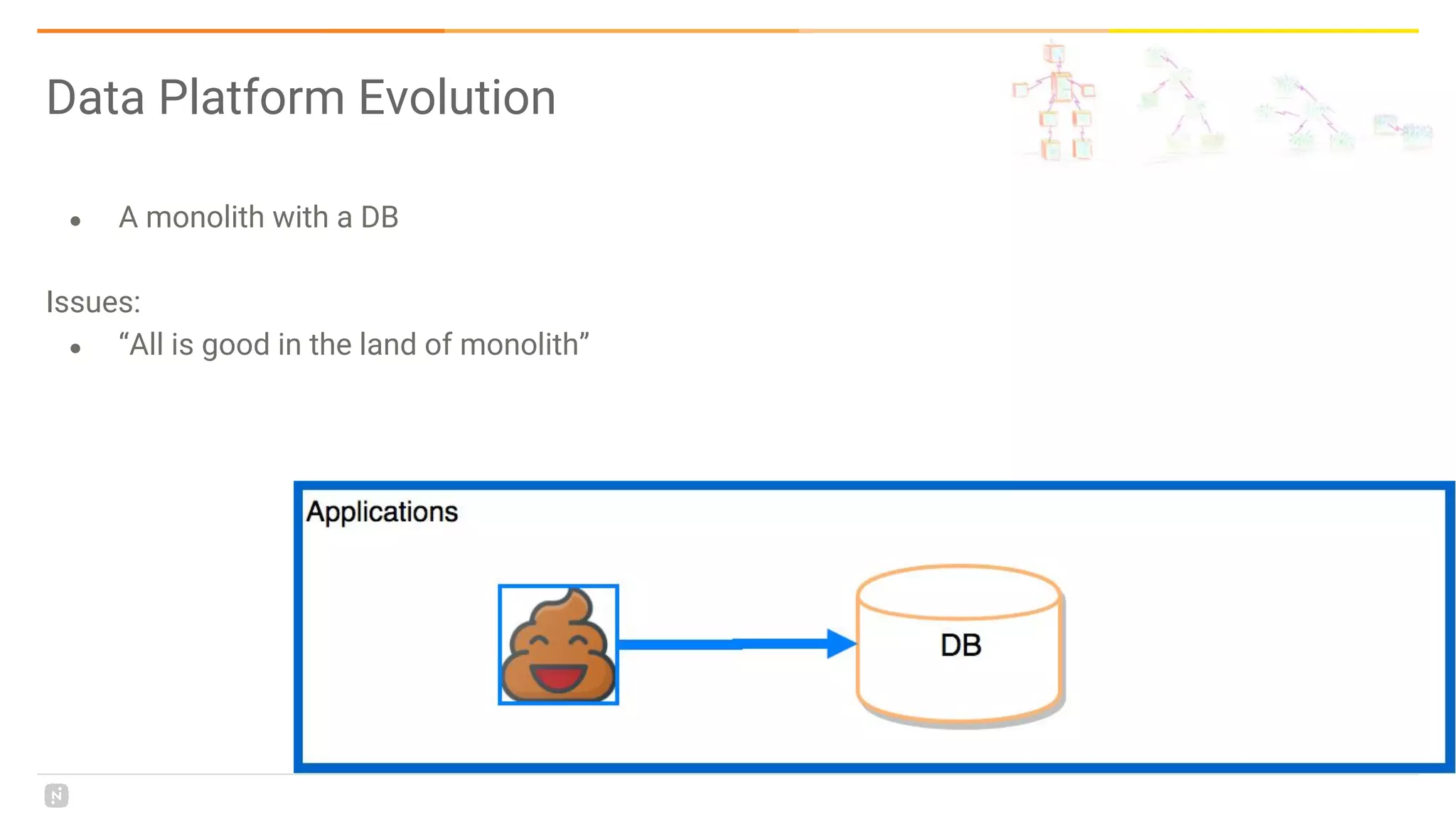
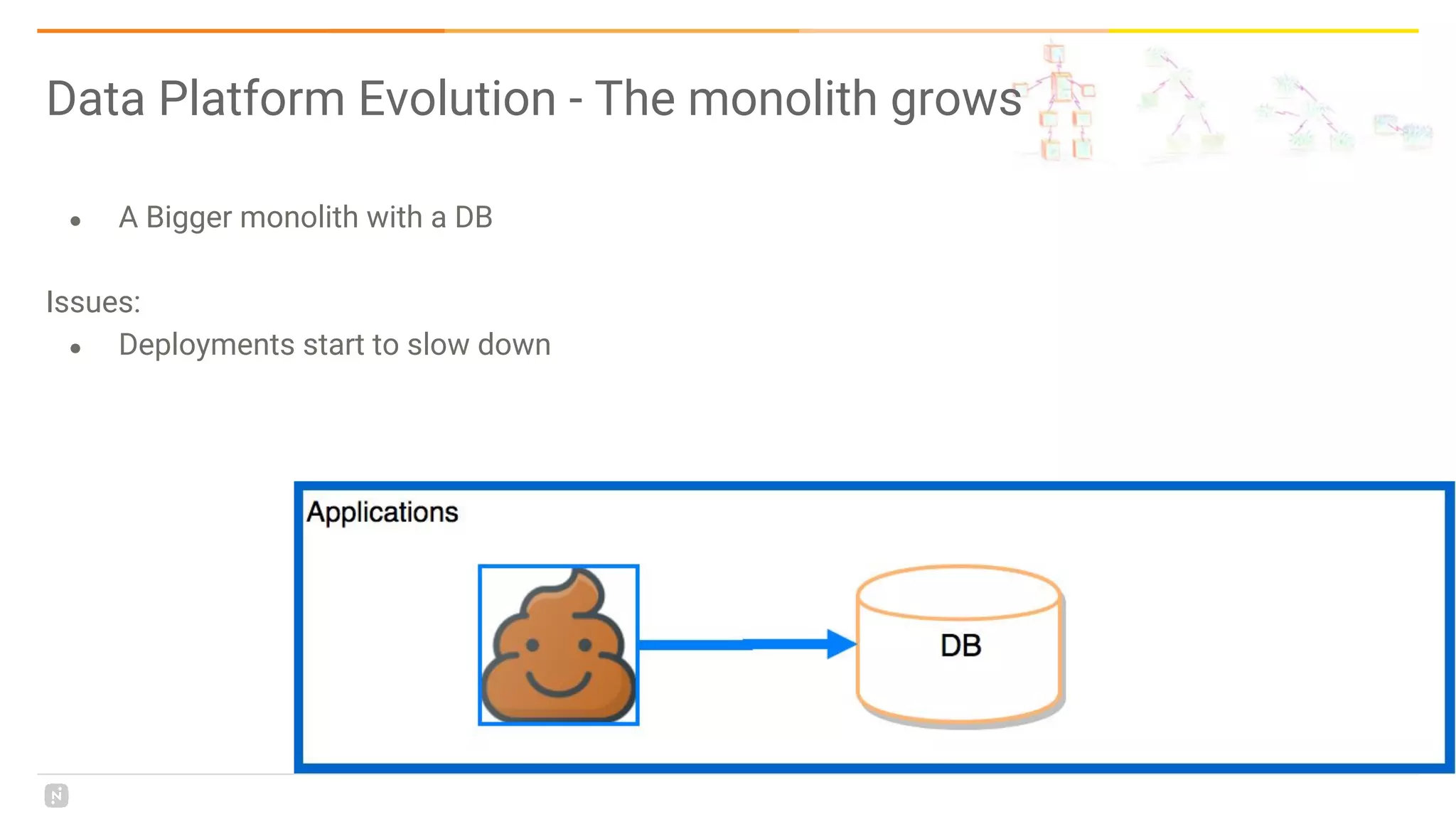
