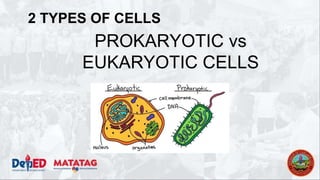
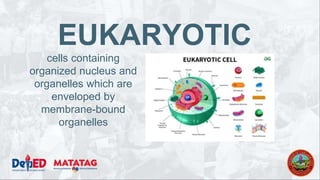
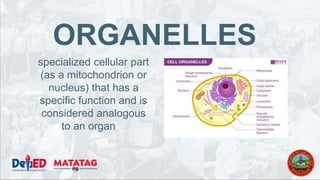
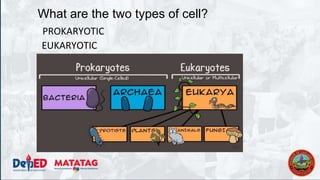
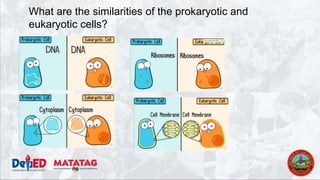
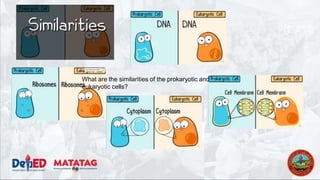
The document provides a preparatory outline for a biology class focusing on cells, discussing their definition and historical context. It differentiates between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, highlighting their structures and functions, and includes interactive activities such as a group game. The importance of cells in providing structure, energy conversion, and heredity is emphasized.