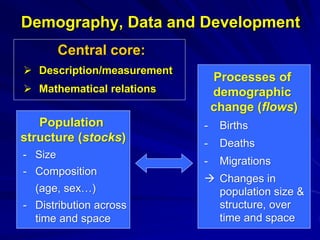
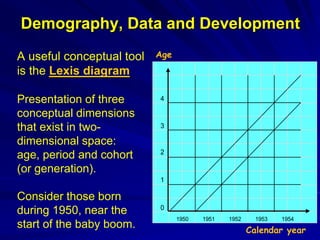
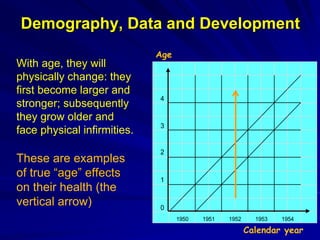
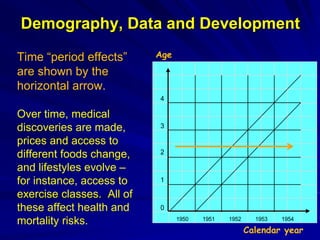
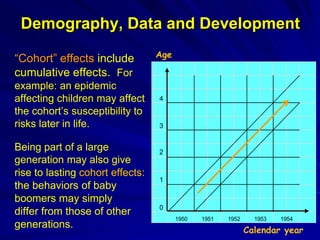
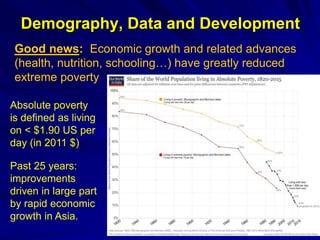
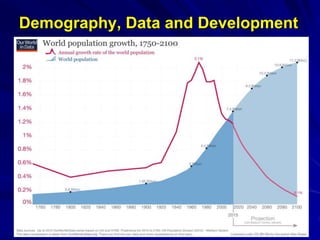
The document discusses the intersection of demography, data, and development, highlighting the importance of understanding population dynamics through new data sources, including social media. It emphasizes the need for rigorous data quality assessments to ensure effective decision-making in relation to global sustainable development goals (SDGs) amidst rapid population growth and environmental challenges. The text calls for a 'data revolution' to enhance policy design and includes the role of demographers and computer data scientists in this endeavor.




















![Demography, Data and Development
Achieving this will be extraordinarily difficult.
Not achieving it will be a catastrophe: continued misery
for large parts of the world population, and risking
disastrous environmental change.
Improvements to the evidence base – the “Data
Revolution” – will be of real value for the design of
more effective policy and interventions.
The participation of cutting-edge computer data scientists
and demographers in Data Revolution work is critical.
[Examples: Big Data and the Well-Being of Women and Girls
Applications on the Social Scientific Frontier (Bapu Vaitla et al.,
4/2017, http://data2x.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Big-Data-
and-the-Well-Being-of-Women-and-Girls.pdf]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icwssdemographydataanddevelopmenttlegrand-170517203051/85/Demography-data-and-development-28-320.jpg)