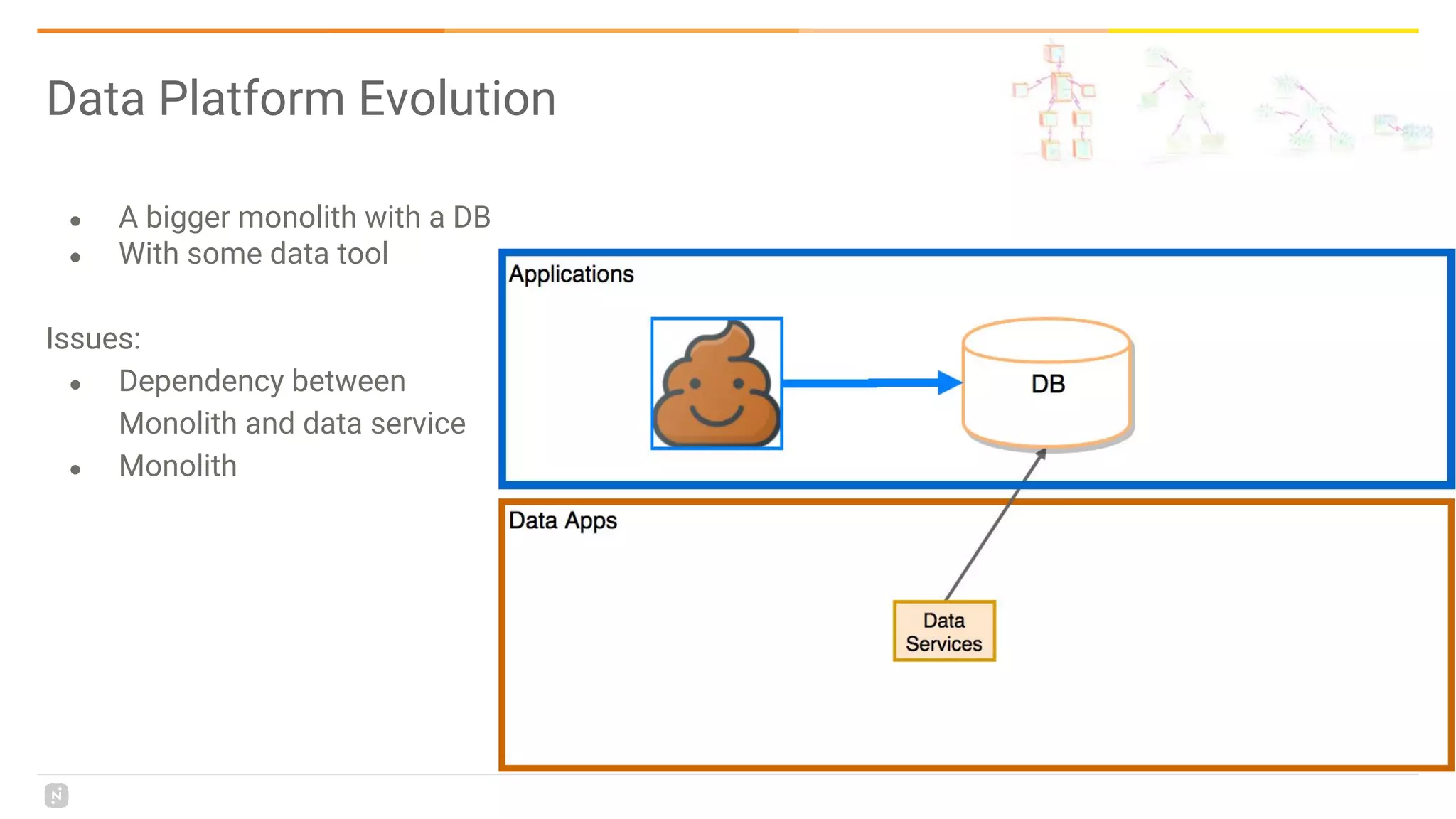
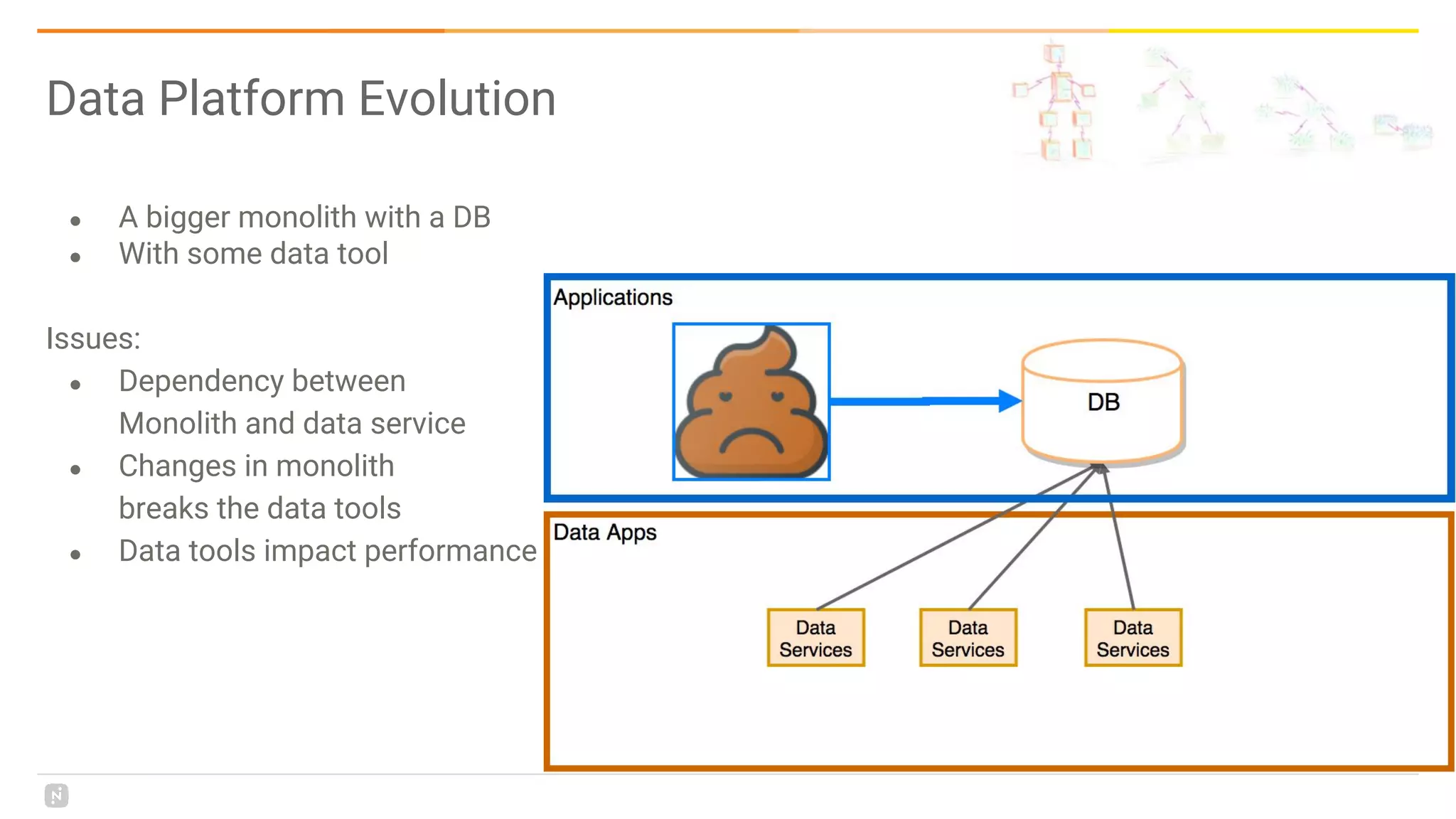
