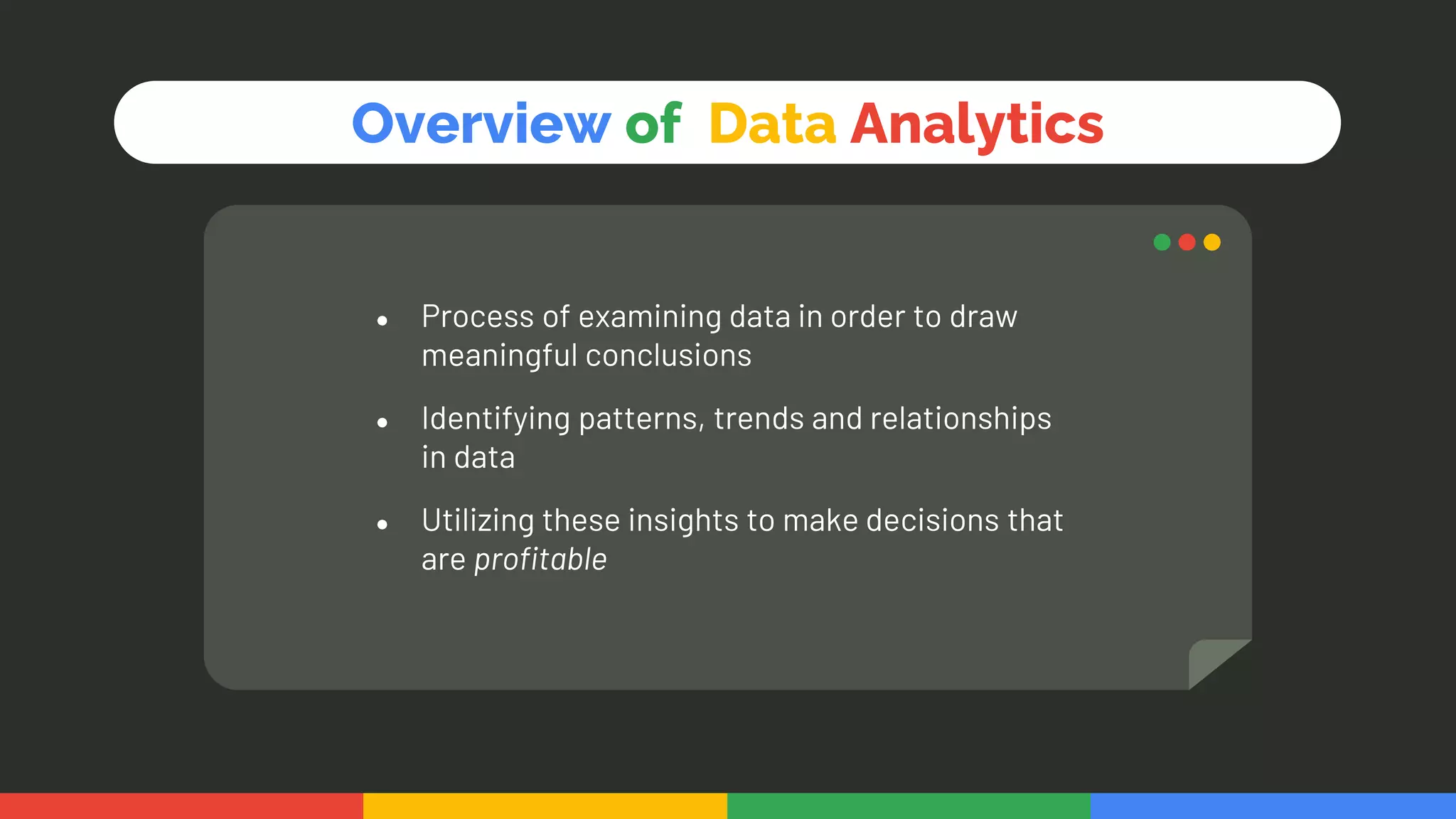
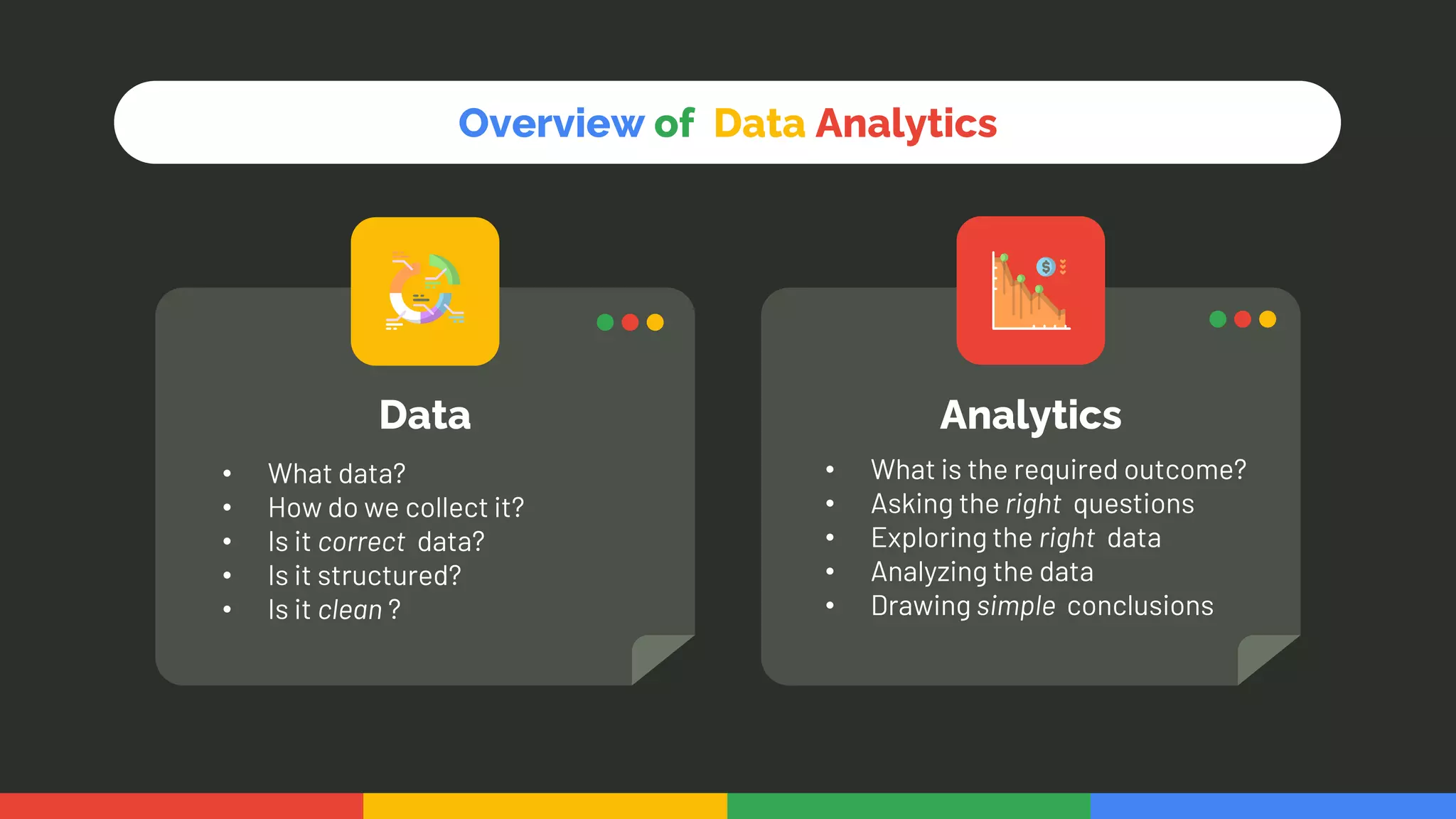
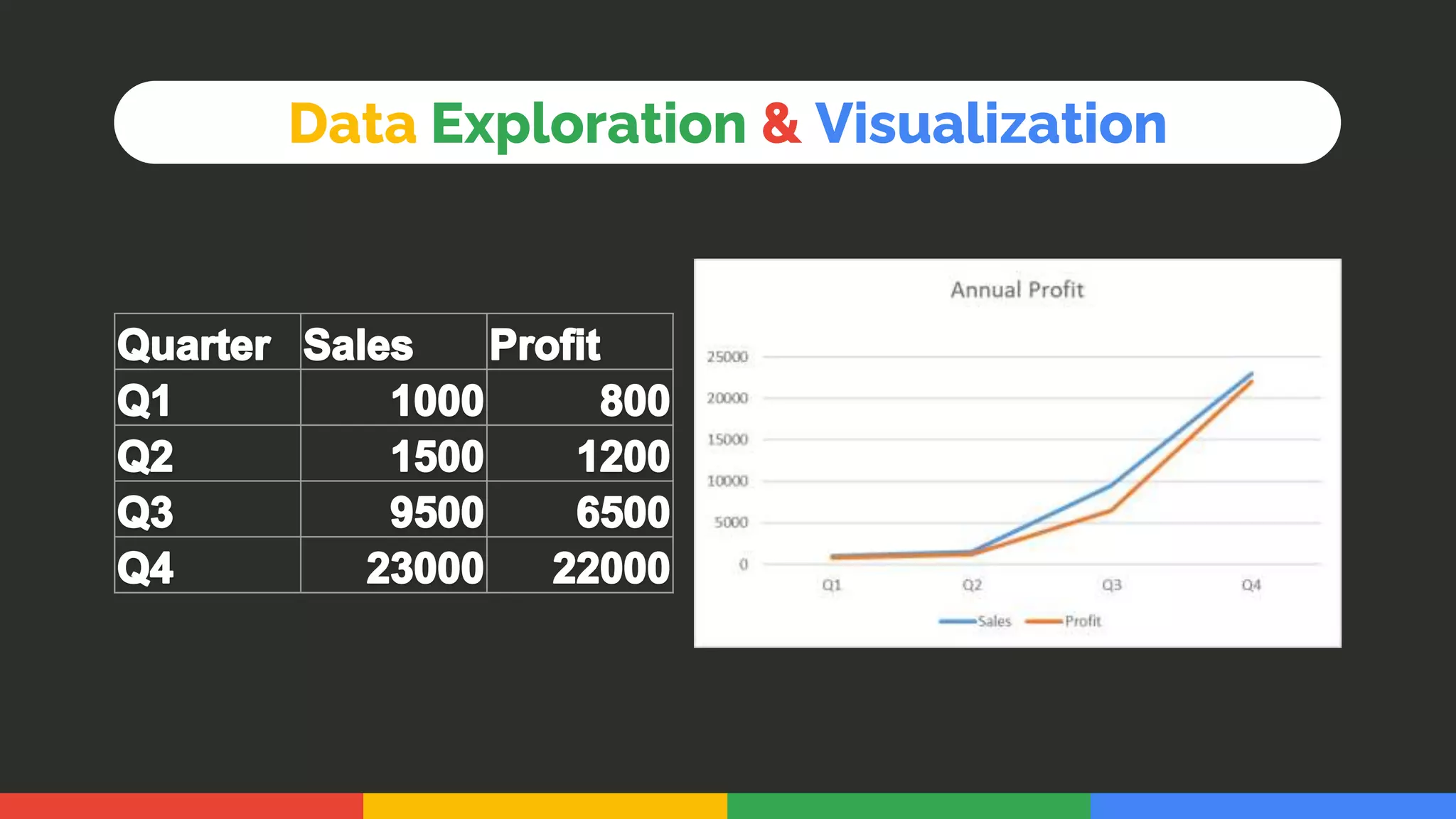
