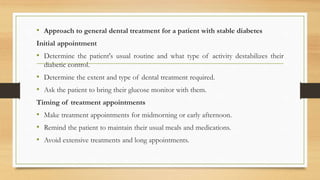
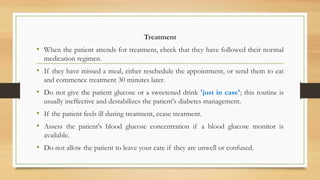
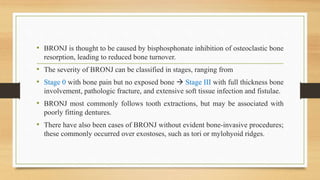
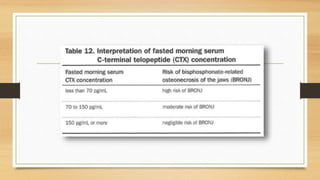
This document outlines the dental management of medically compromised patients, emphasizing the significance of various endocrine conditions, particularly diabetes, thyroid disorders, adrenal disorders, and bisphosphonate-related issues. It highlights how these conditions affect dental treatment, the importance of monitoring blood glucose levels, and the need for careful planning for patients on certain medications to prevent complications such as delayed healing or emergencies. Additionally, it stresses the necessity of thorough medical histories and monitoring when treating patients with bisphosphonates to prevent osteonecrosis of the jaws.