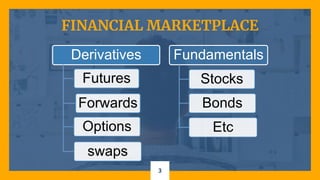
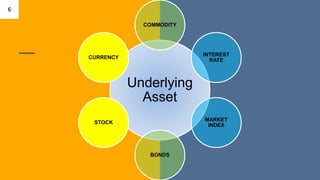
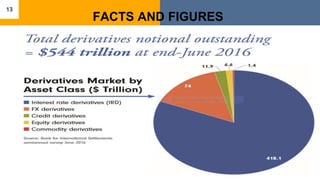
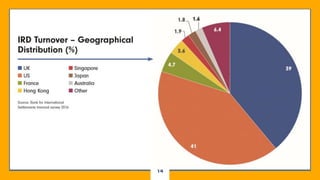
This document discusses derivatives in financial markets. It defines derivatives as any security whose value is determined by or derived from the value of another asset, known as the underlying asset. Common types of derivatives include futures, forwards, options, and swaps. Derivatives are mainly used for two purposes - hedging risk related to volatility in interest rates, stock prices, exchange rates, and commodity prices, and speculating to potentially gain large returns but also face extremely high risks. The document provides examples of how derivatives can be used to hedge risks and outlines the key types of derivatives.