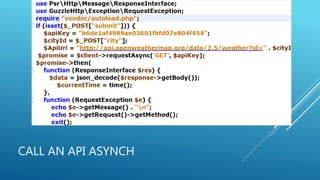
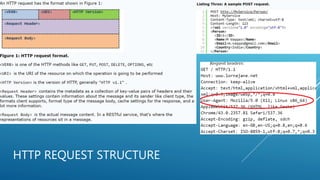
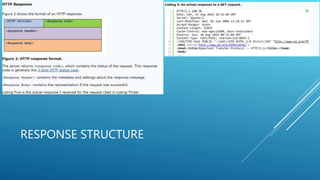
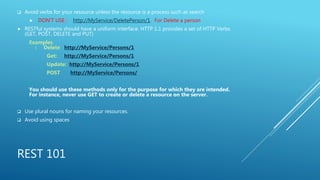
This document discusses Guzzle, a PHP HTTP client library, and creating RESTful APIs with PHP. It explains what Guzzle is, how to install it using Composer, and how to make asynchronous and concurrent requests with Guzzle. It then covers REST API concepts like HTTP verbs, request and response structures, status codes, and building a basic RESTful API in PHP. Code examples are provided to demonstrate creating a RESTful API using PHP.















![FAKING THE USER AGENT VIA PHP
REMEMBER :
$_SERVER[“HTTP_USER_AGENT”]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day02-api-190220223059/85/Day02-a-pi-21-320.jpg)


![ PUT : The PUT method replaces all current representations of the target resource with the
request payload..
Access PUT using PHP
$_PUT= json_decode(file_get_contents("php://input"),true);
Delete /addresses.php?id=1
update the address which number is 1 with current payload
$_SERVER[“REQUEST_METHOD”] : gives which verb was used GET OR POST,
Delete](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day02-api-190220223059/85/Day02-a-pi-25-320.jpg)
![ Delete : Request that a resource be removed; however, the resource
does not have to be removed immediately. It could be an
asynchronous or long-running request.
Delete /addresses.php?id=1
delete the address which number is 1
$_SERVER[“REQUEST_METHOD”] : gives which verb was
used GET OR POST, Delete](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day02-api-190220223059/85/Day02-a-pi-26-320.jpg)



![http://MyService/Persons?id=1
OR http://MyService/Persons/1
The query parameter approach works just fine and REST does not stop you from using
query parameters. However, this approach has a few disadvantages.
Increased complexity and reduced readability, which will increase if you have more
parameters
Use http://localhost/rest01.php/items/10
Not http://localhost/rest01.php?Resources=items&&id=10
$url_piecies = explode("/",$_SERVER["REQUEST_URI"]);
$resource = (isset($url_piecies[2]))? $url_piecies[2] : "" ;
$resource_id =(isset($url_piecies[3]) && is_numeric($url_piecies[3]) ) ?$url_piecies[3] : 0;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day02-api-190220223059/85/Day02-a-pi-31-320.jpg)



![REMEMBER BEFORE SEE THE WHOLE
THING THAT
$method = $_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD’];
Use http://localhost/rest01.php/items/10
Not http://localhost/rest01.php?Resources=items&&id=10
$url_piecies = explode("/",$_SERVER["REQUEST_URI"]);
$resource = (isset($url_piecies[2]))? $url_piecies[2] : "" ;
$resource_id =(isset($url_piecies[3]) && is_numeric($url_piecies[3]) ) ?$url_piecies[3] : 0;
header (“Content-Type: application/json”);
$input = json_decode(file_get_contents('php://input'),true);
http_response_code(404)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/day02-api-190220223059/85/Day02-a-pi-35-320.jpg)