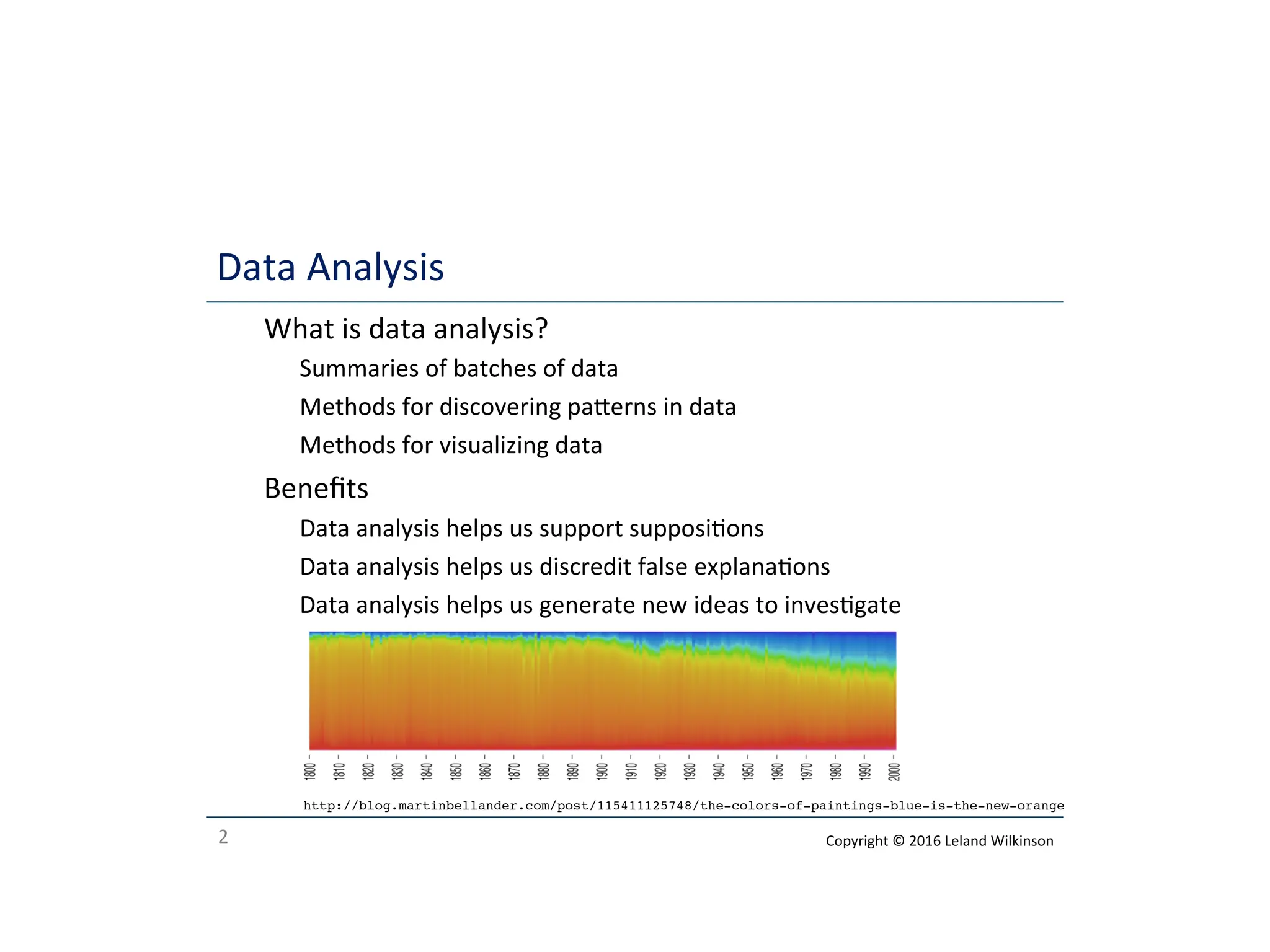
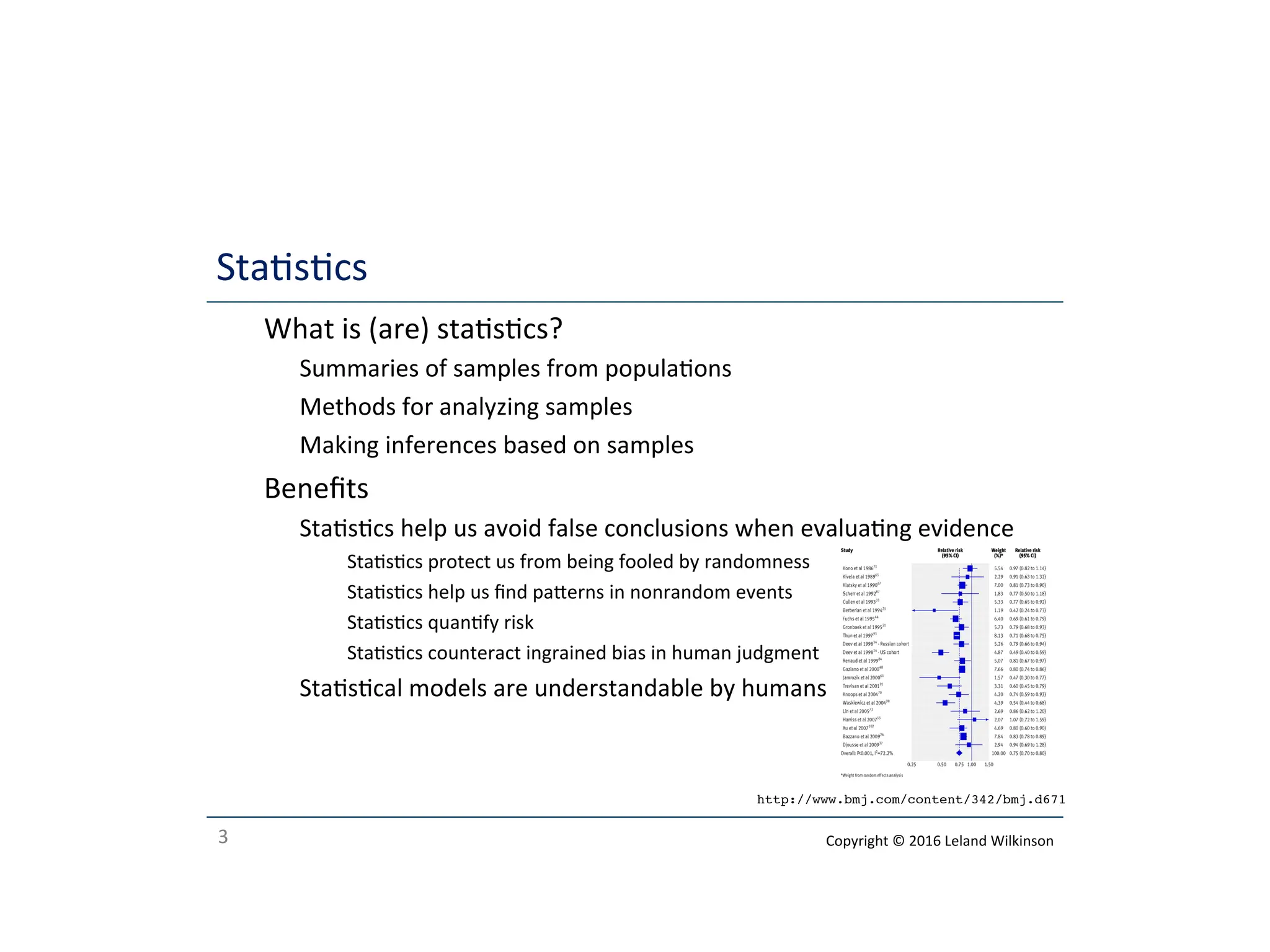
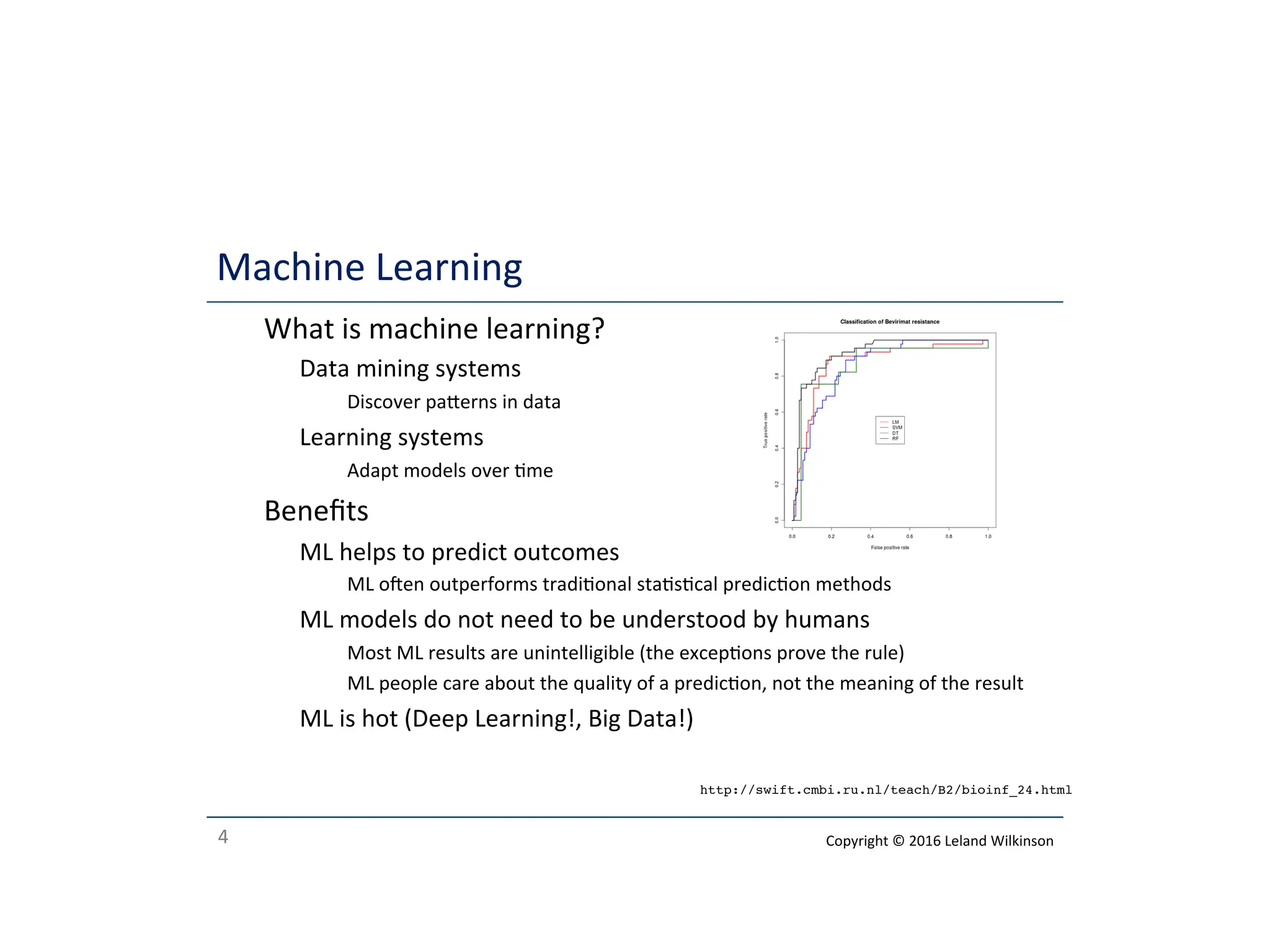
The document outlines the roles of data analysis, statistics, and machine learning, highlighting their methods, benefits, and applications. It emphasizes how data analysis can support hypotheses, while statistics help avoid false conclusions, and machine learning can predict outcomes effectively. Additionally, it provides a course outline covering various topics related to these fields.