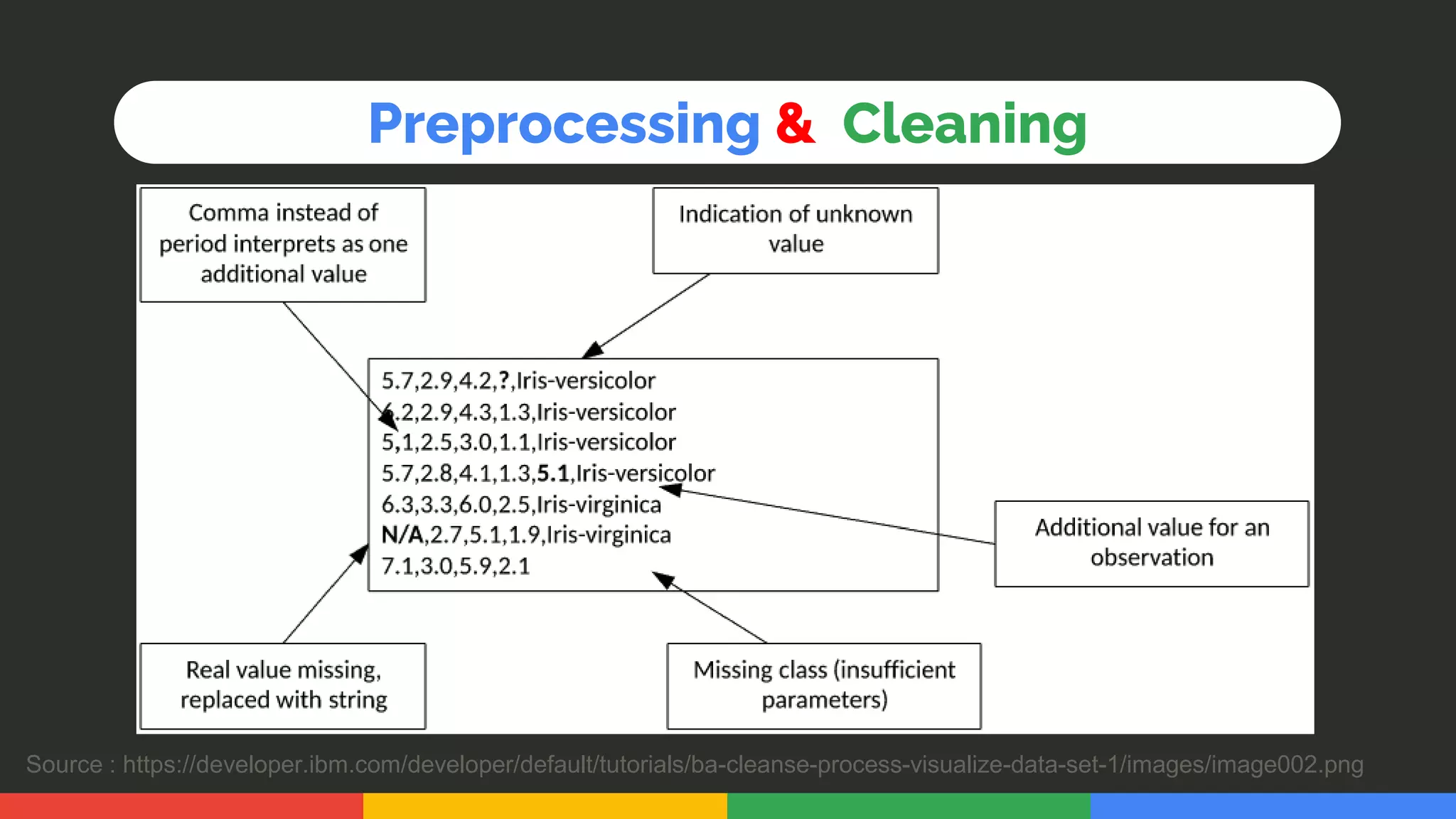
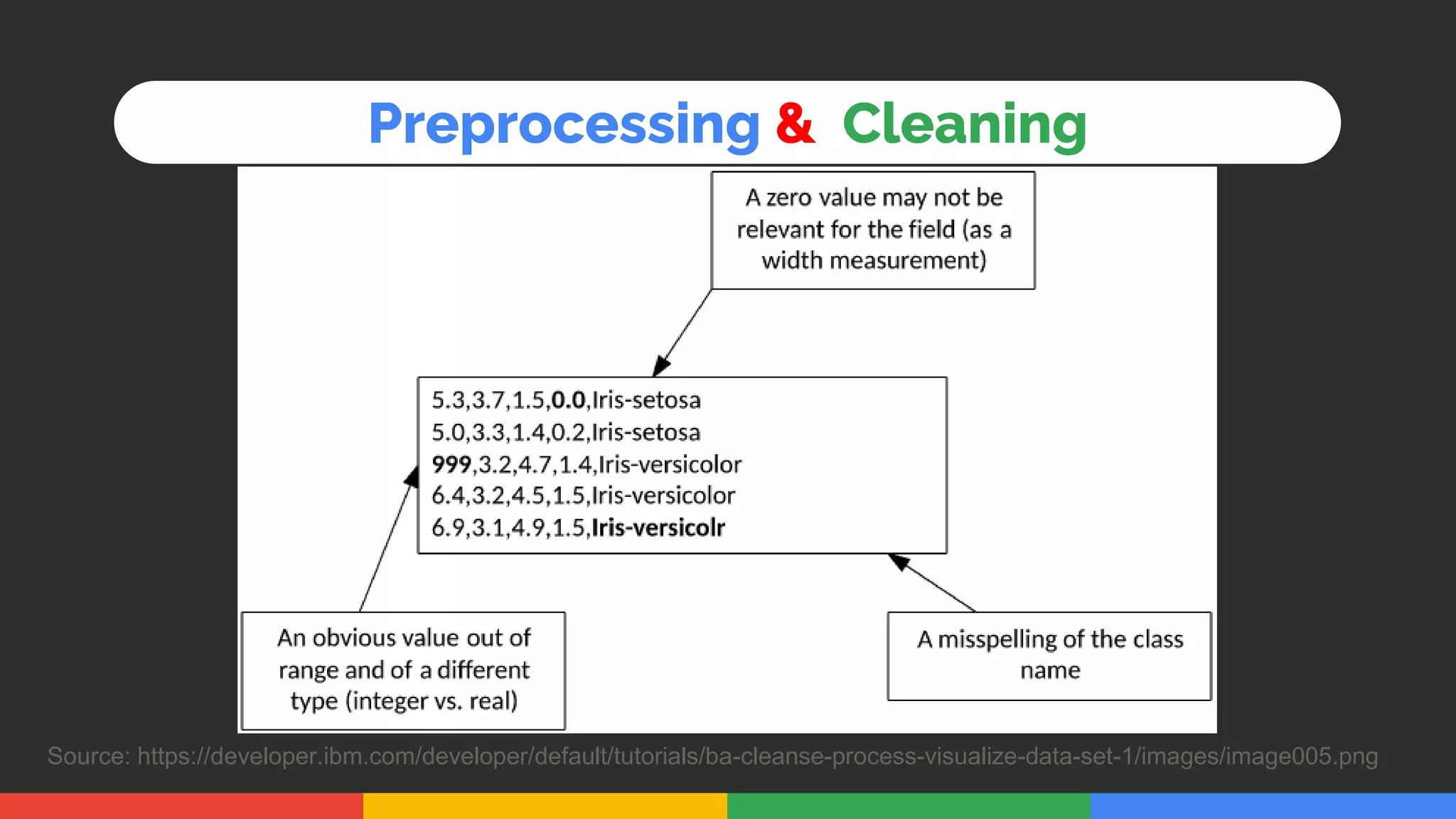
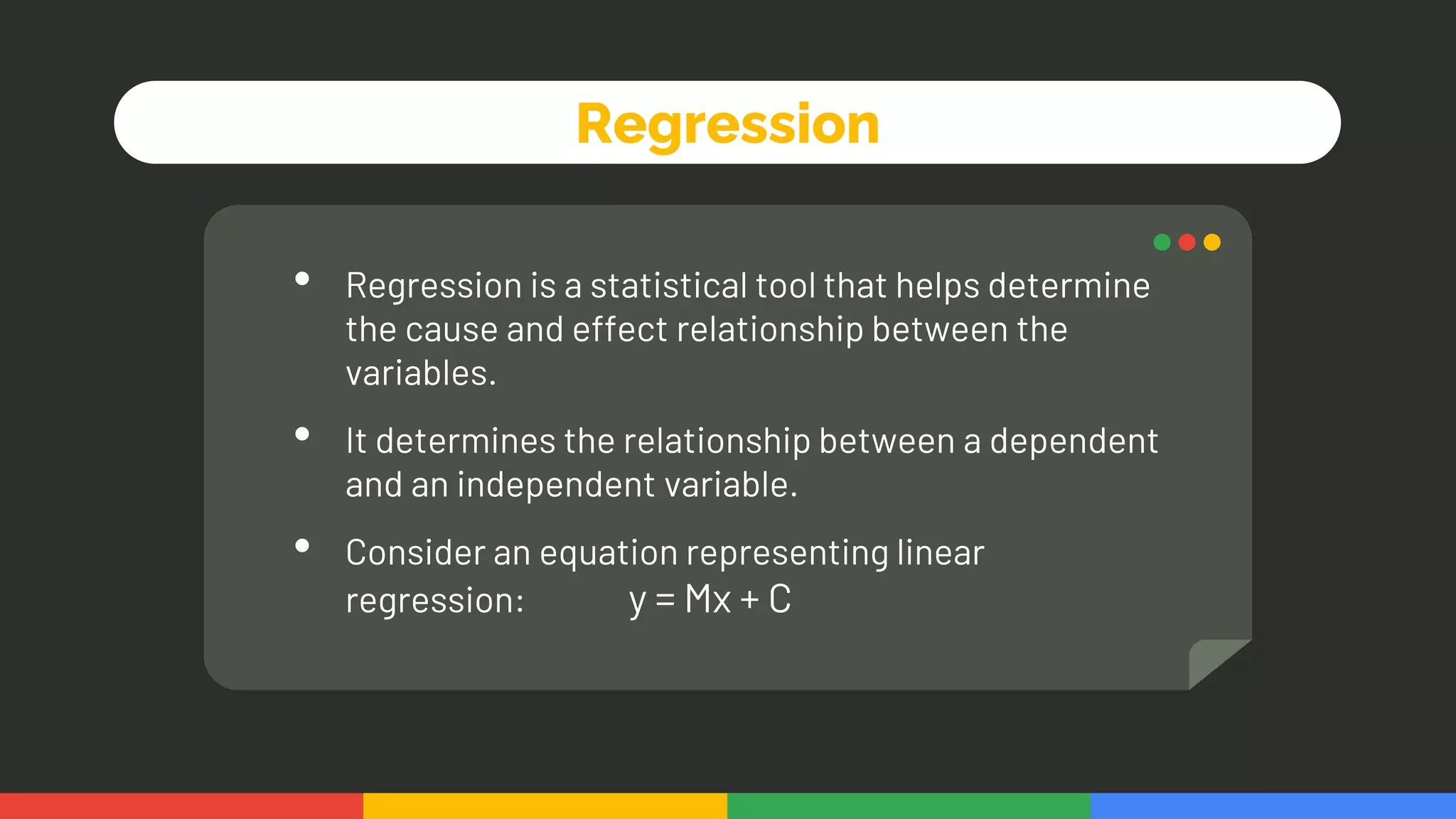