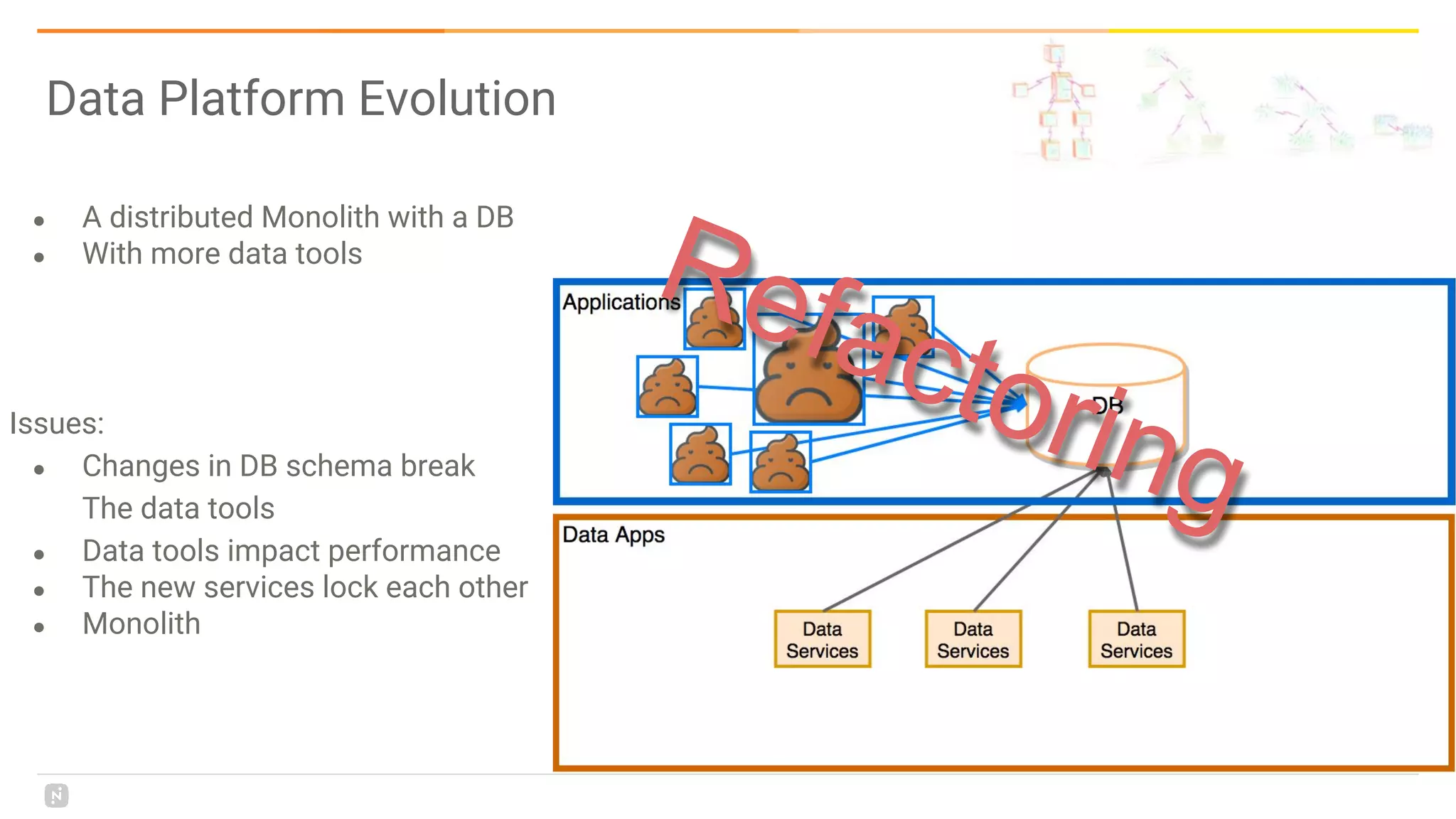
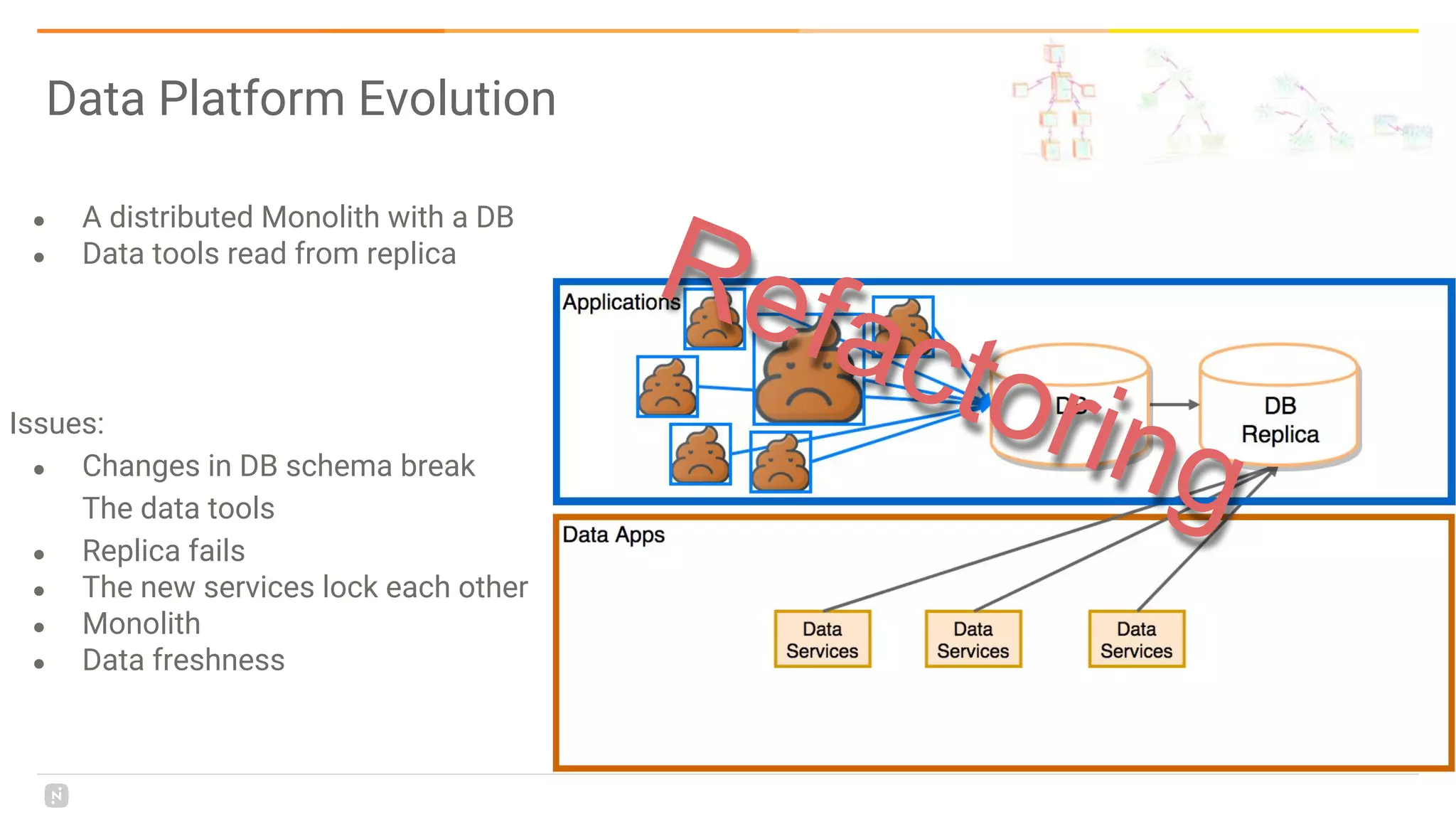
