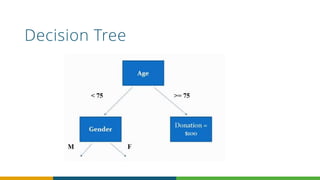
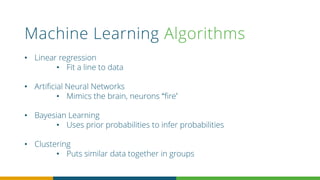
The document discusses the importance of data in fundraising, outlining what data to collect, analyze, and how to keep it clean for better insights. It emphasizes the use of quantitative and qualitative data, and introduces machine learning as a means to predict donor behavior and campaign effectiveness. Ultimately, it provides strategies for leveraging data to enhance fundraising efforts and make informed decisions.