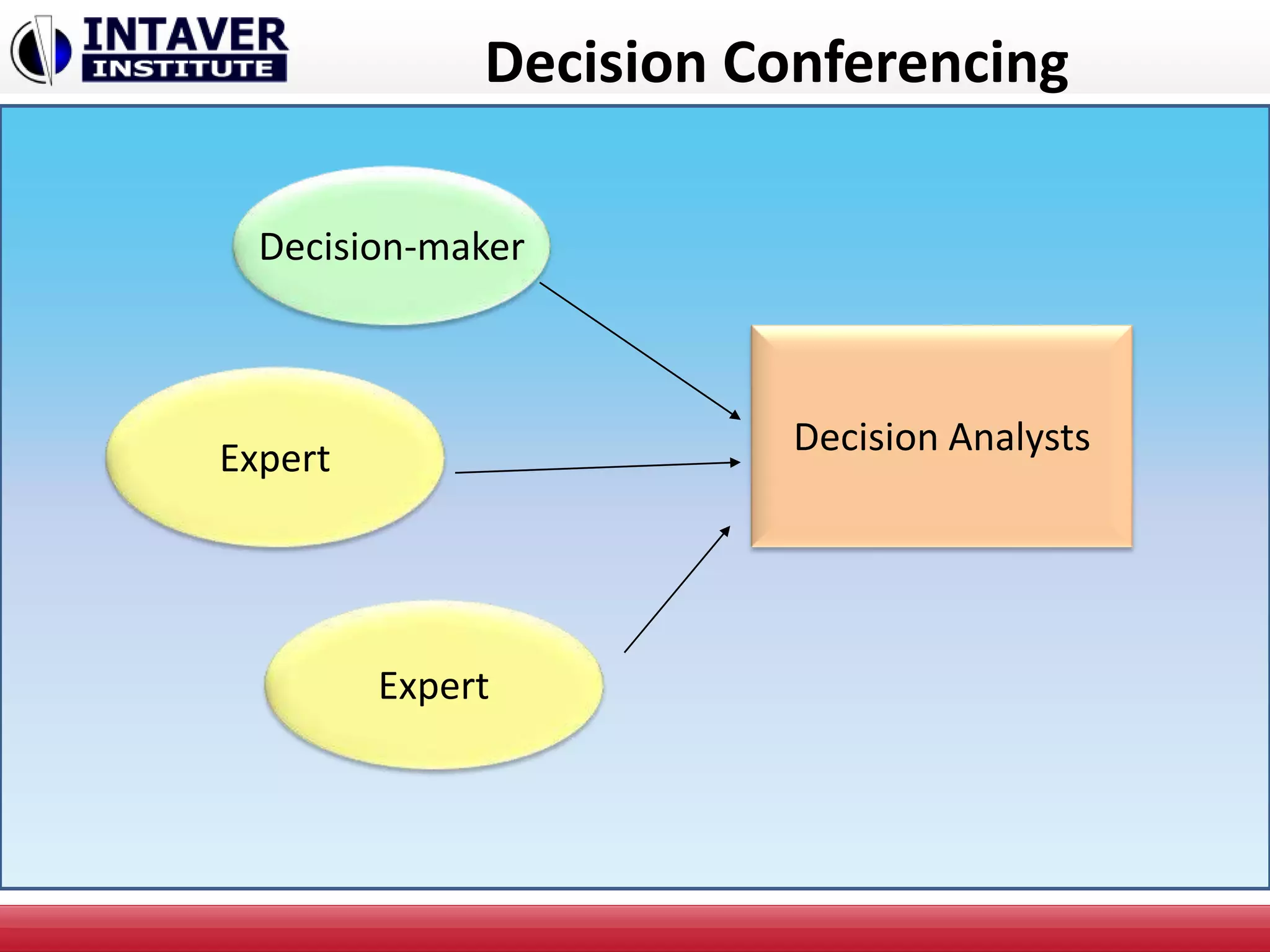
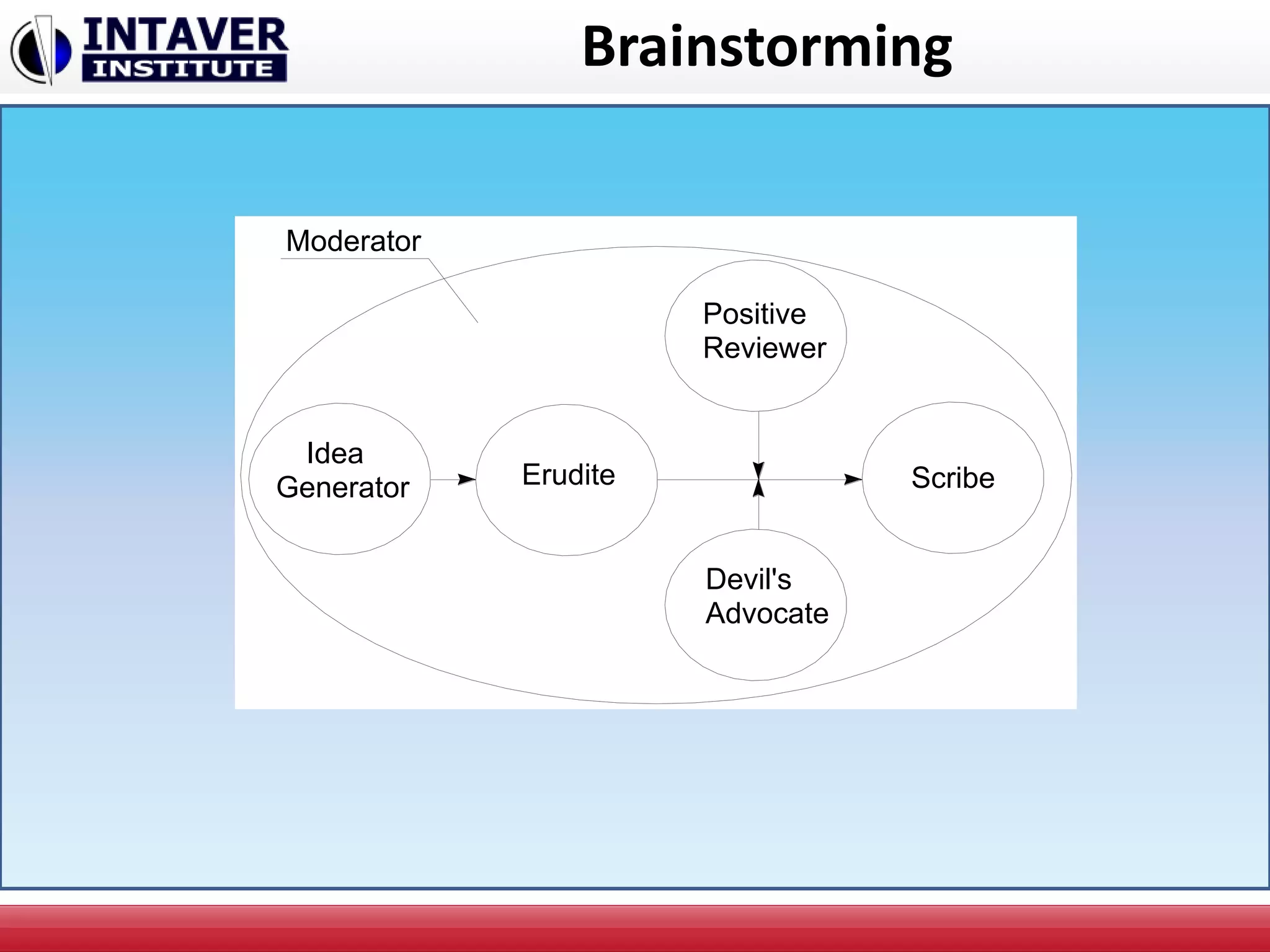
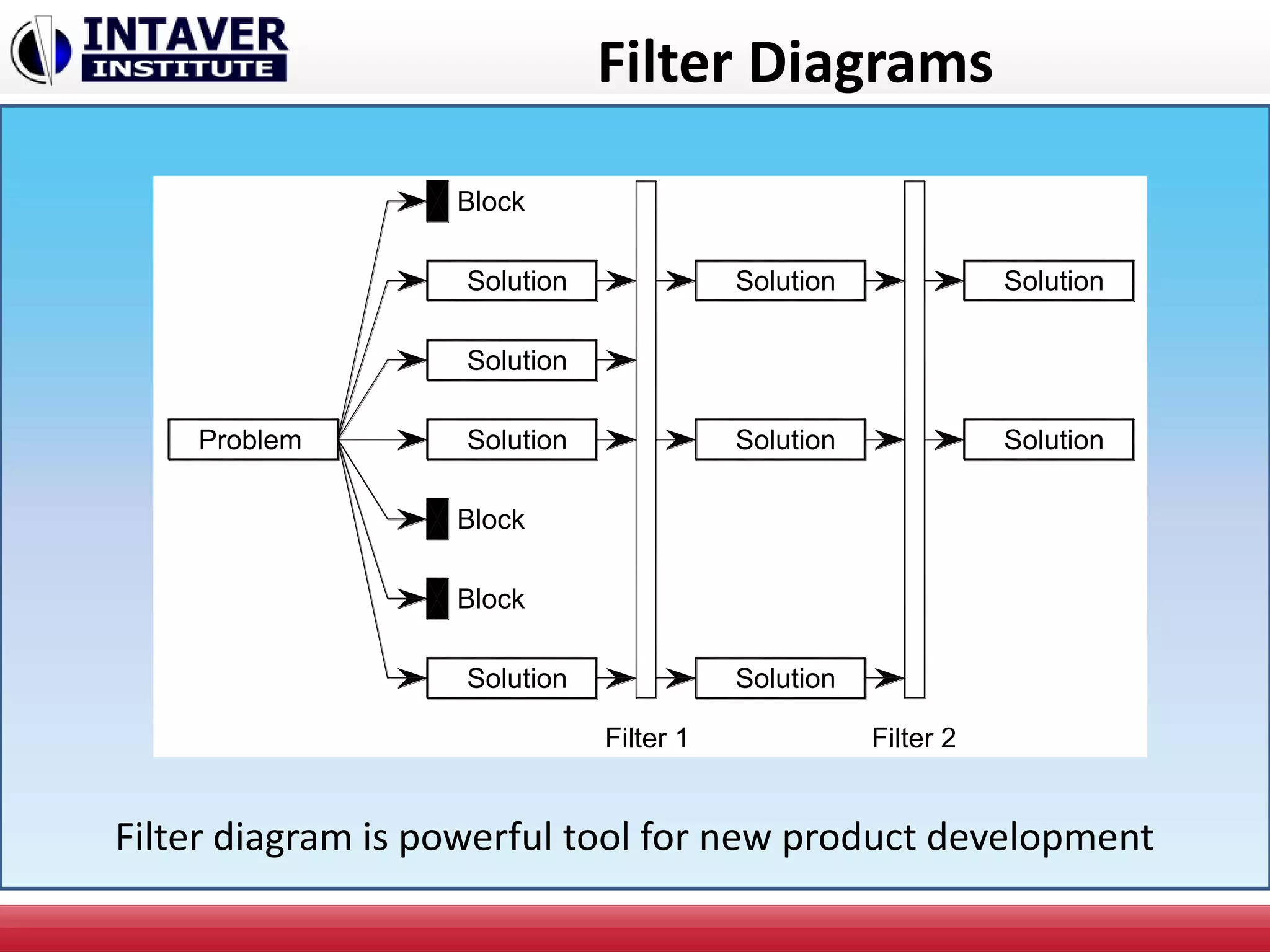
