The document is an in-depth overview of dependency management in PHP, focusing on tools like Composer, Satis, and Packagist, and their roles in resolving and installing library dependencies for software projects. It discusses various legacy solutions and contrasts them with modern practices, highlighting the complexity of dependency management and providing examples of command usage and configuration settings. Additionally, it covers managing project metadata, conflict resolution, and the importance of repositories in facilitating dependency management.
















![Executing install/update hooks
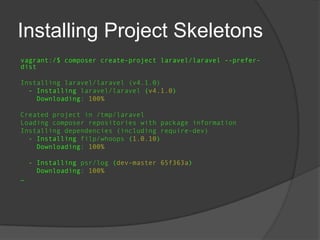
vagrant:/$ composer create-project
laravel/laravel --prefer-dist
Installing laravel/laravel (v4.1.0)
- Installing laravel/laravel (v4.1.0)
Downloading: 100%
…
Writing lock file
Generating autoload files
Generating optimized class loader
Application key
[TzvXWZSq0MTEuqAEhzO0Vsq3yMbJZHP0] set
successfully.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dependencymanagementwithcomposer-140107033412-phpapp02/85/PHP-Dependency-Management-with-Composer-20-320.jpg)
![How to Setup Install/Update
Hooks
{
"scripts": {
"post-install-cmd": [
"php artisan optimize"
],
"post-update-cmd": [
"php artisan clear-compiled",
"php artisan optimize"
],
"post-create-project-cmd": [
"php artisan key:generate"
]
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dependencymanagementwithcomposer-140107033412-phpapp02/85/PHP-Dependency-Management-with-Composer-21-320.jpg)



![Managing Project Metadata:
Example
{
"name": "composer/composer",
"description": "Dependency Manager",
"keywords": ["package", "dependency", "autoload"],
"homepage": "http://getcomposer.org/",
"type": "library",
"license": "MIT",
"authors": [
{
"name": "Nils Adermann",
"email": "naderman@naderman.de",
"homepage": "http://www.naderman.de"
}
],
"support": {
"irc": "irc://irc.freenode.org/composer",
"issues": "https://github.com/composer/composer/issues"
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dependencymanagementwithcomposer-140107033412-phpapp02/85/PHP-Dependency-Management-with-Composer-25-320.jpg)


![Applying Forks as
Dependencies: Example
{
"repositories": [
{
"type": "vcs",
"url": "https://github.com/my/monolog"
}
],
"require": {
"symfony/monolog-bundle": "2.0",
"monolog/monolog": "dev-myfix as 1.0.x-dev”
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dependencymanagementwithcomposer-140107033412-phpapp02/85/PHP-Dependency-Management-with-Composer-28-320.jpg)

![Packagist.org Repository
Will be the final repository searched
Enabled by default but can be disabled:
{
"repositories": [
{
"packagist": false
}
]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dependencymanagementwithcomposer-140107033412-phpapp02/85/PHP-Dependency-Management-with-Composer-30-320.jpg)
![Composer Repository
Provides a packages.json file.
Defined by URL. Path contains file.
Example inclusion:
{
"repositories": [
{
"type": "composer",
"url": http://packages.example.com
}
]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dependencymanagementwithcomposer-140107033412-phpapp02/85/PHP-Dependency-Management-with-Composer-31-320.jpg)

![Pear Repository
Composer access to existing PEAR channels.
{
repositories: [
{
"type": "pear",
"url": “pear.phpunit.de”,
“vendor-alias”: “phpunit”
}
]
}
Access repository packages via channel or alias
“pear.phpunit.de/PHPUnit”: “>=3.7.0”
“phpunit/PHPUnit”: “>=3.7.0”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dependencymanagementwithcomposer-140107033412-phpapp02/85/PHP-Dependency-Management-with-Composer-33-320.jpg)
![Artifact Repository
Scans directory of zip files with composer.json files in
the root of the zip.
Uses package and version in composer.json file.
{
"repositories": [
{
"type": "artifact",
"url": "path/to/zips/dir”
}
]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dependencymanagementwithcomposer-140107033412-phpapp02/85/PHP-Dependency-Management-with-Composer-34-320.jpg)

![Package Repository
Example
{“packages”: [
{
"type": "package",
"package": {
"name": ”smarty/smarty",
"version": ”3.1.7",
"dist": {
"url": "http://www.smarty.net/files/Smarty3.1.7.zip",
"type": "zip”
}
}
}
]}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dependencymanagementwithcomposer-140107033412-phpapp02/85/PHP-Dependency-Management-with-Composer-36-320.jpg)



![Satis Metadata Example
{
"name": "My Repository",
"homepage": "http://satis.my.org",
"repositories": [
{
"type": "vcs",
"url": "http://github.com/my/repo"
}
],
"require-all": true
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dependencymanagementwithcomposer-140107033412-phpapp02/85/PHP-Dependency-Management-with-Composer-40-320.jpg)