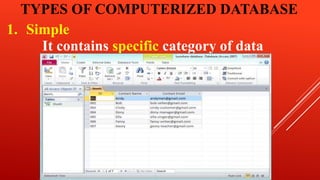
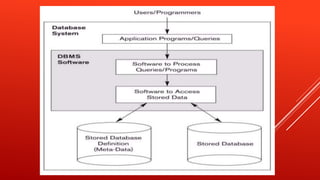
A database is a collection of data organized for rapid search and retrieval. There are two main types of databases: manual and computerized. A manual database does not use computers and includes things like address books and diaries, while a computerized database uses database management software and can store thousands of data points without much space. Computerized databases can be simple, containing one type of data, or relational, containing different related data sets organized into categories. A database management system (DBMS) is a collection of programs that allows users to store, access, and analyze data in a database. Common DBMS software includes Oracle, IBM DB2, Microsoft SQL Server, and MySQL.