Embed presentation
Download to read offline








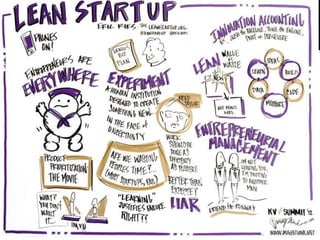


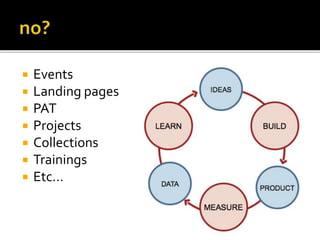
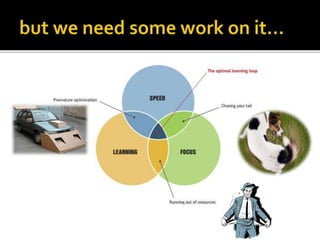




The document discusses the evolution of business education and the differences between managing large corporations versus startups. It notes that startups operate in risky environments with limited resources, so techniques used by large companies may not apply. The lean startup methodology emerged from courses on startups and books that focus on validating ideas and pivoting quickly. The document argues that the company discussed should take a lean startup approach, as it has the characteristics of a startup like uncertainty and limited resources. It proposes a LeanAKademy program to help develop and launch products using the lean methodology over two months.















