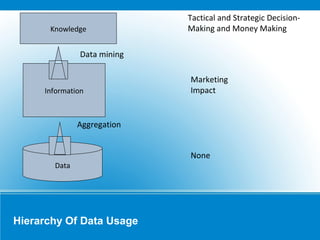
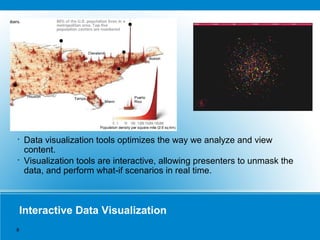
This document discusses data science and provides examples of how data science has been applied in various industries. It defines key components of data science including data acquisition, data munging, math/statistics/data mining, and data visualization. It then provides several case studies showing how data science has been used to develop customer segmentation models, create scored customer databases, conduct online customer panels, model customer preferences, and conduct structural equation modeling. The case studies demonstrate how data science can help target customers, increase product usage, and inform strategic business decisions.