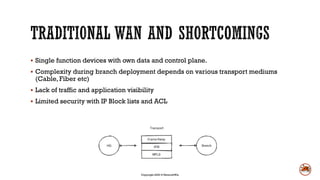
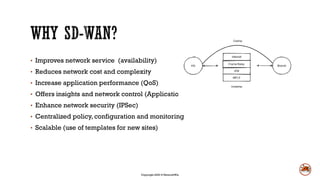
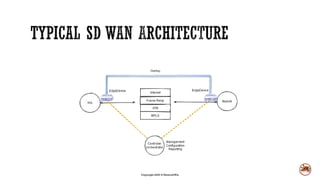
Software defined wide area networks (SD-WAN) abstract network hardware to create an overlay network. This allows for policy-based routing, dynamic path selection, and quality of service combined with application visibility. SD-WANs improve network availability and performance, reduce costs and complexity, and enhance security and insights compared to traditional branch deployment methods. While SD-WANs offer benefits, they also have some disadvantages like upfront hardware costs, licensing fees, and less direct troubleshooting control.