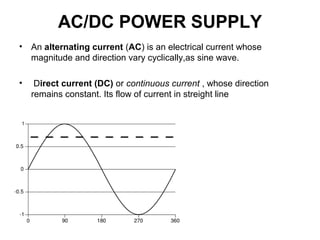
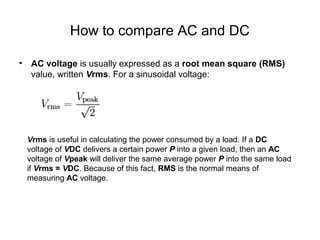
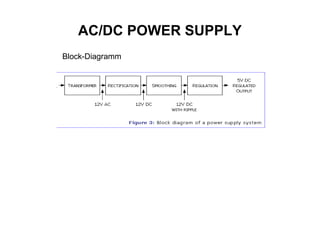
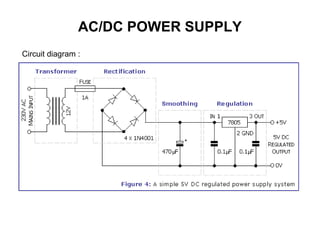
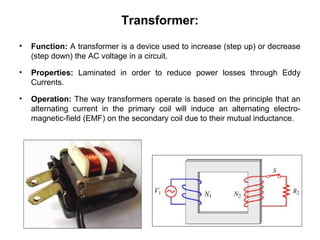
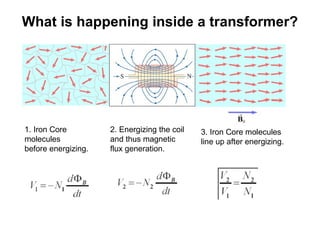
The document discusses the differences between alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC), highlighting that AC varies cyclically while DC maintains a constant direction. It explains how power loss occurs differently in AC and DC systems and introduces the concept of root mean square (RMS) for measuring AC voltage. Additionally, it covers the function and operation of transformers, which are used to adjust AC voltage in circuits.