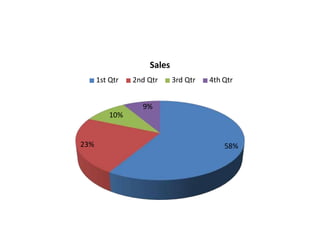
The document discusses demography, the scientific study of human populations, covering aspects such as population size, composition, distribution, and how these affect health service planning. It details demographic processes including fertility, mortality, marriage, migration, and social mobility, along with methods for data collection like surveys and censuses. The 2011 Census of India is highlighted as a significant event, marking the preparation of the National Population Register, with the next census postponed to after 2024.