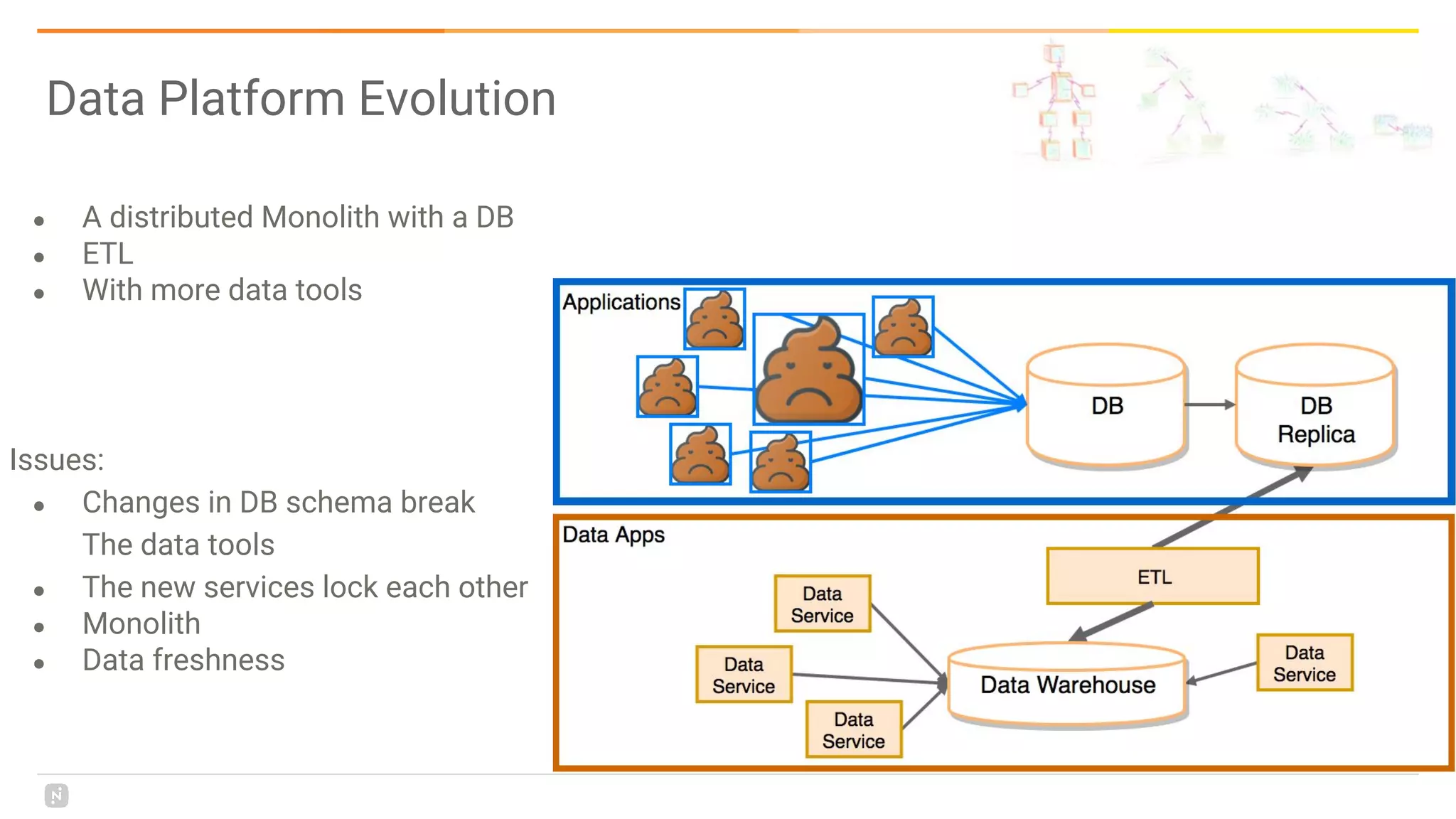
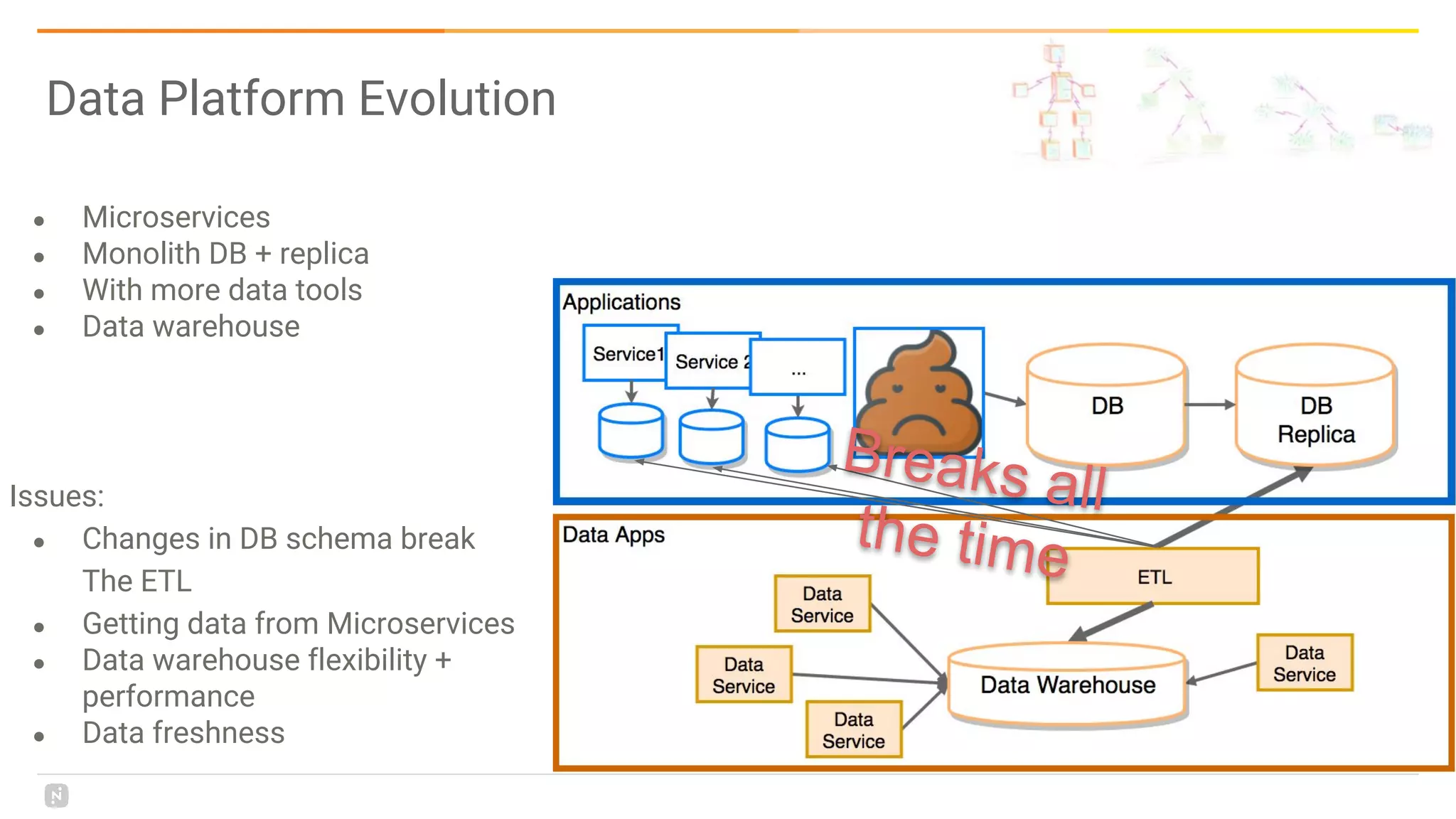
