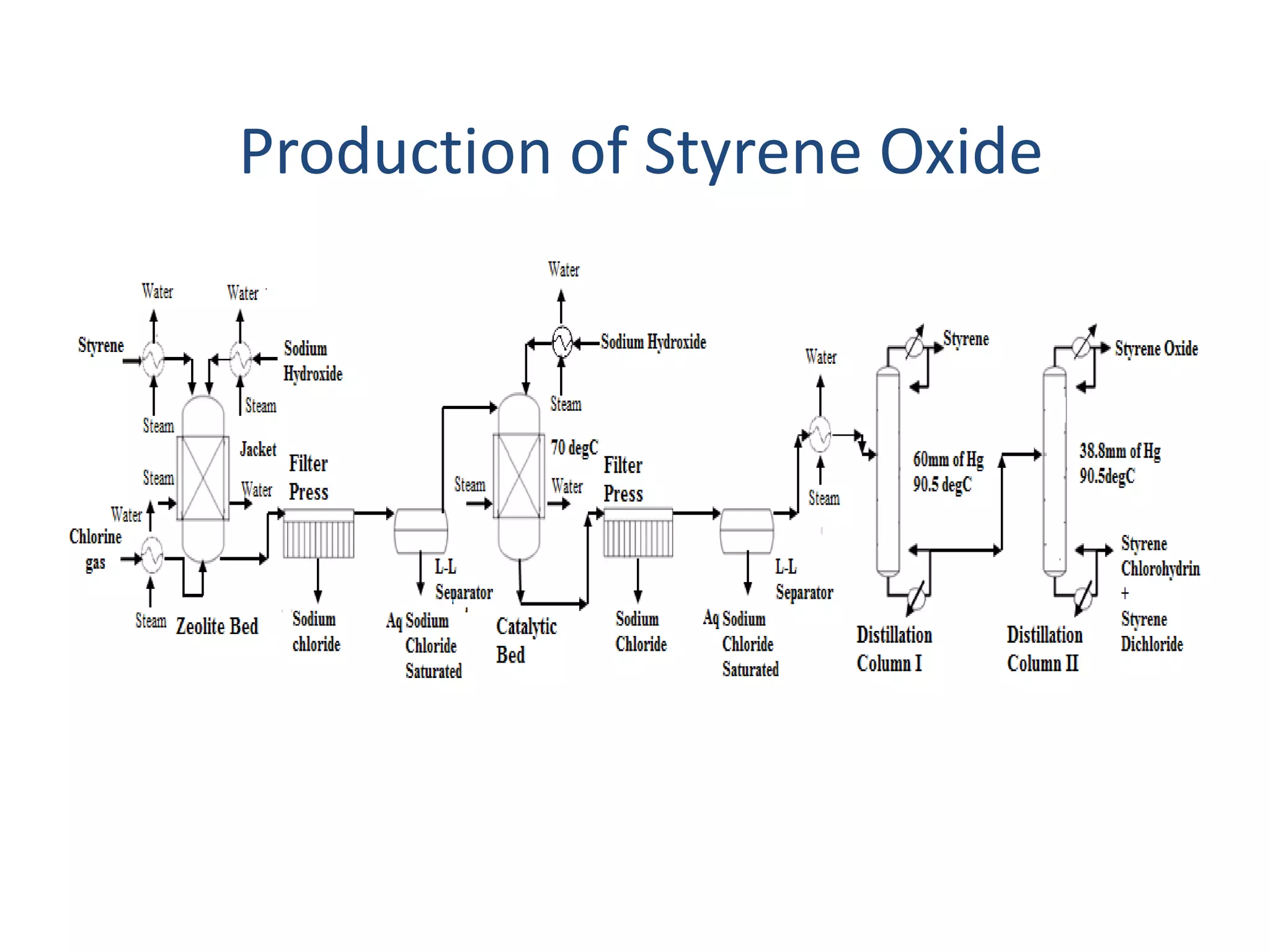
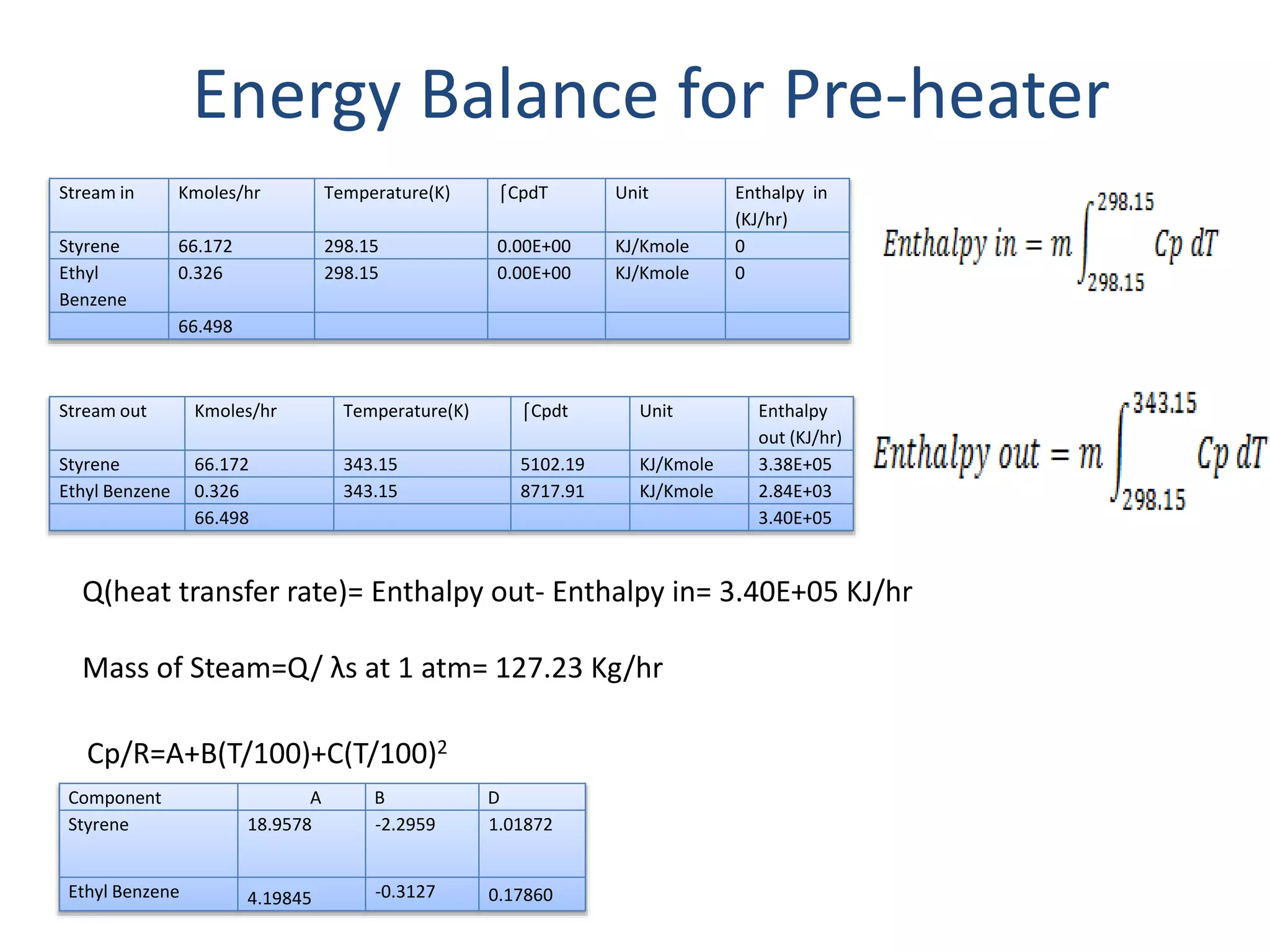
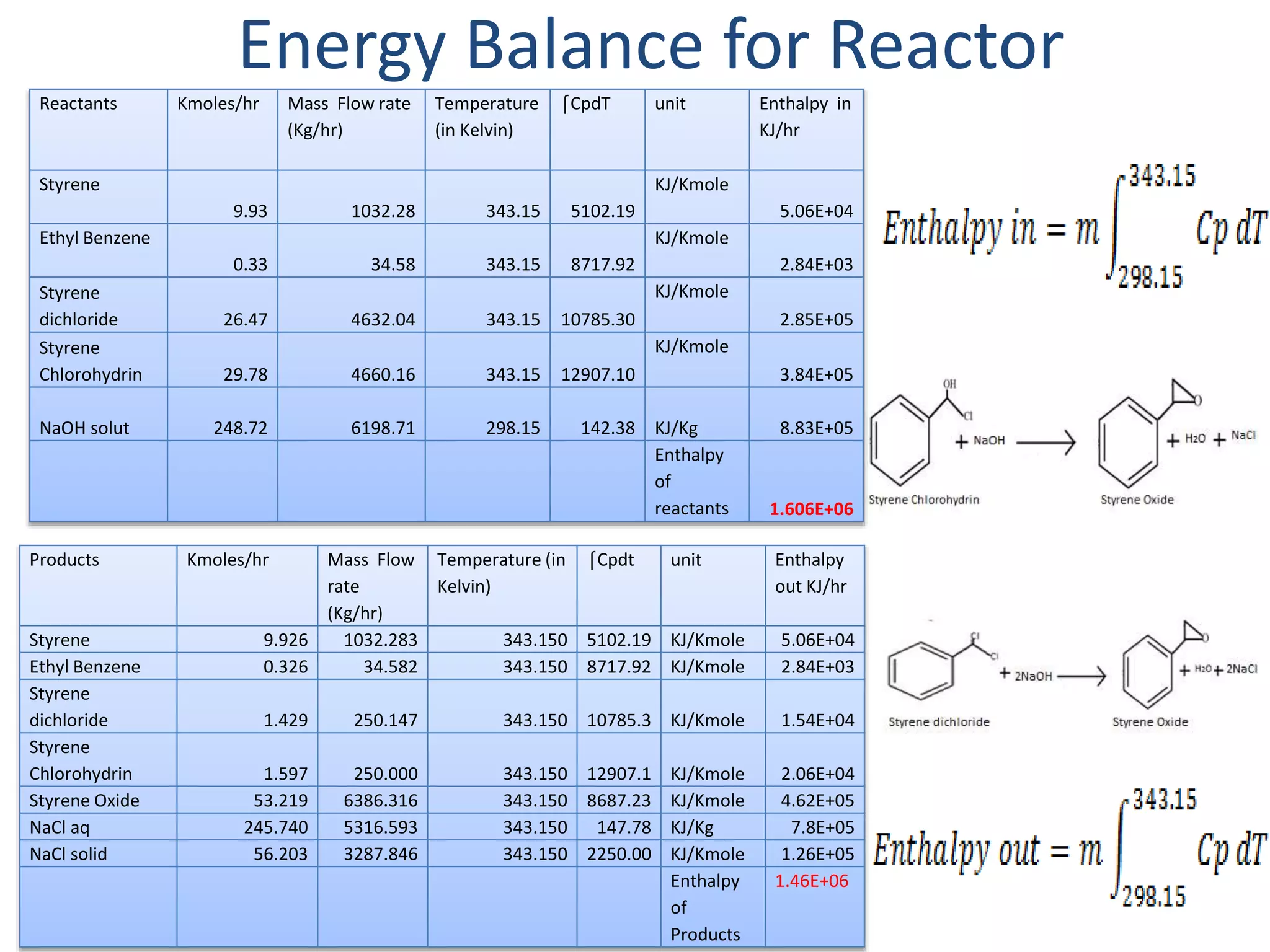
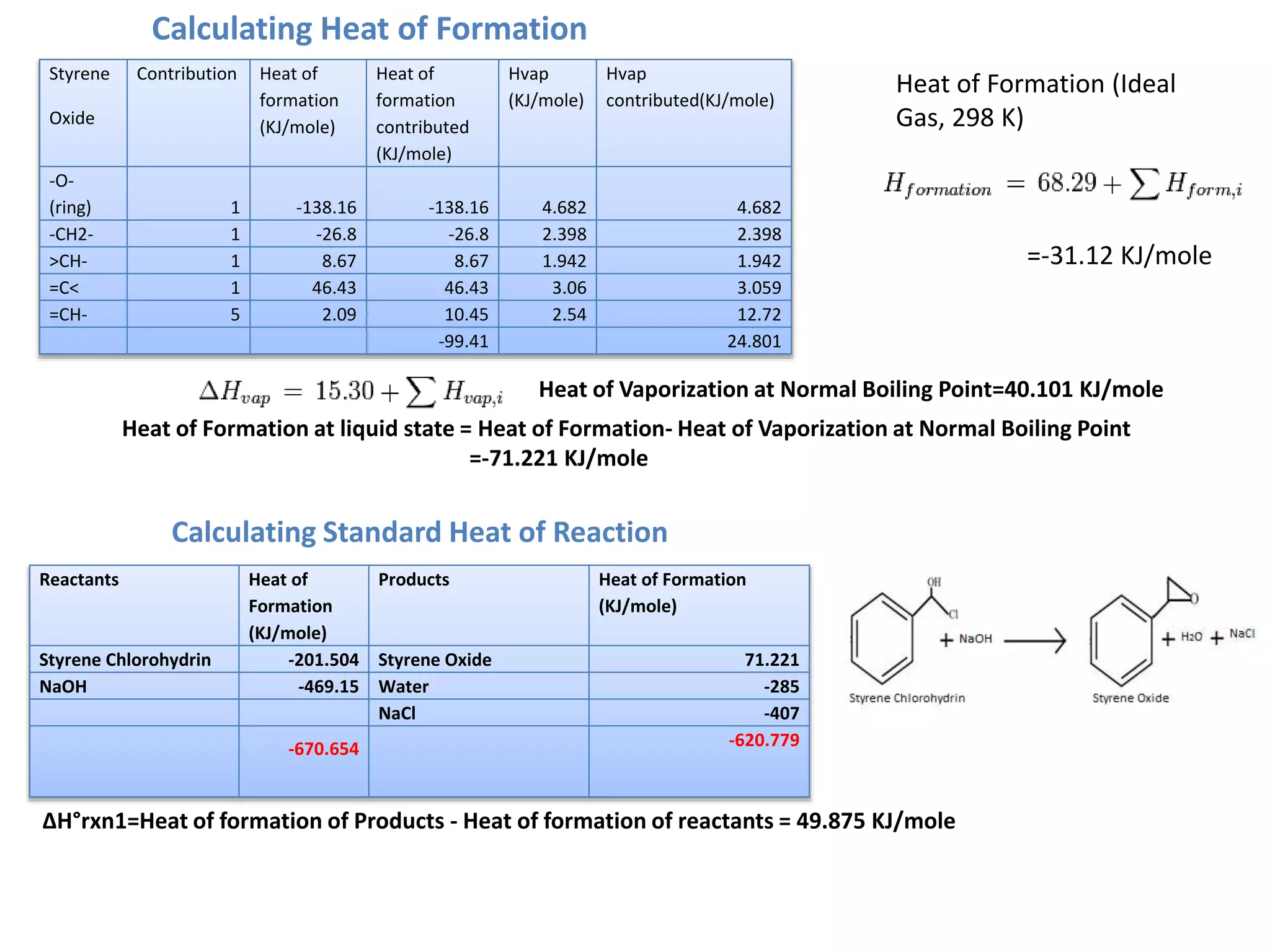