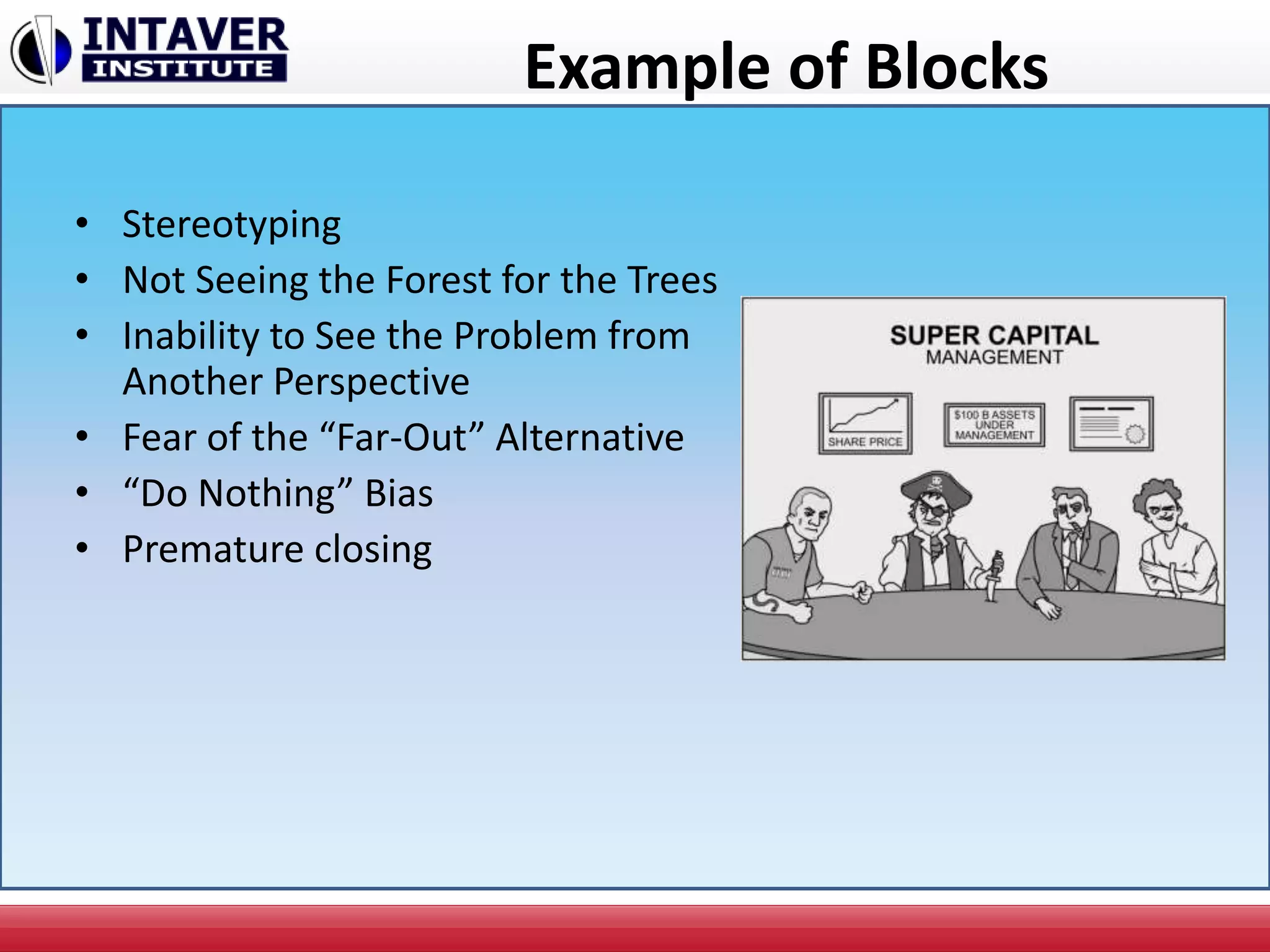
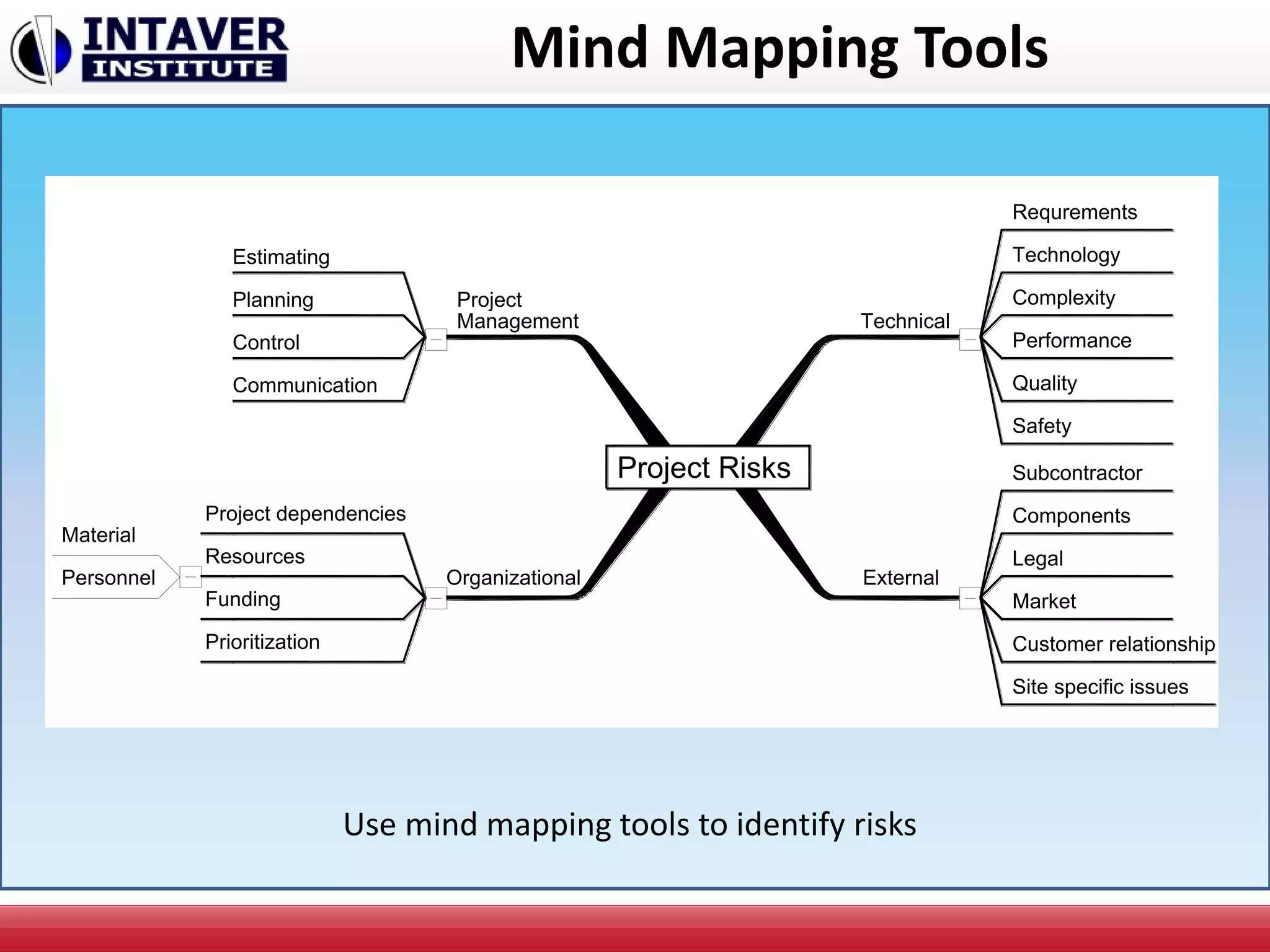
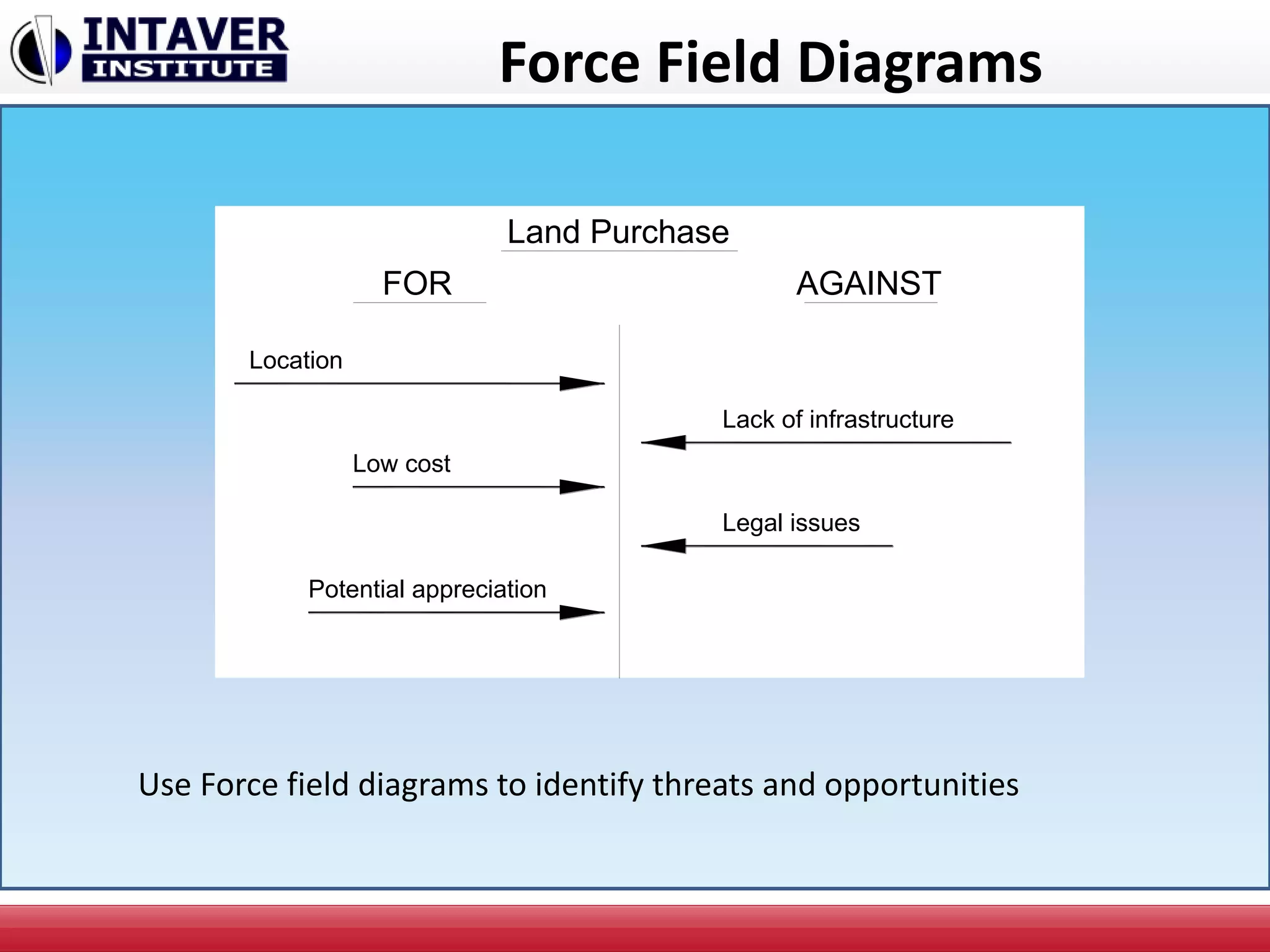
