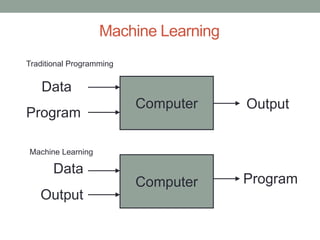
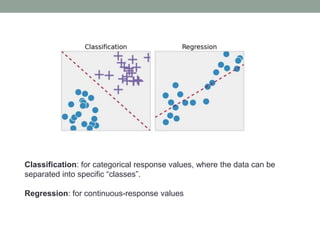
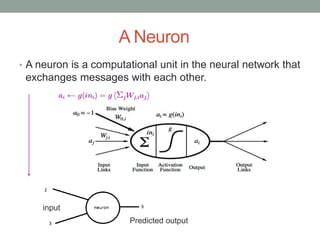
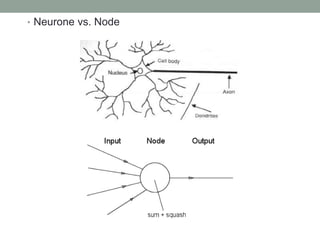
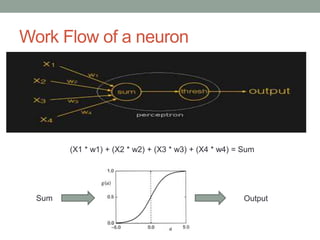
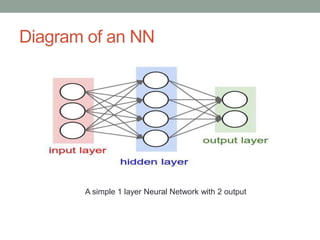
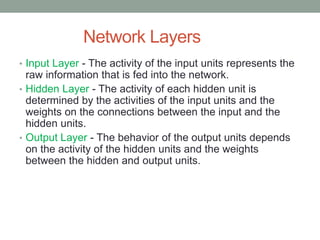
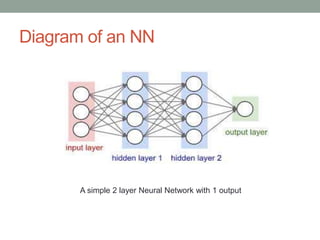
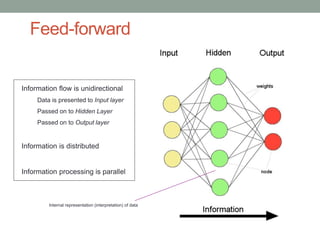
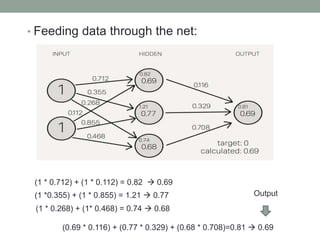
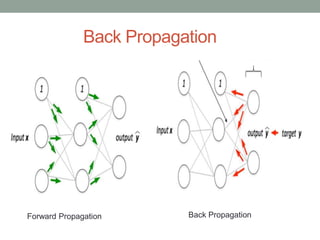
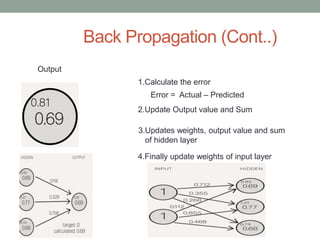
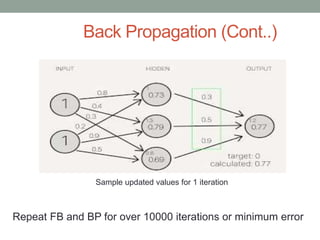
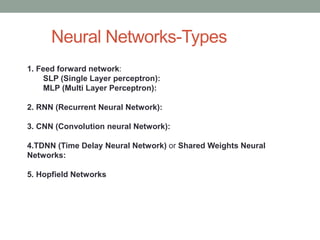
Madhu Babu Sanjeevi is a software engineer skilled in various programming languages and technologies, particularly in machine learning and neural networks. The document outlines key concepts such as the structure of neural networks, types of neural networks, and processes like forward and back propagation. It also highlights practical applications of neural networks in fields like speech recognition and natural language processing.