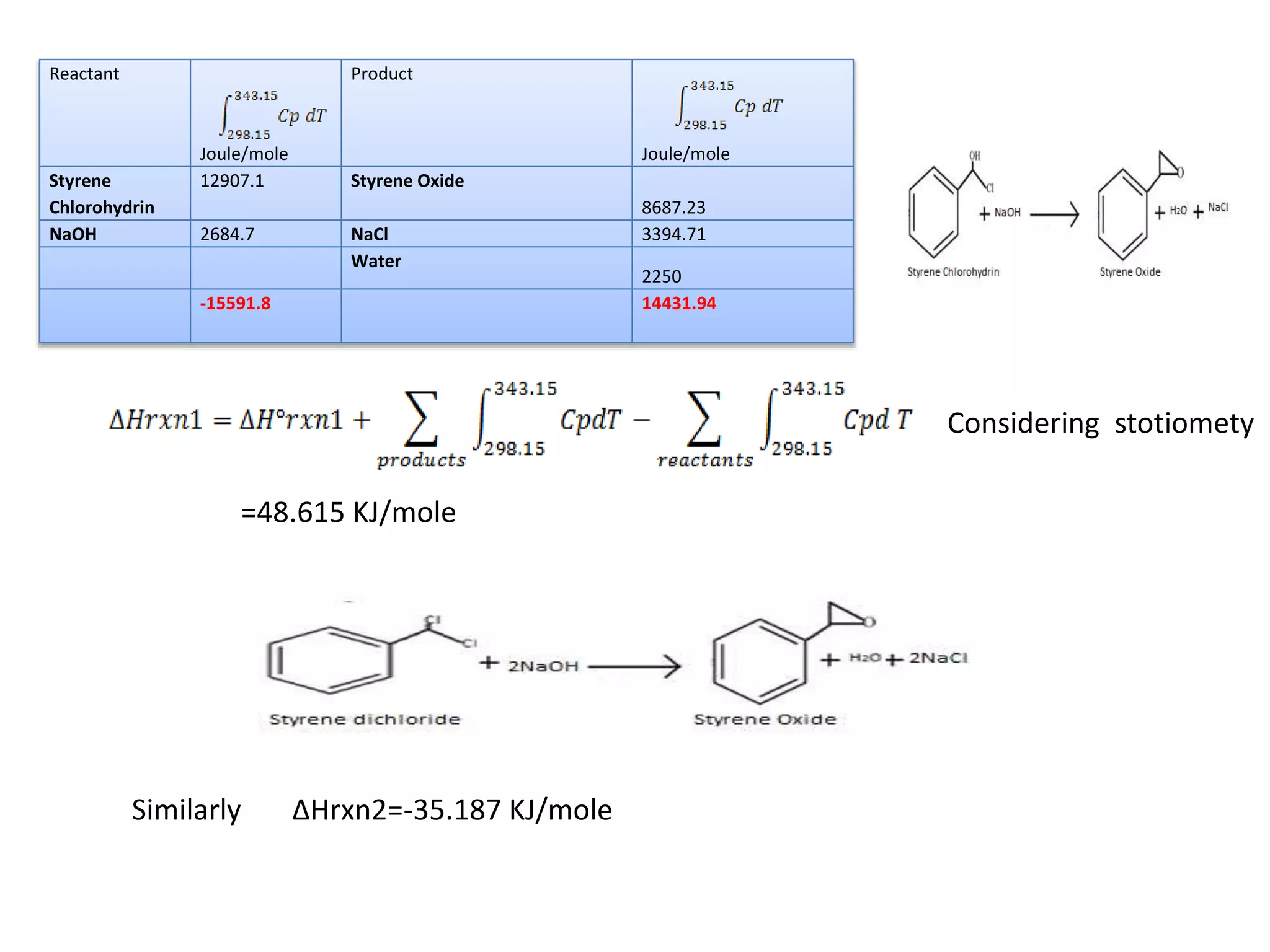
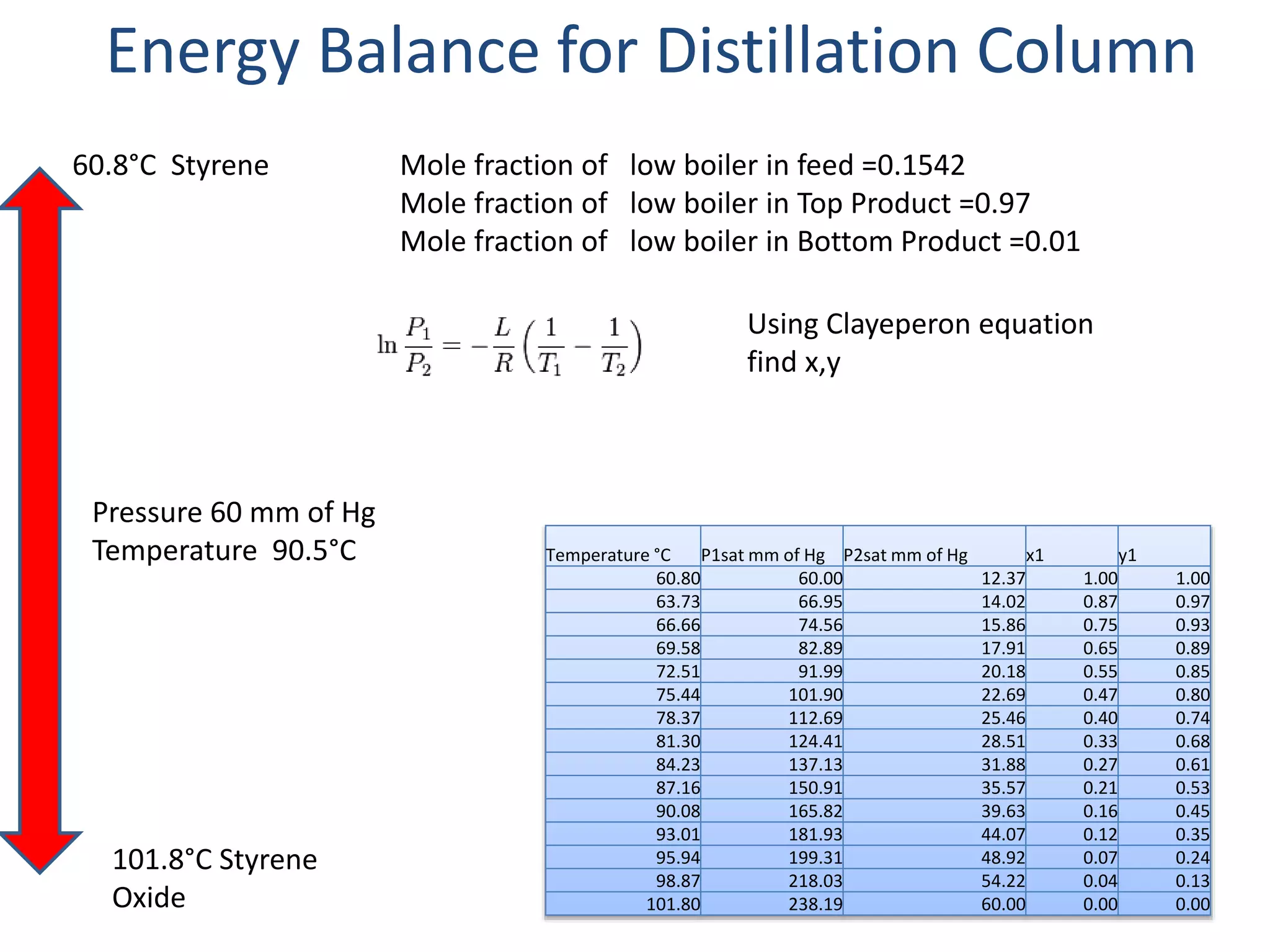
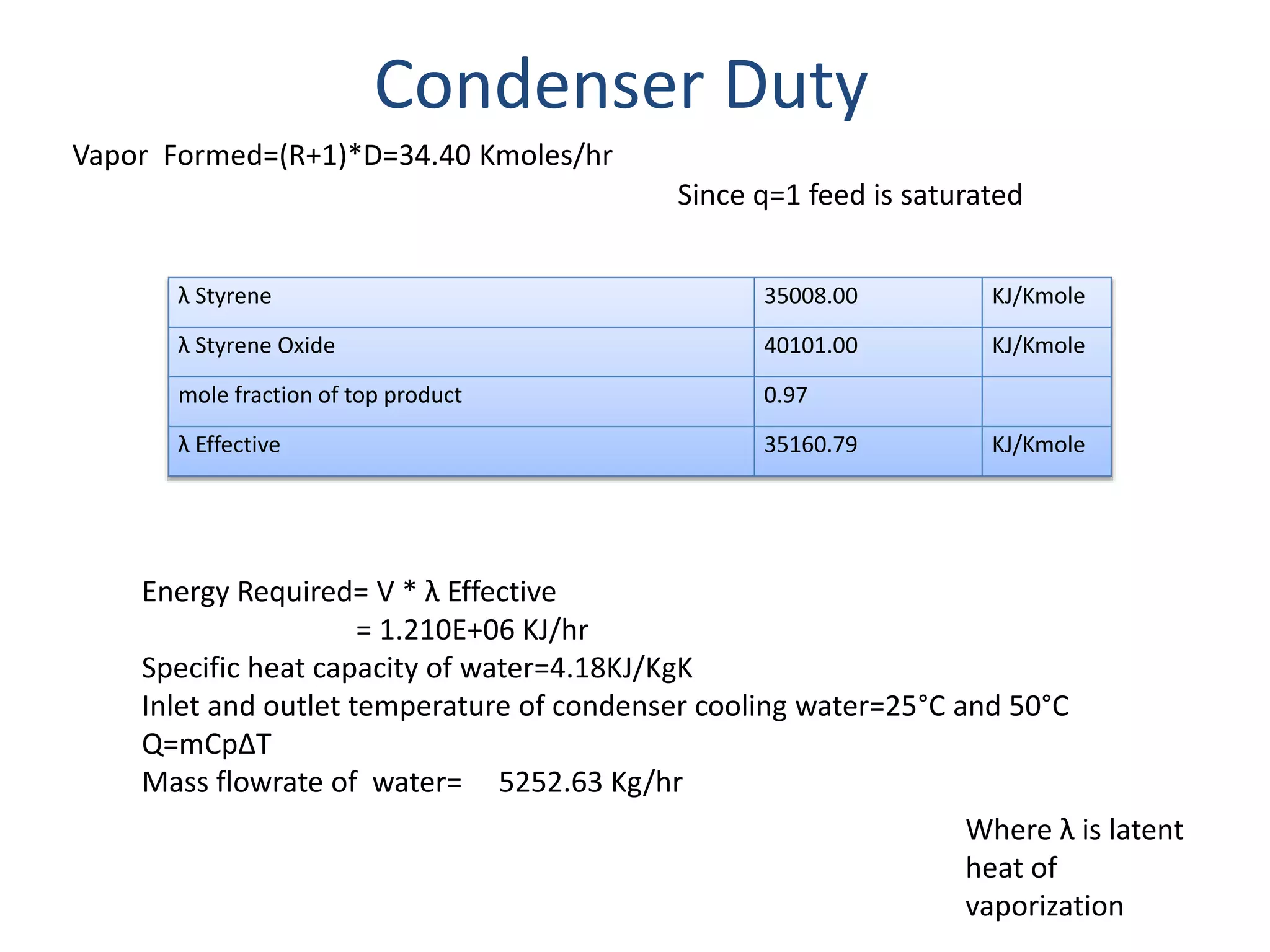
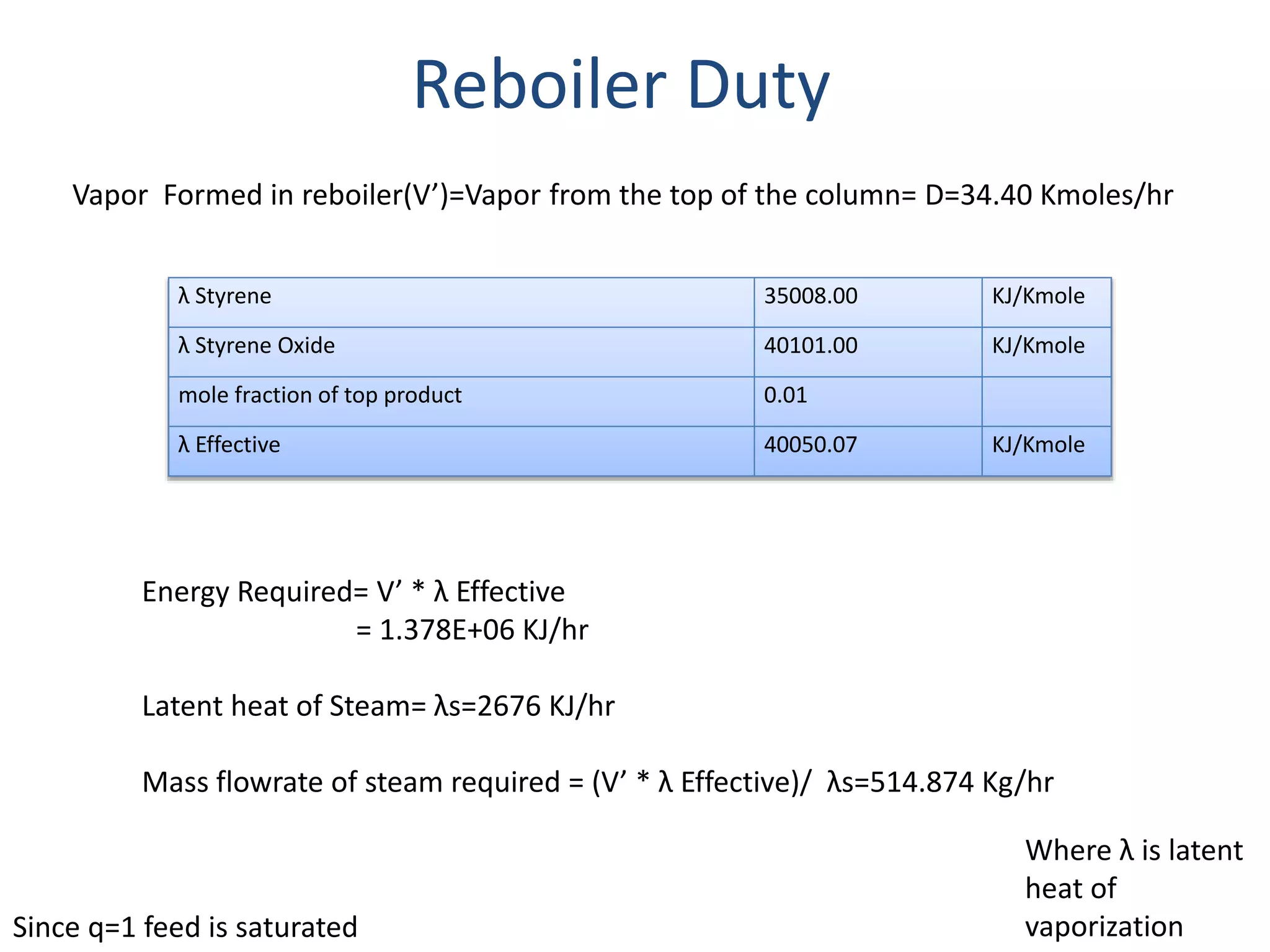
This project report summarizes the design of a plant to manufacture 50,000 tons per annum of styrene oxide. Key aspects of the design include:
1) Energy and mass balances are presented for the pre-heater, reactor, and distillation column sections. Steam and cooling water requirements are calculated.