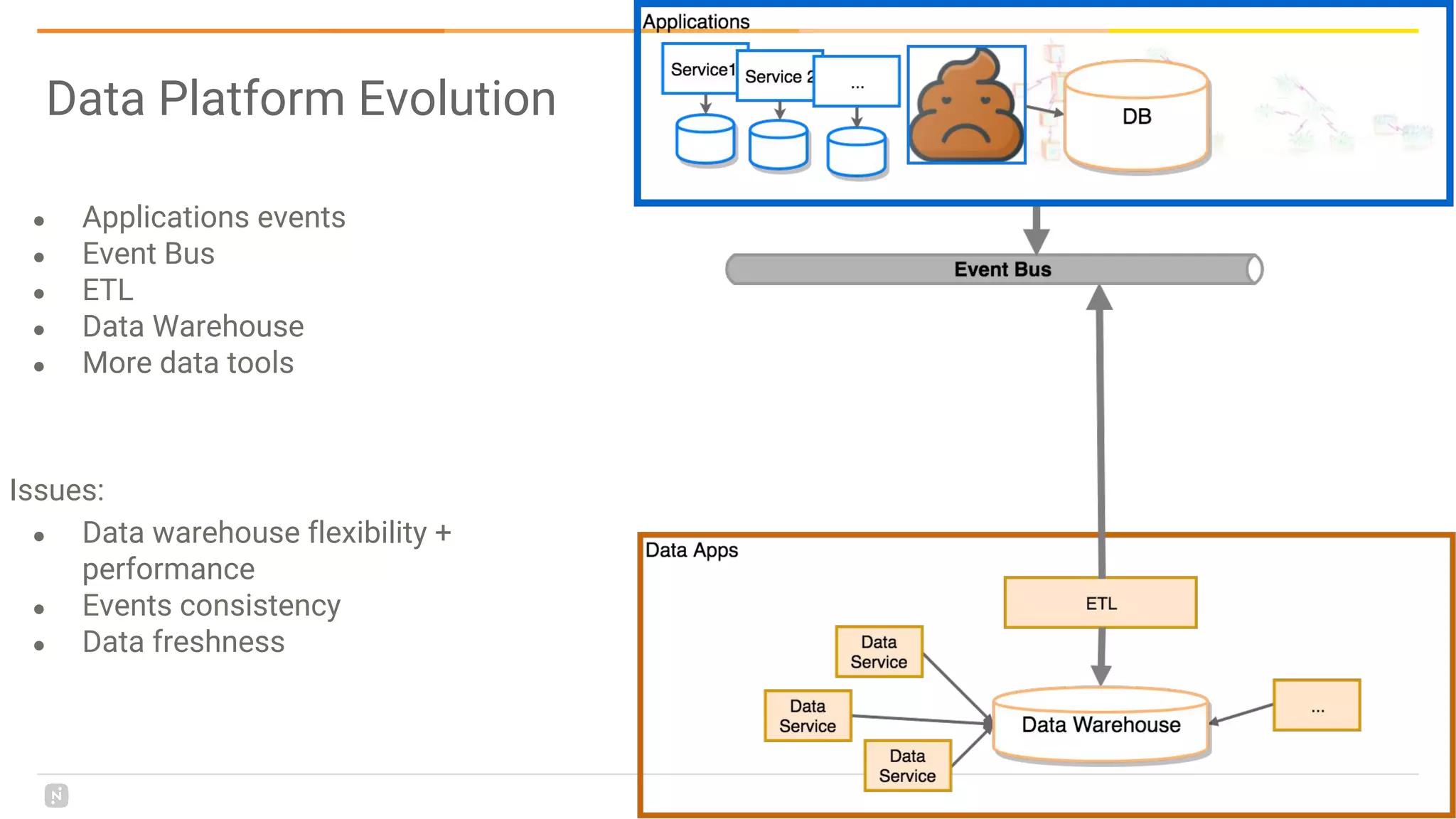
