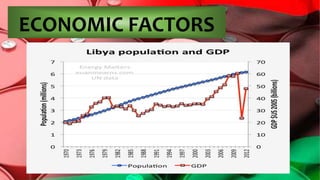
After Gaddafi's regime fell in 2011, Libya transitioned to democracy. In 2012, Libyans voted in the first national election since Gaddafi's ouster, electing the General National Congress. However, Libya faced challenges including political instability, as powerful militias vied for influence and the unemployment rate rose to 30%. Additionally, while over 97% of the population is Sunni Muslim, Libya sought to establish religious freedom and rebuild its education system after decades under Gaddafi's rule.