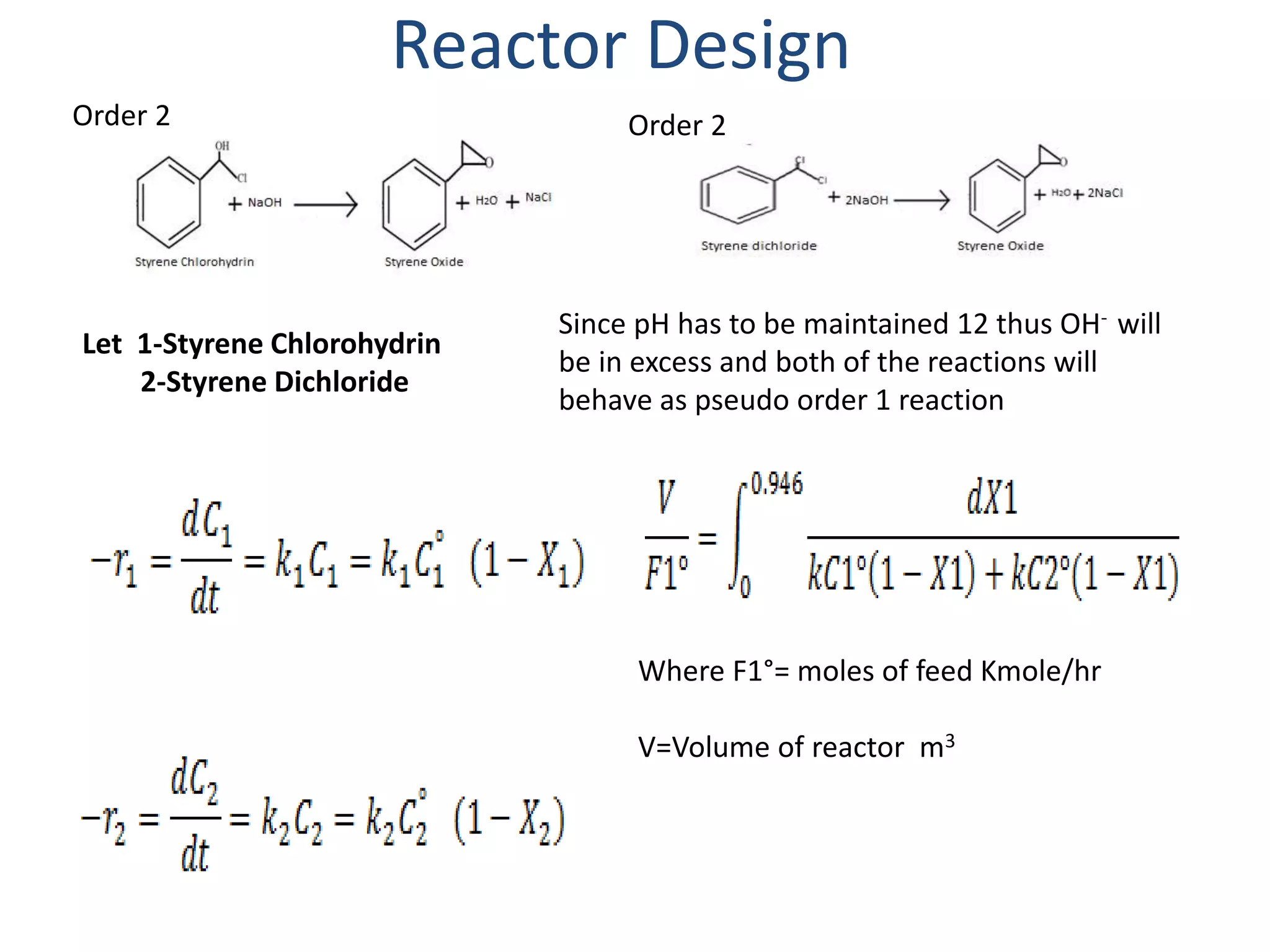
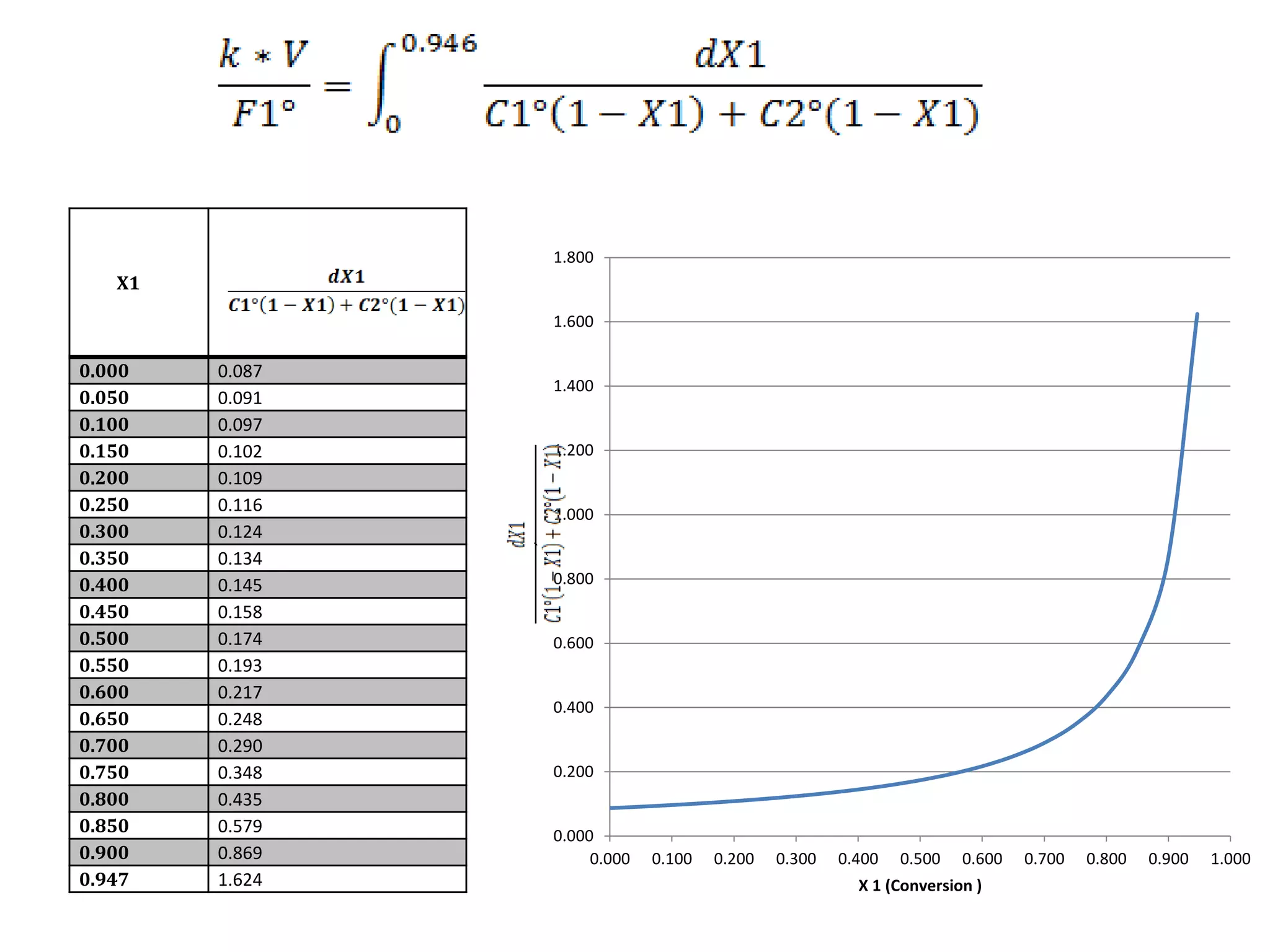
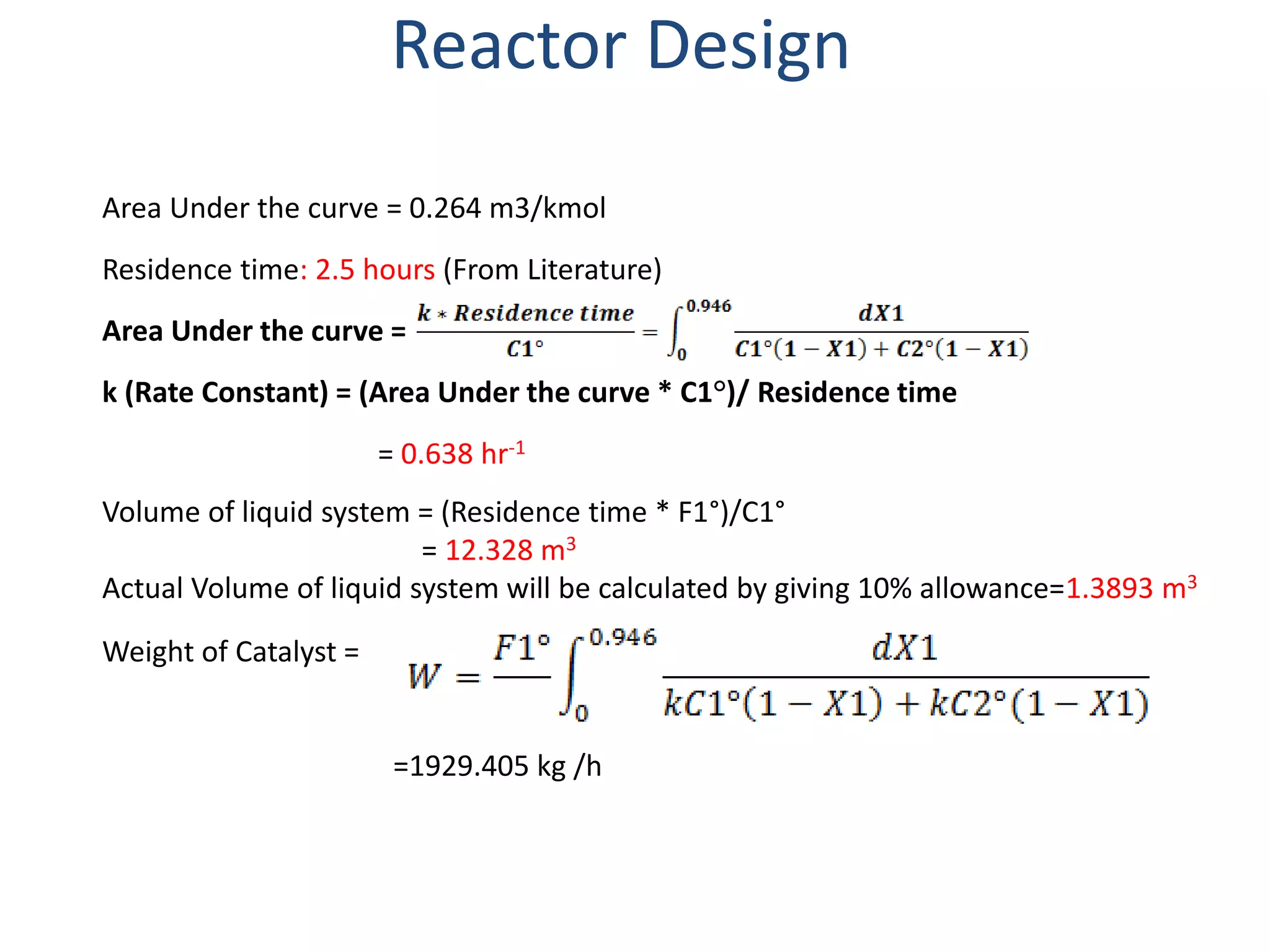
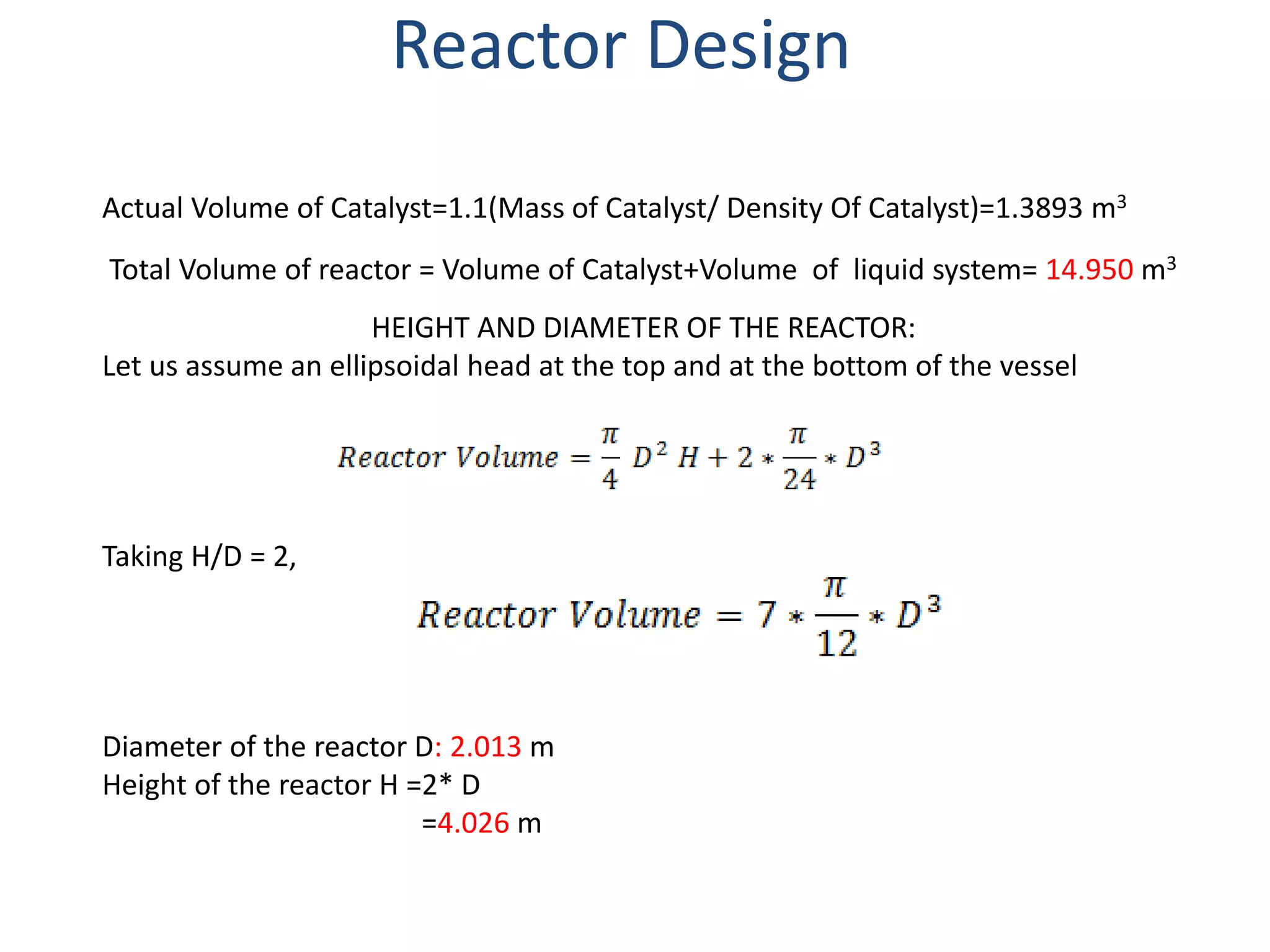