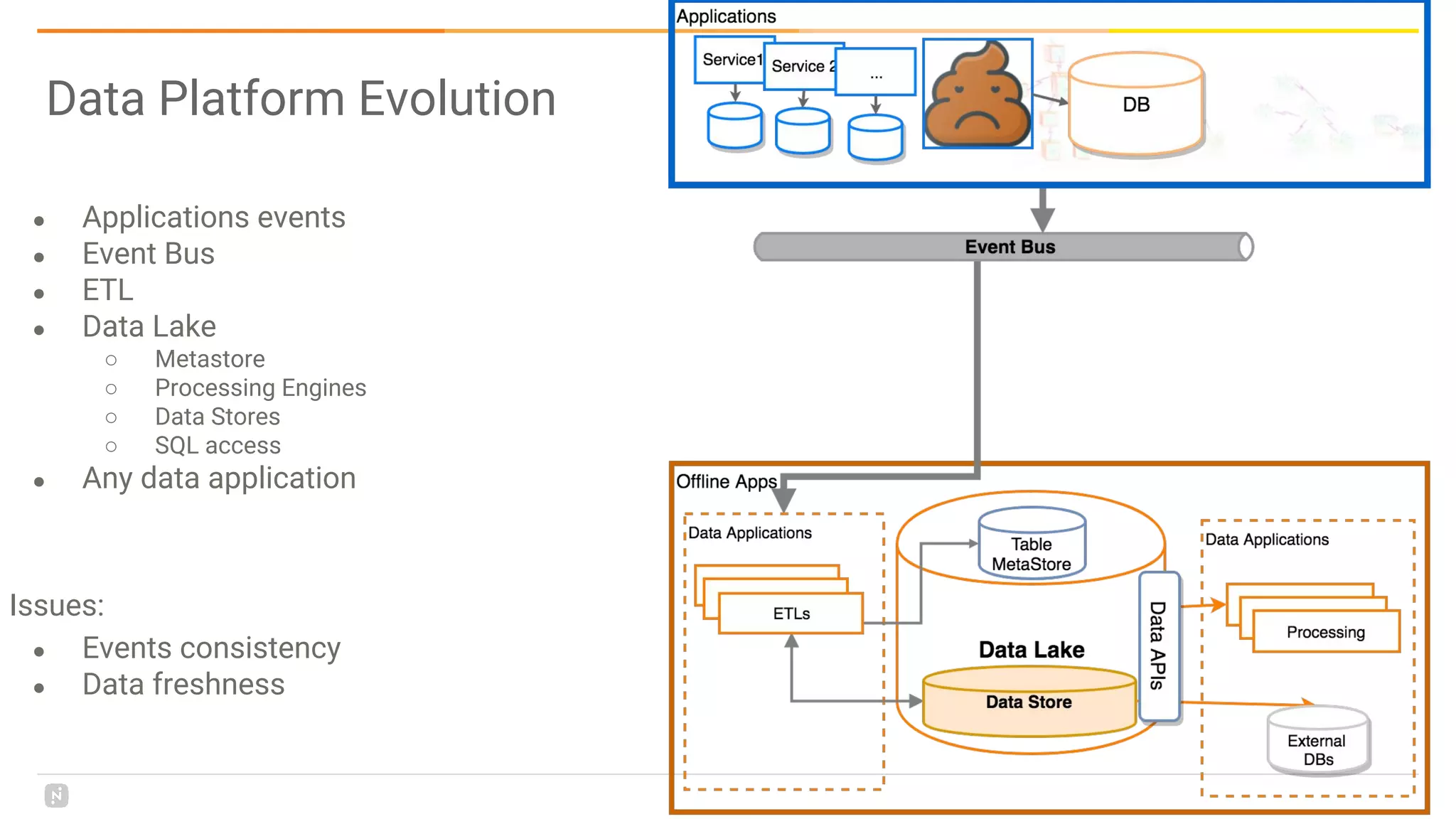
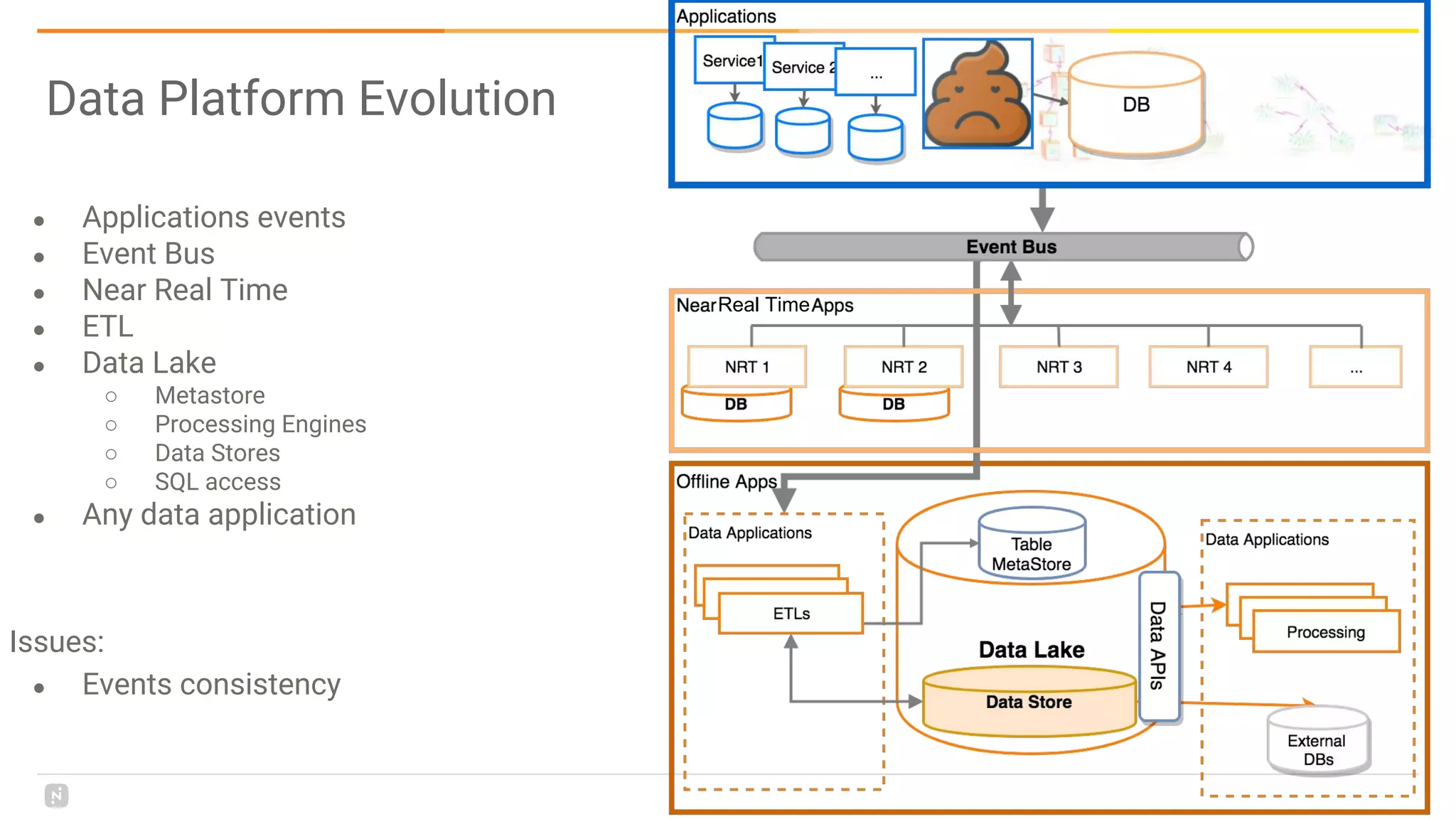
