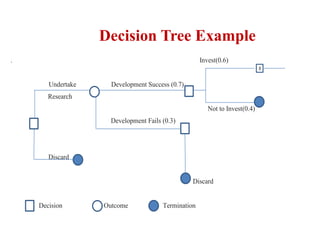
This document discusses decision tree analysis as a tool for management decision making. It provides an example of a decision tree to analyze whether to invest in expensive permanent equipment or cheaper temporary tooling for a new product. The key points are:
- Decision trees depict sequential decisions and probabilities graphically to analyze options.
- An example decision tree shows options to invest or not invest in development, and potential outcomes of success or failure.
- Decision trees are read from left to right, with decision nodes as squares and chance events as circles connected by branches showing probabilities.
- The process involves identifying problems and alternatives, delineating the decision tree, specifying probabilities and outcomes, and evaluating alternatives.