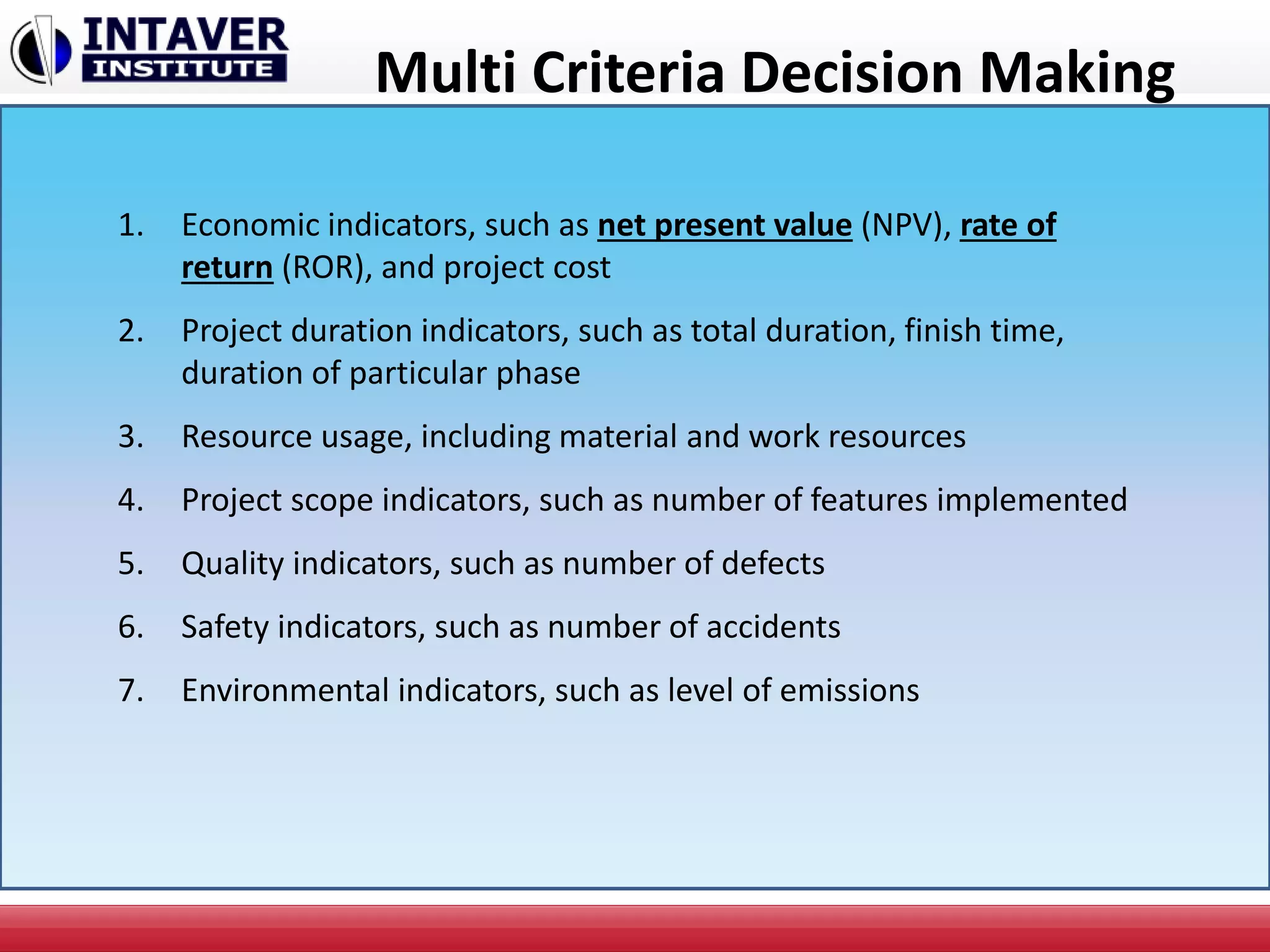
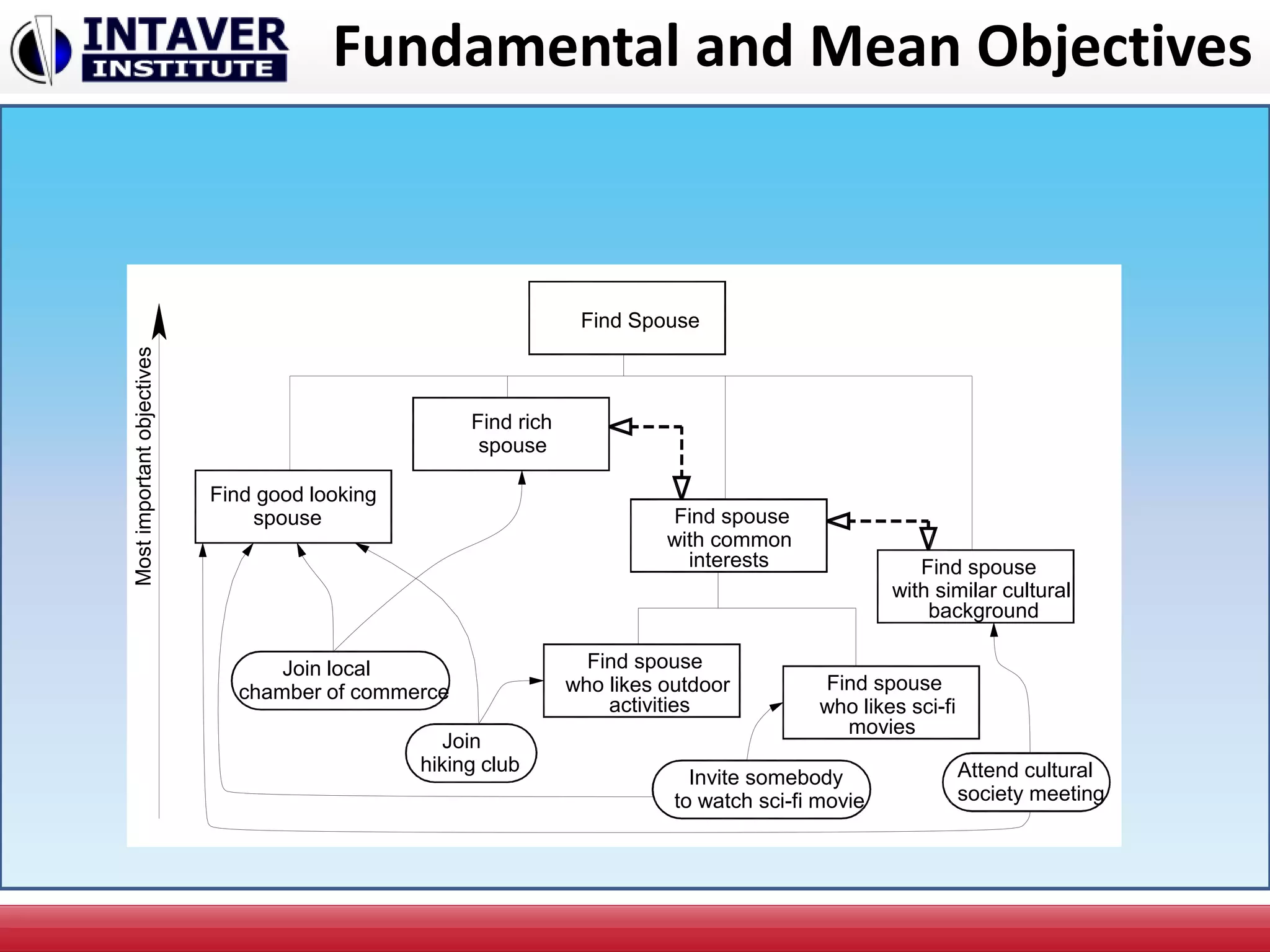
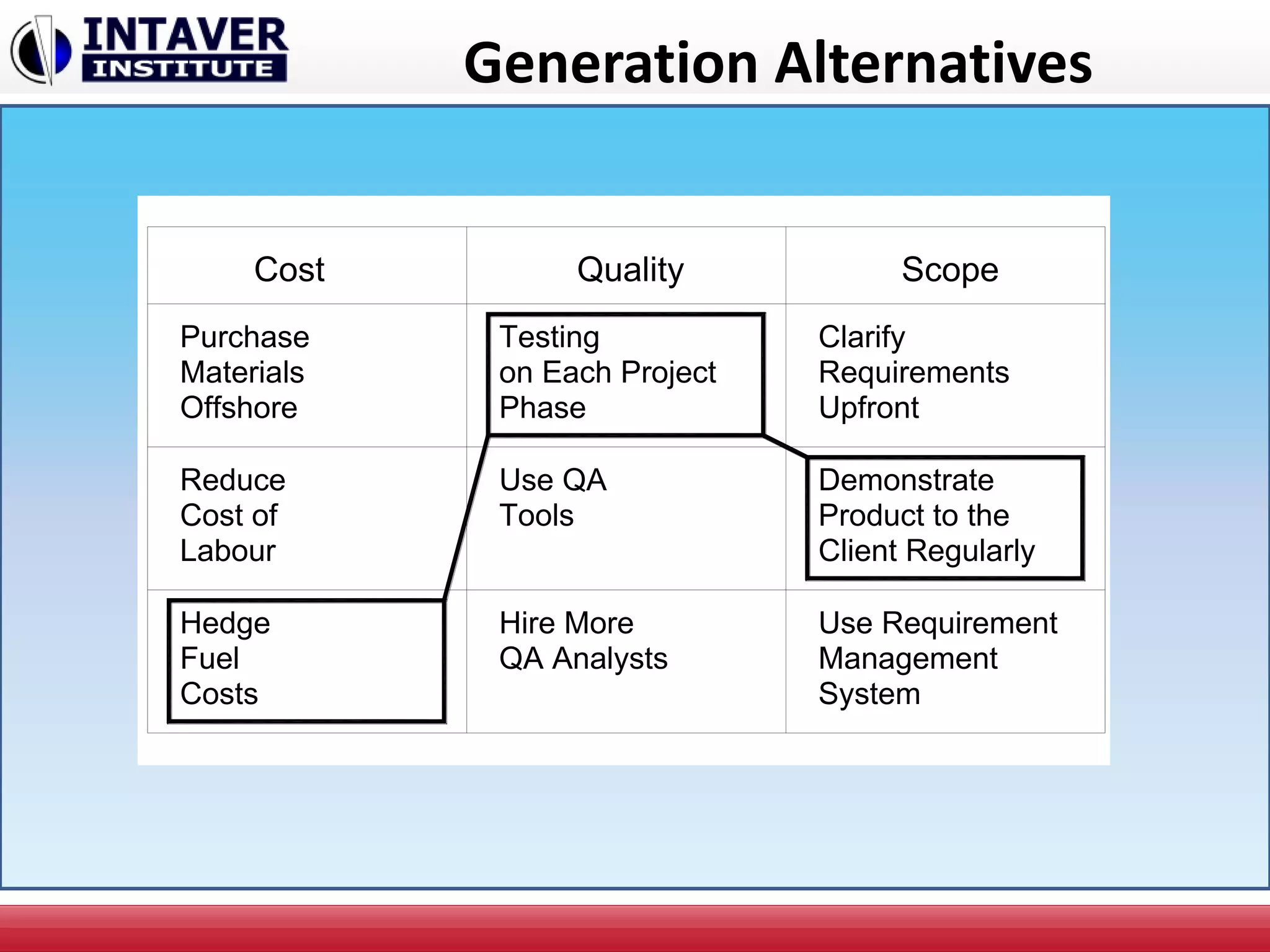