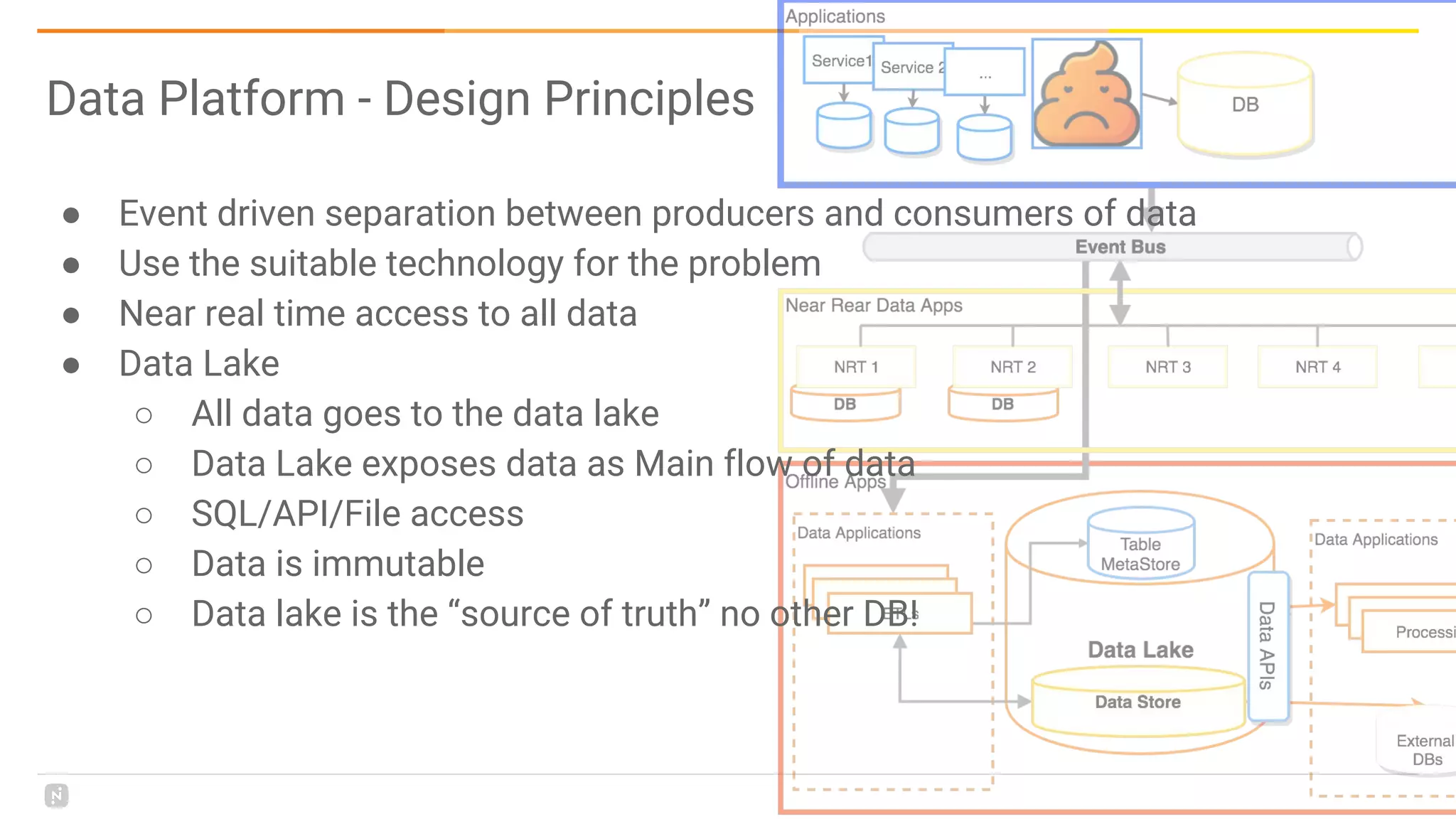
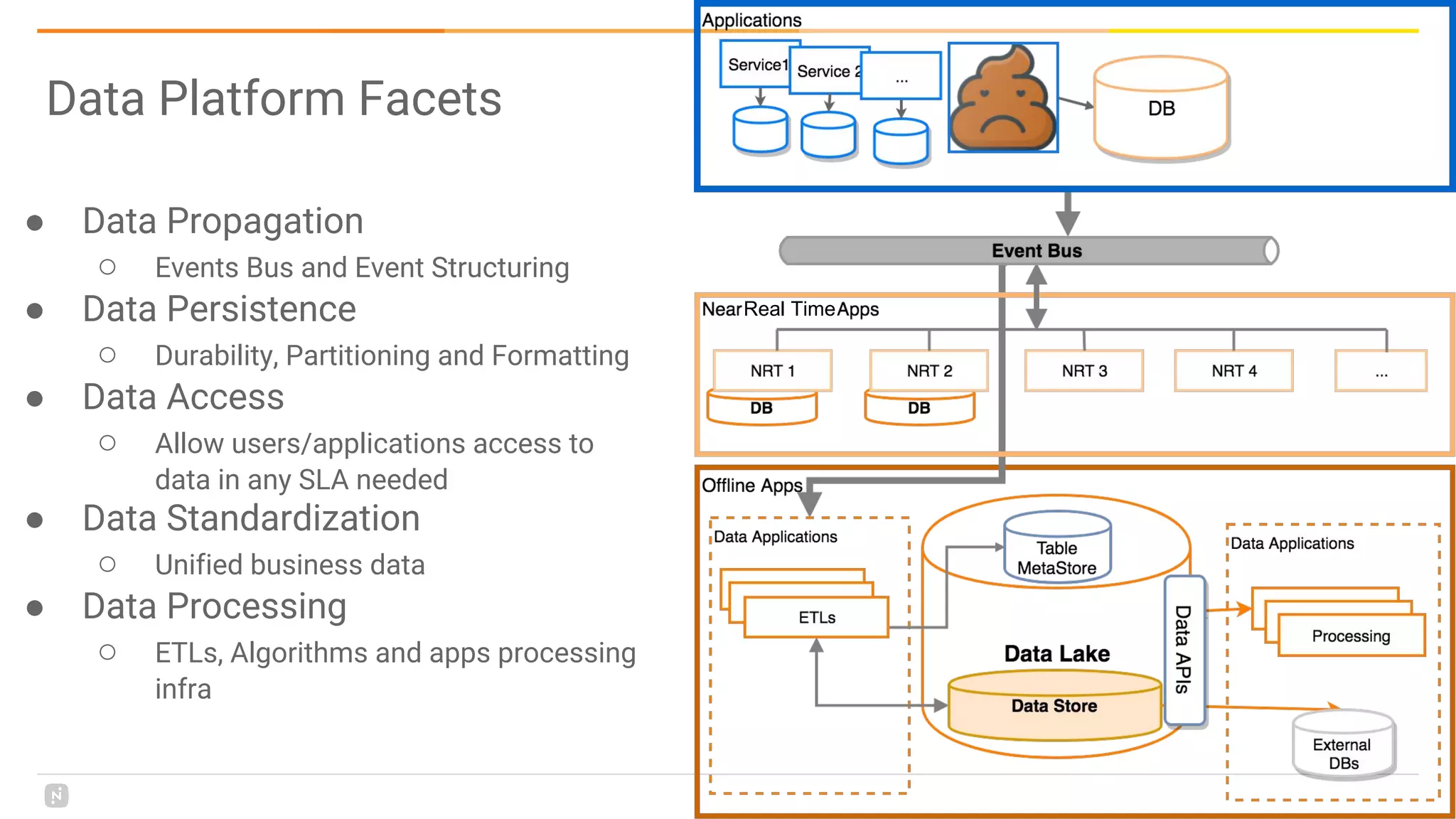