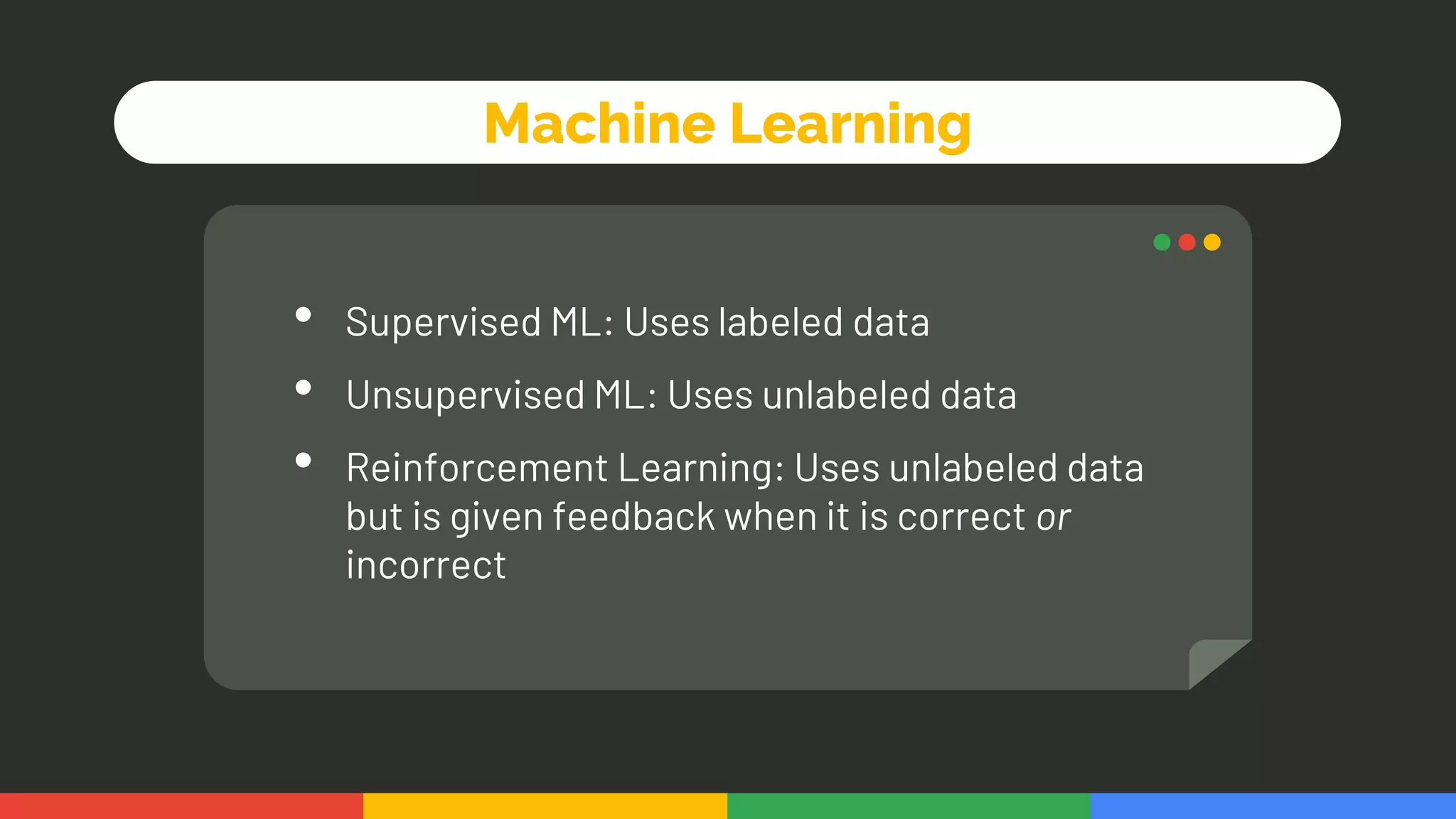
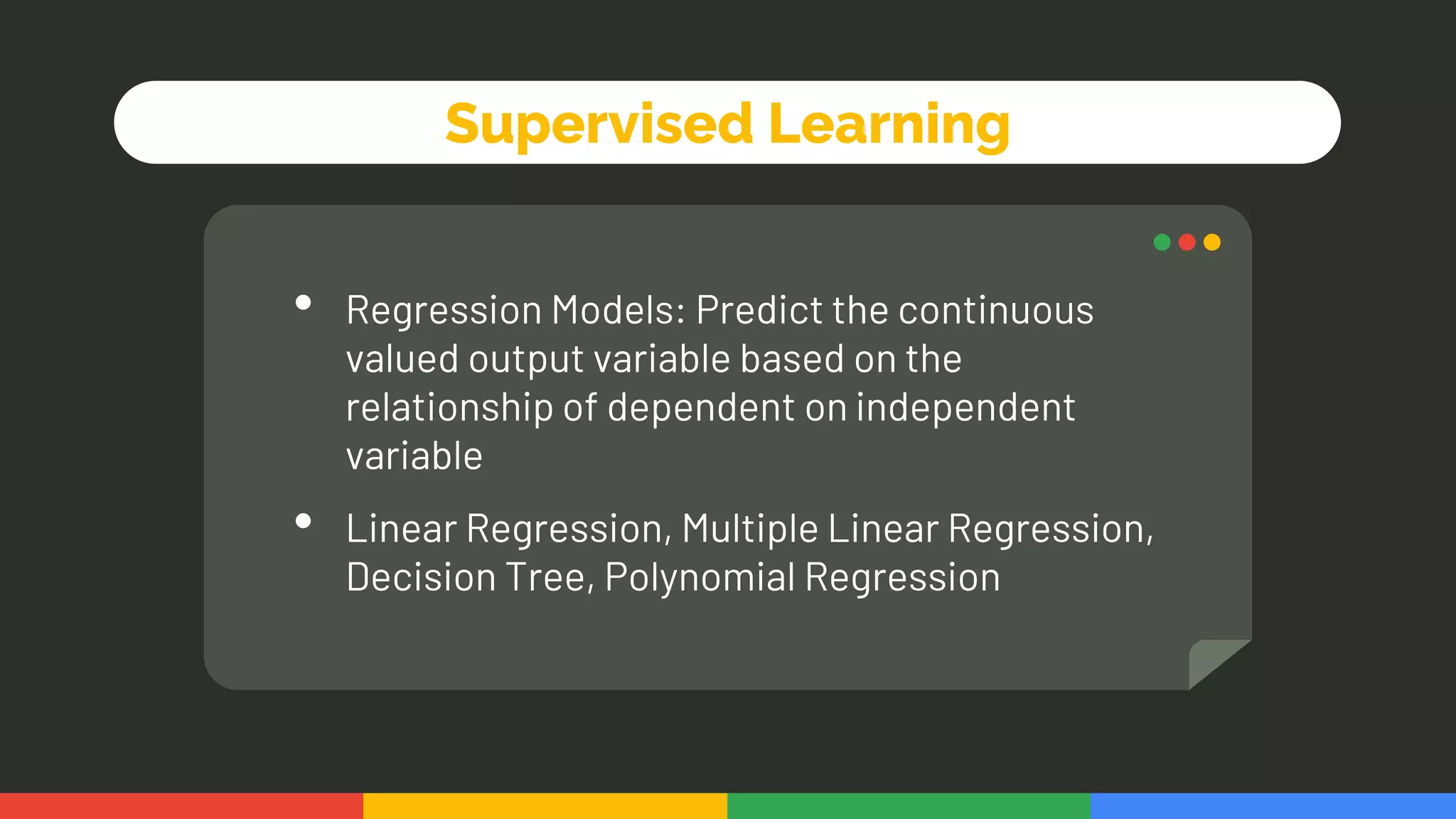
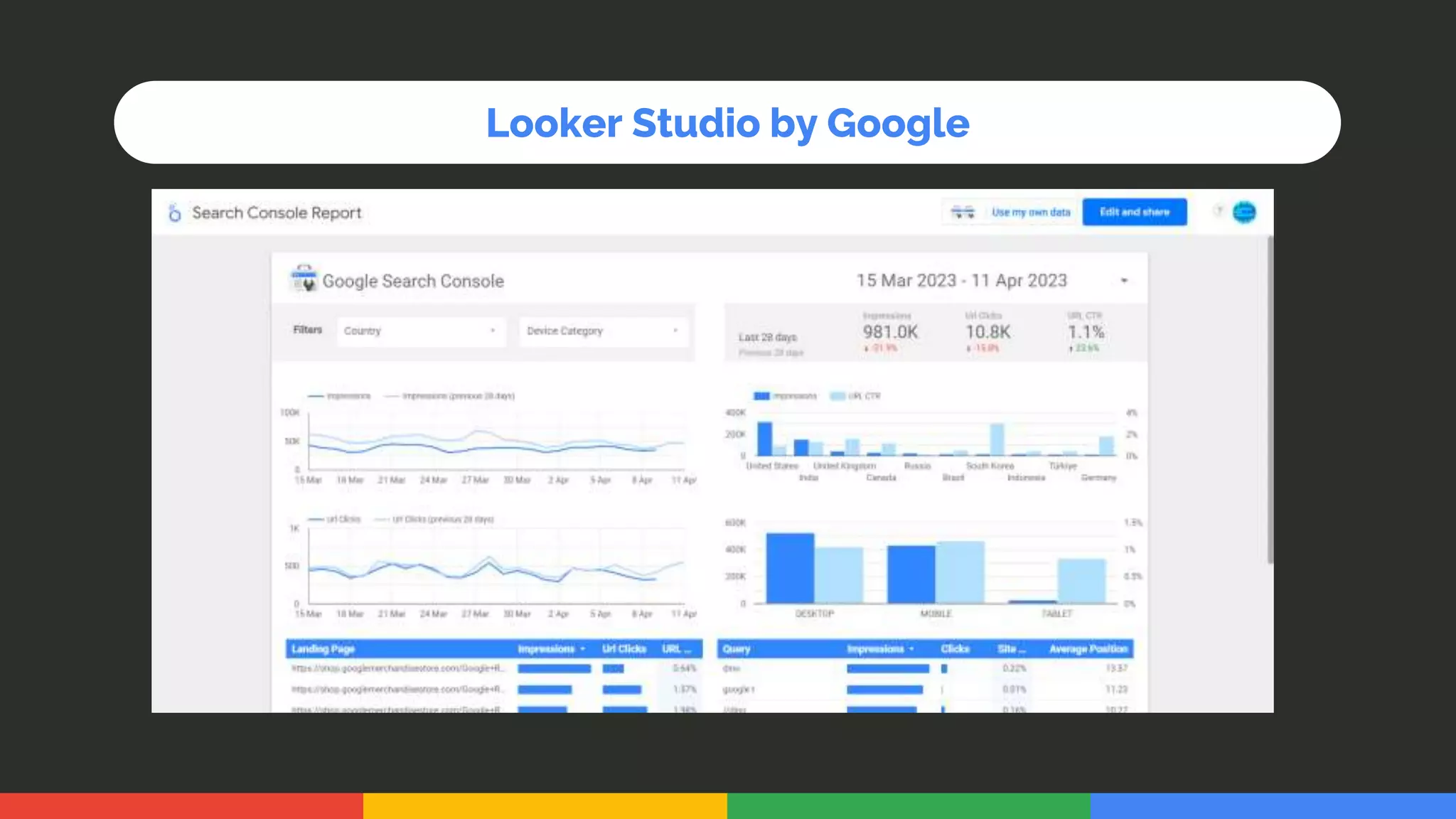