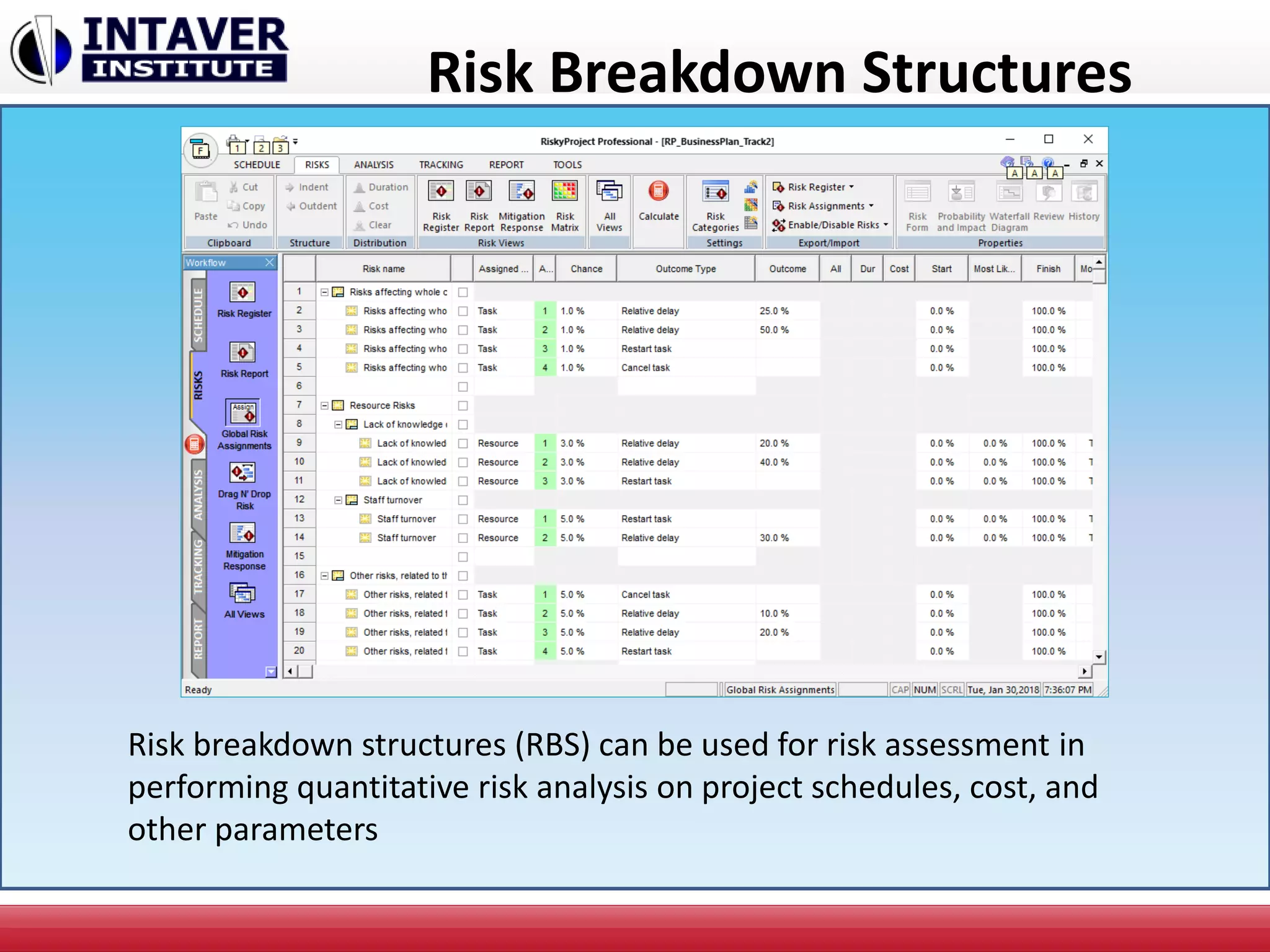
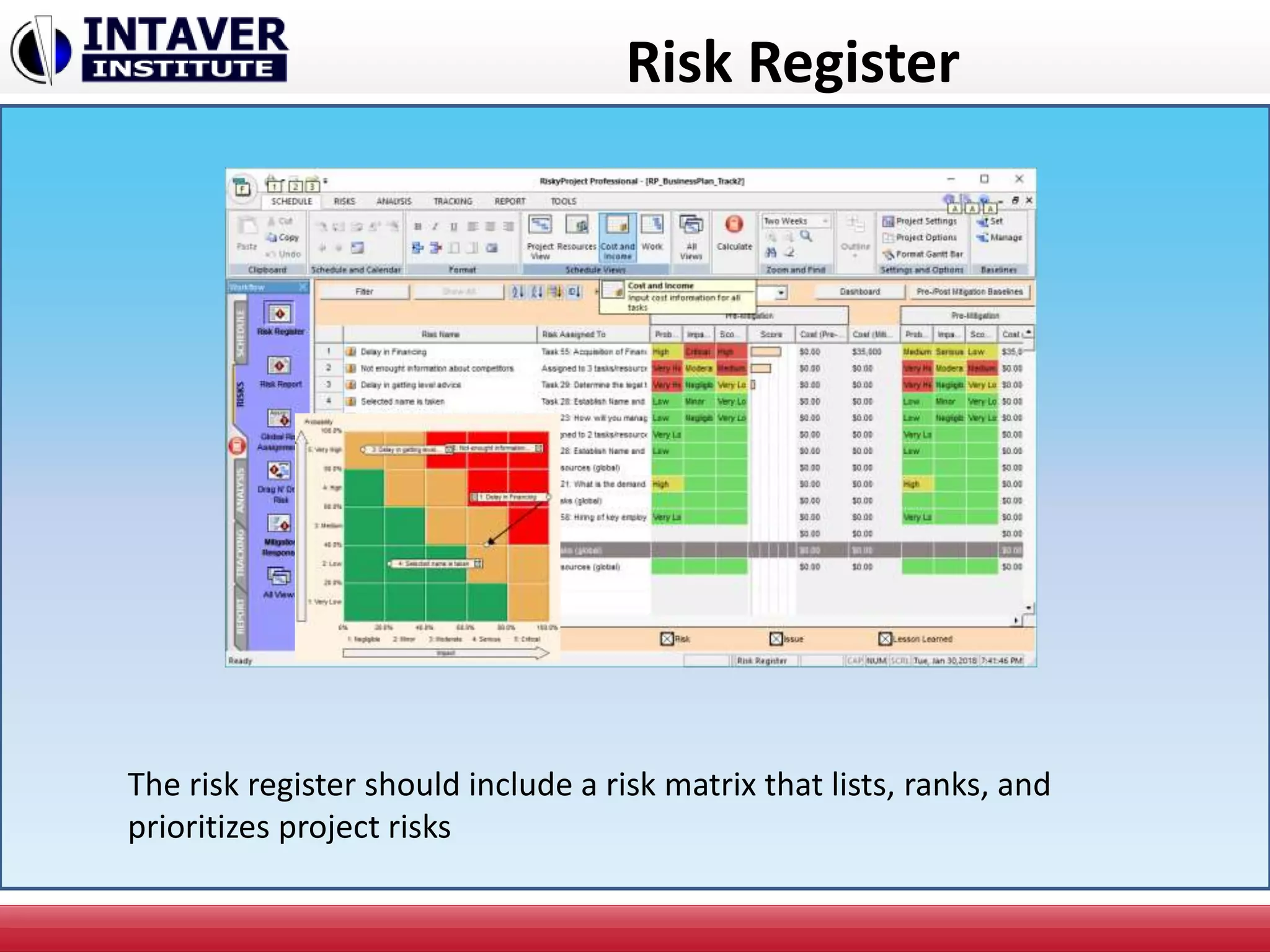
The document discusses decision-making in project management, emphasizing the importance of decision framing, risk assessment, and alternative generation for effective project execution. It highlights the need to consider various factors including resource availability, market conditions, and organizational suitability while employing tools like mind mapping and multi-criteria decision-making. Additionally, it outlines methods for identifying and managing risks, as well as the significance of a risk register in prioritizing project challenges.