2) The reactor is designed as a batch reactor with calculations showing a volume of 14.95 m3 and diameter of 2.013 m based on the desired residence time and conversions.
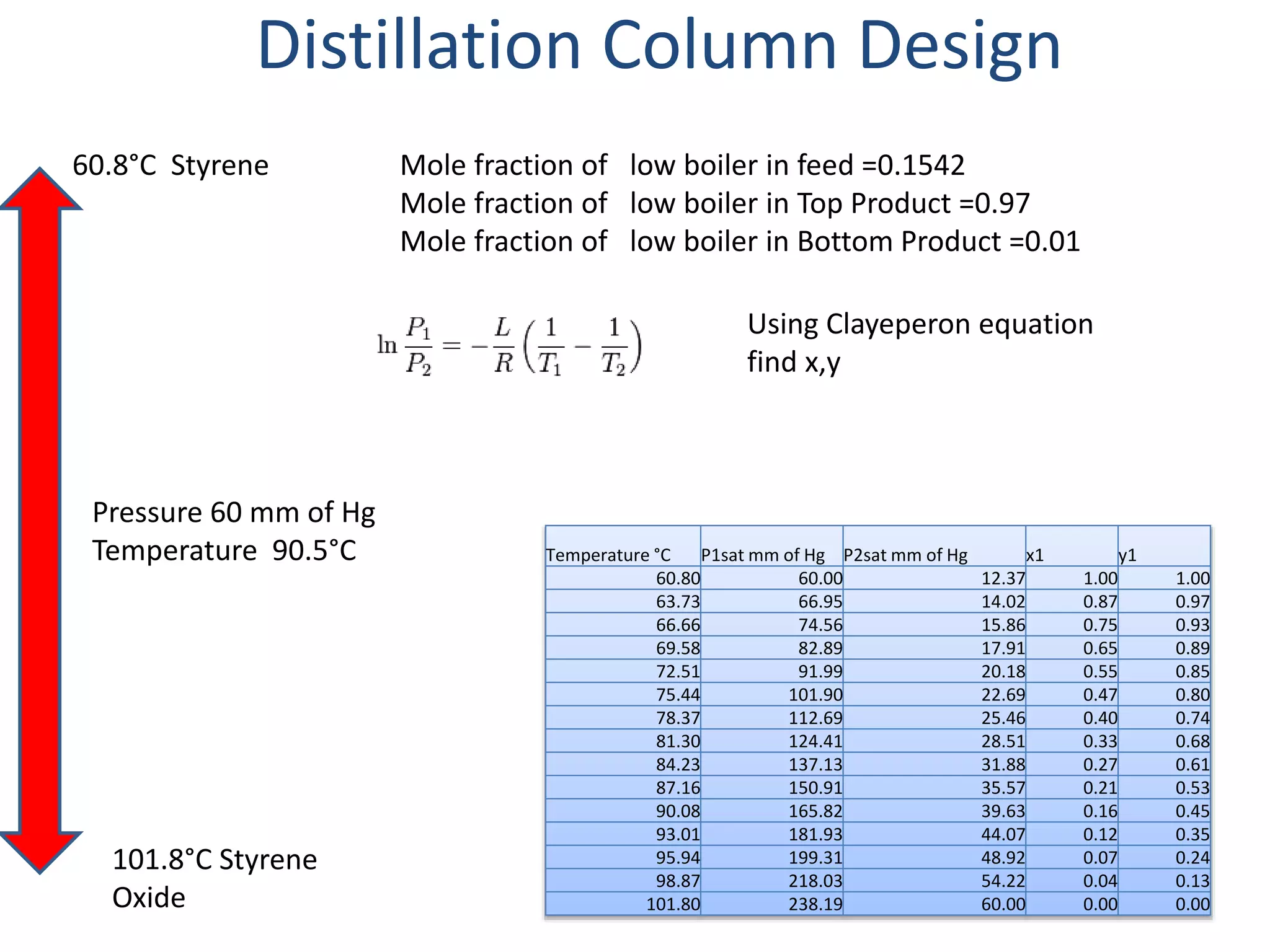
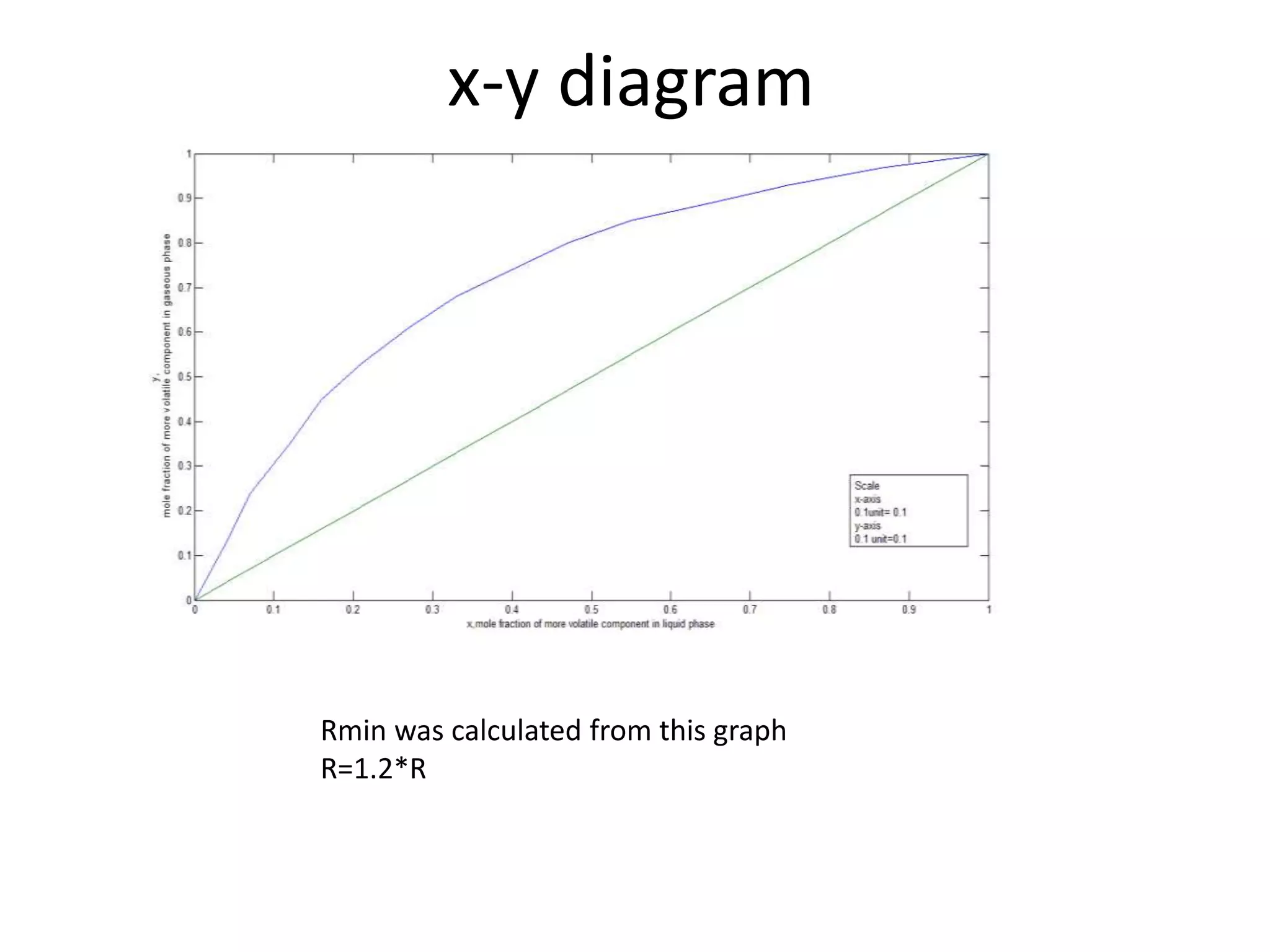
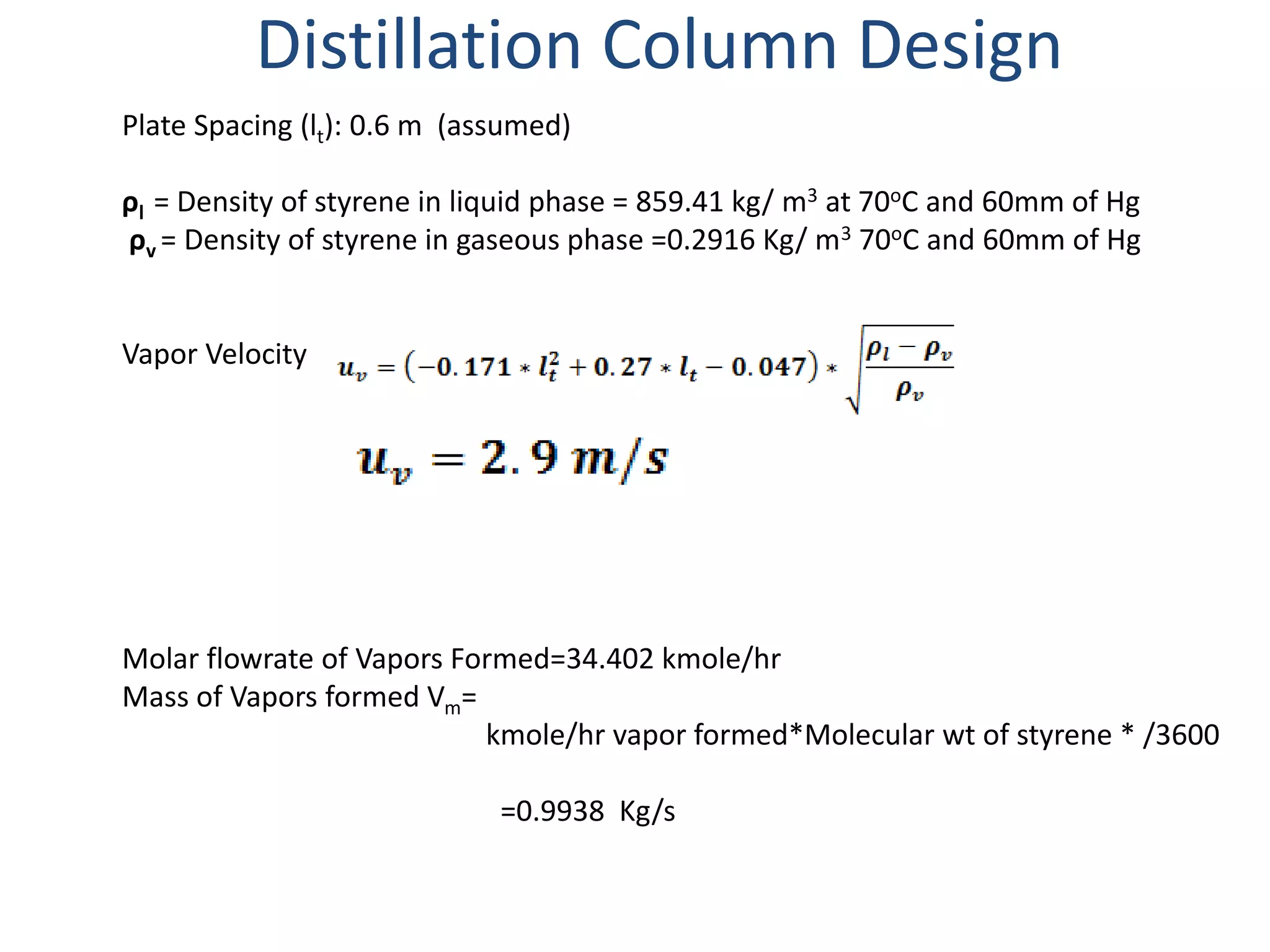
3) The distillation column is designed with 19 actual trays based on calculations from vapor liquid equilibrium data. The column has a height of 12 m and diameter of 1.223 m.
4