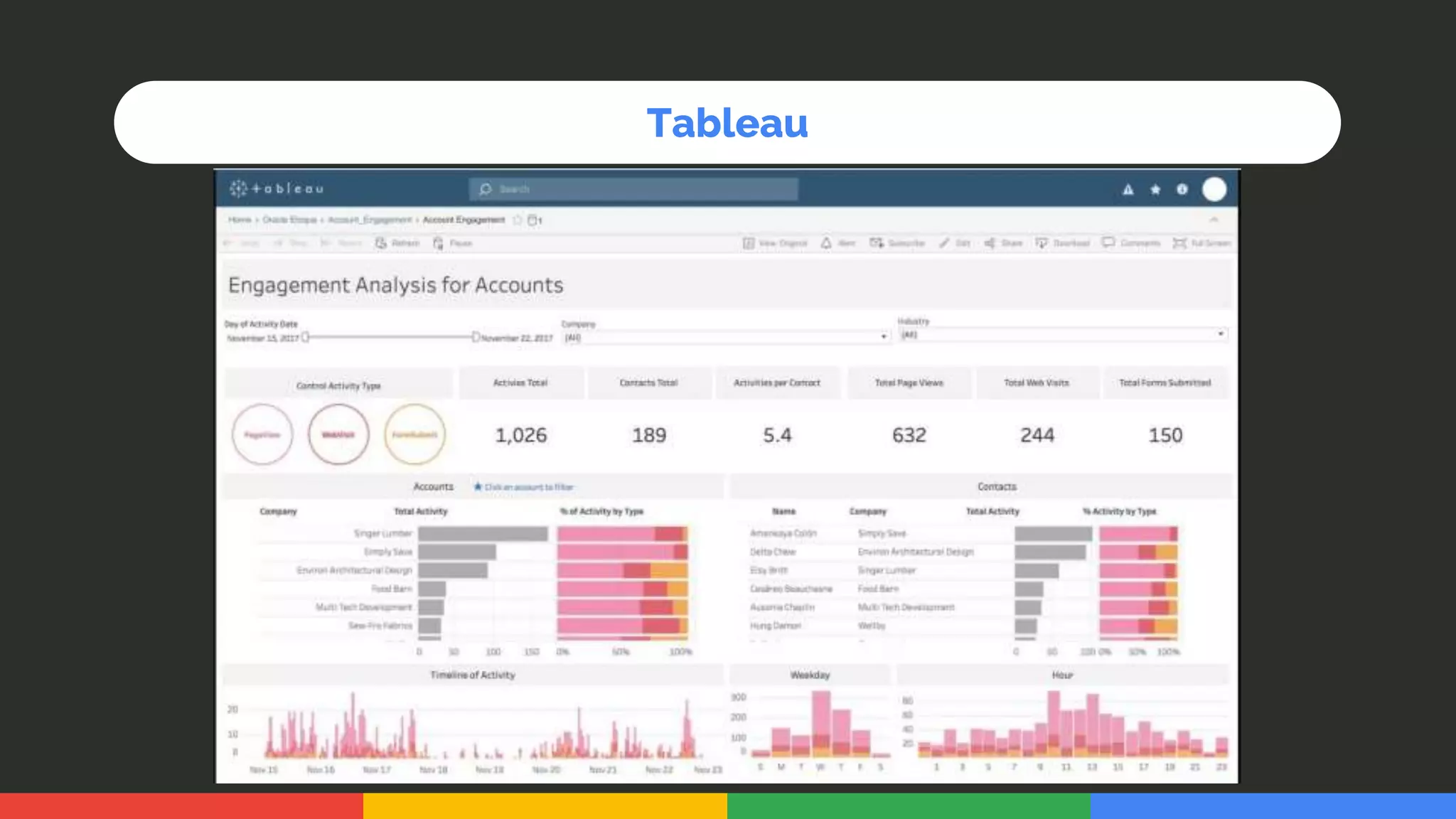
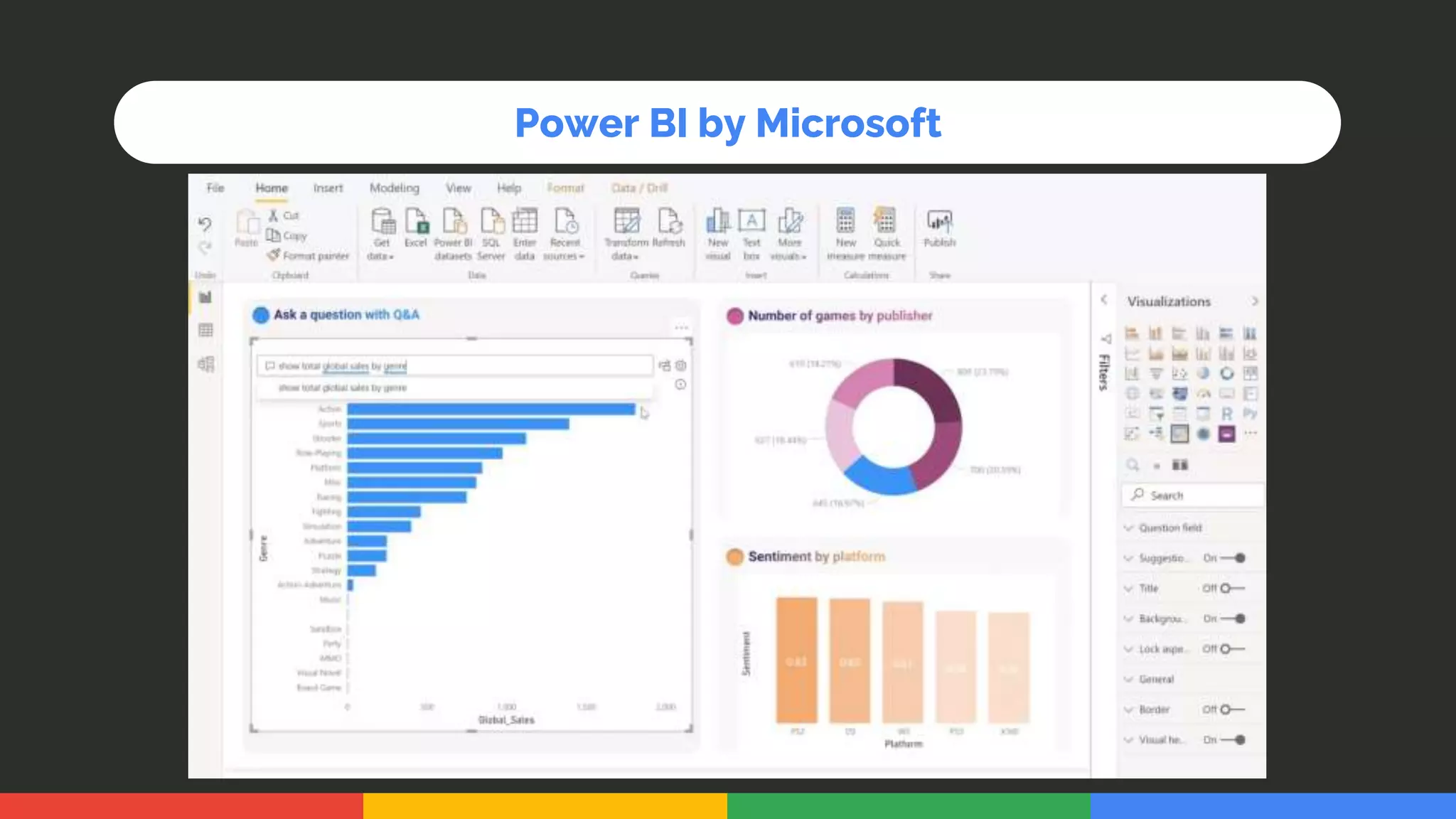
This document provides an introduction and overview of data analytics and machine learning. It discusses the importance of data analytics, how it can be applied in various domains like healthcare, finance and marketing. It covers topics like data exploration, preprocessing, cleaning, analysis and modeling. It also discusses tools used in data analytics like Kaggle, Google Looker Studio, Tableau and Power BI. The document emphasizes the need for data visualization and explores ethical and privacy issues around data.