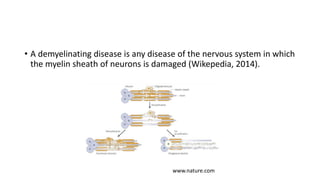
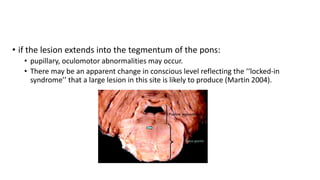
Osmotic demyelination syndrome (ODS), also known as central pontine myelinolysis, is a demyelinating condition that affects the pons region of the brain stem. It occurs when hyponatremia (low sodium levels) are corrected too rapidly, such as when sodium levels increase more than 12 mmol/L in a 24 hour period. Symptoms include paralysis, dysarthria, and dysphagia. Risk factors include chronic alcoholism and hyponatremia. While prognosis was once poor, improved imaging techniques now allow for earlier diagnosis and treatment with rehabilitation. Prevention through controlled correction of hyponatremia is key to avoiding ODS.