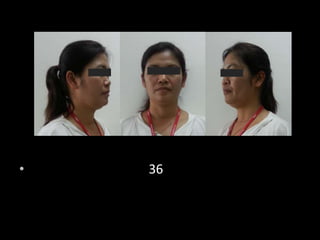
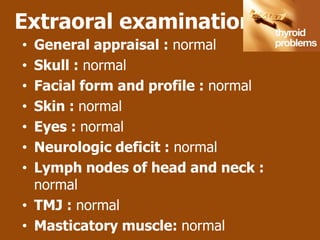
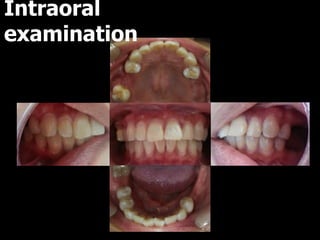
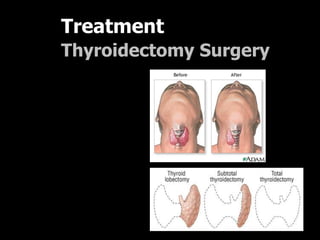
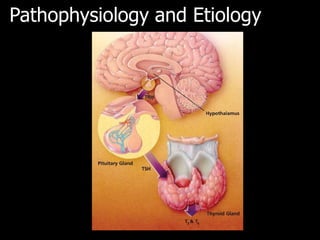
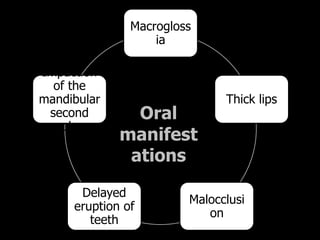
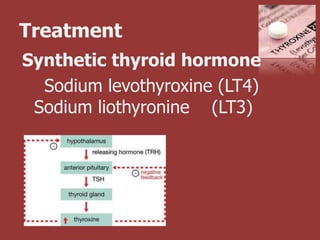
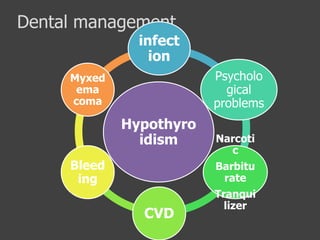
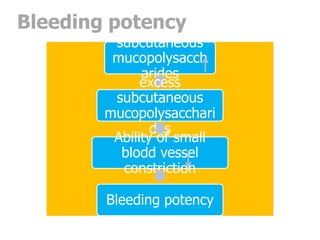
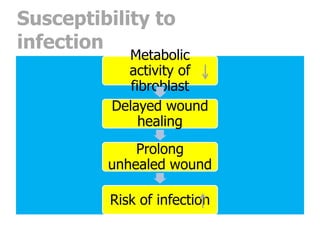
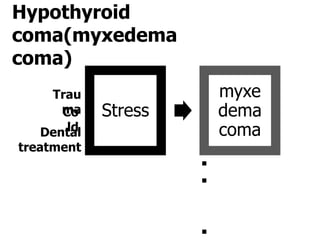
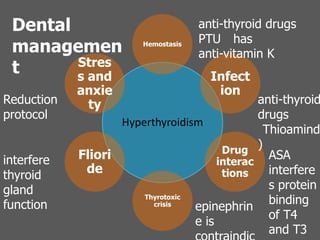
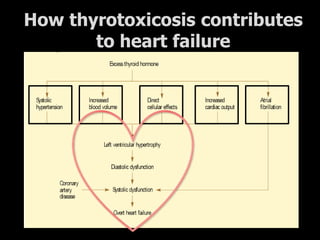
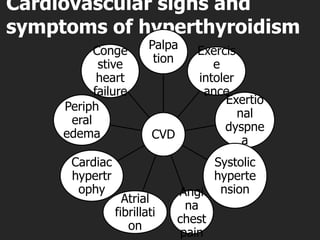
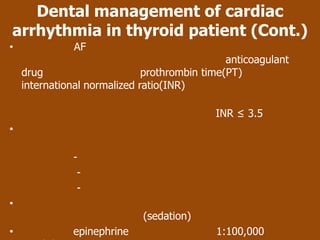
This document outlines the dental management of patients with thyroid disease. It discusses taking a thorough medical history and examination. Treatment plans should consider the patient's thyroid condition and medications. Hyperthyroidism can increase risks of infection, bleeding, and cardiac issues while hypothyroidism increases infection risk. Dental procedures should minimize stress and avoid epinephrine for uncontrolled hyperthyroid patients. Vital signs must be monitored and treatment stopped if issues arise.