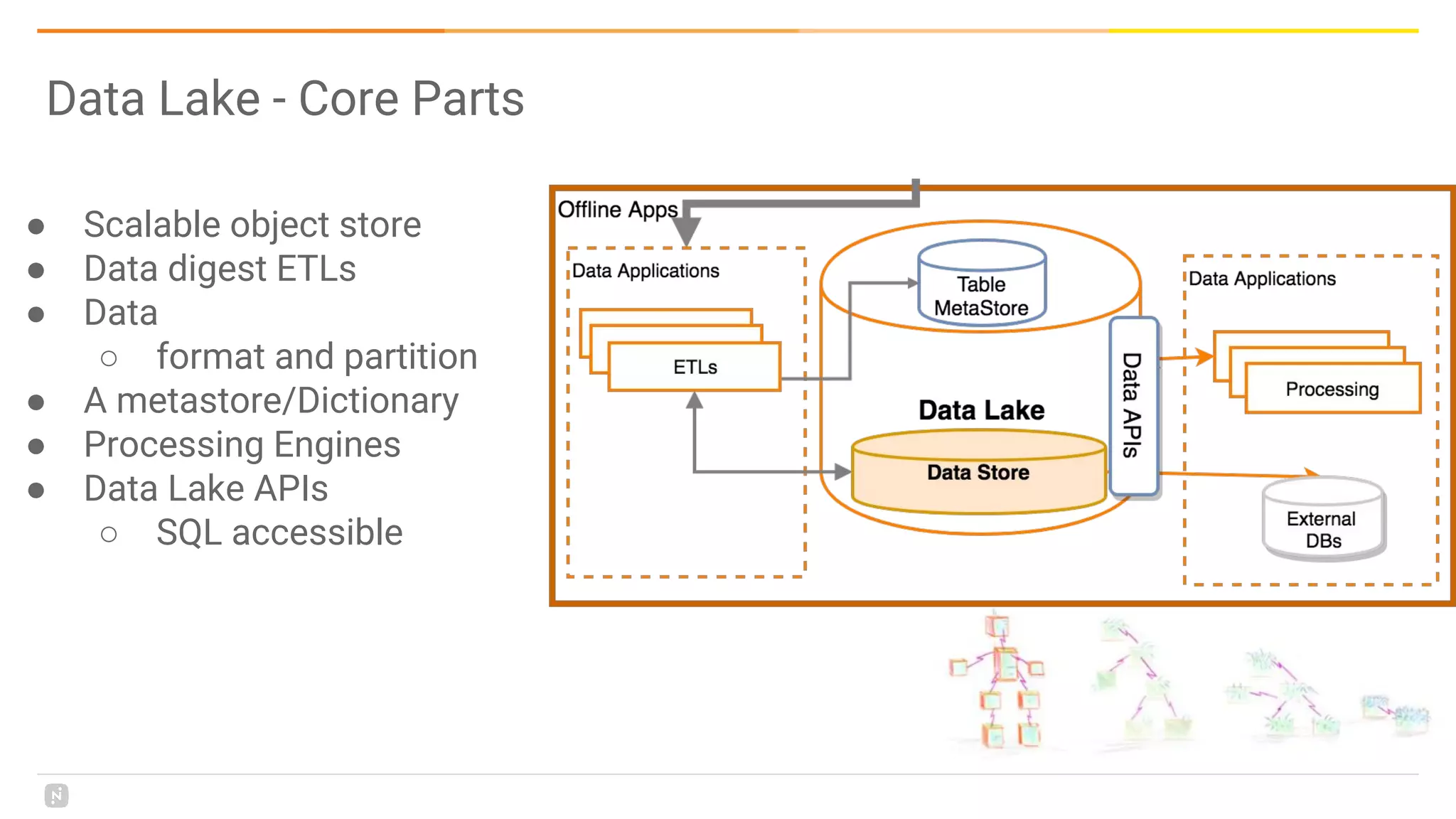
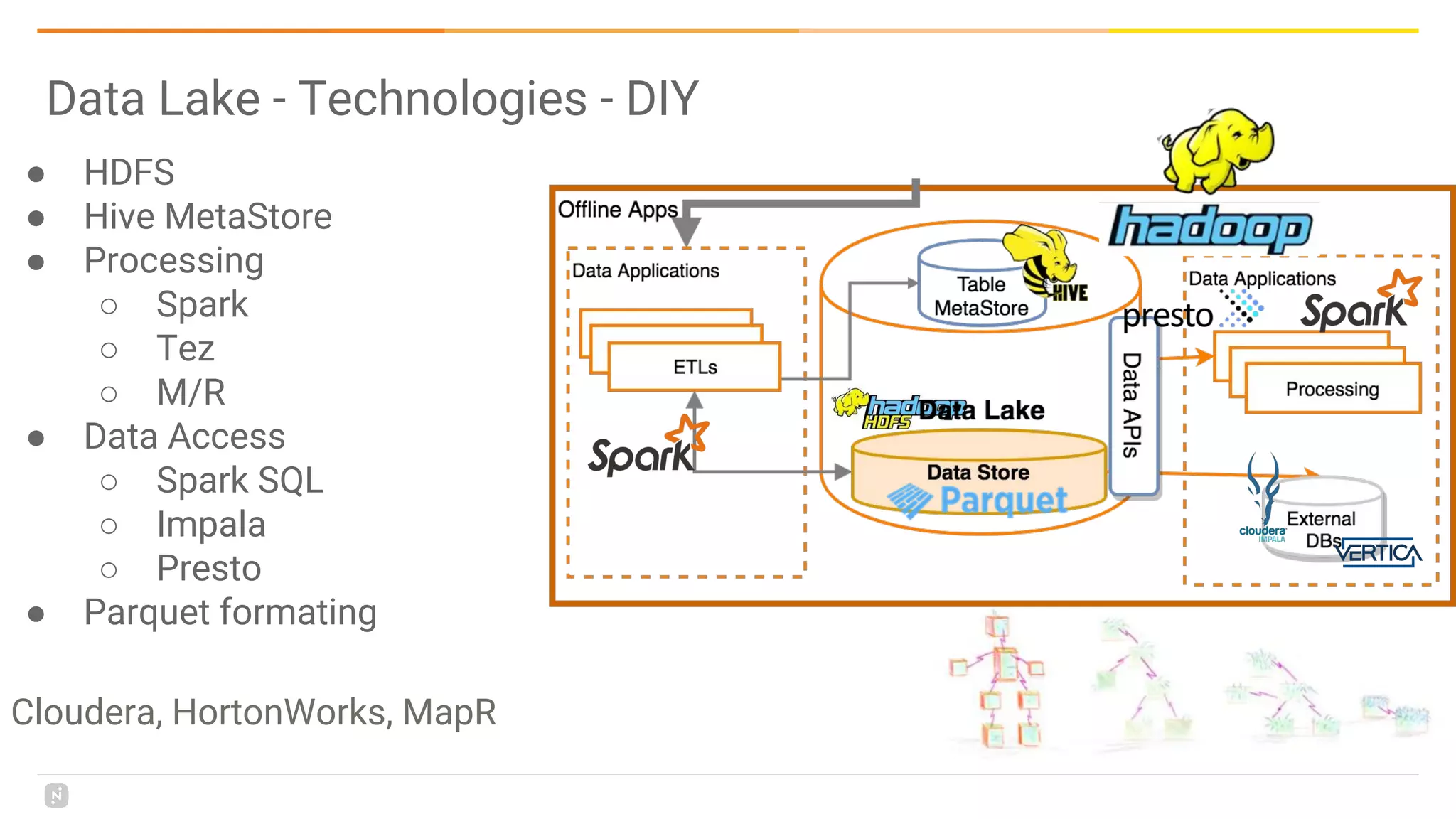
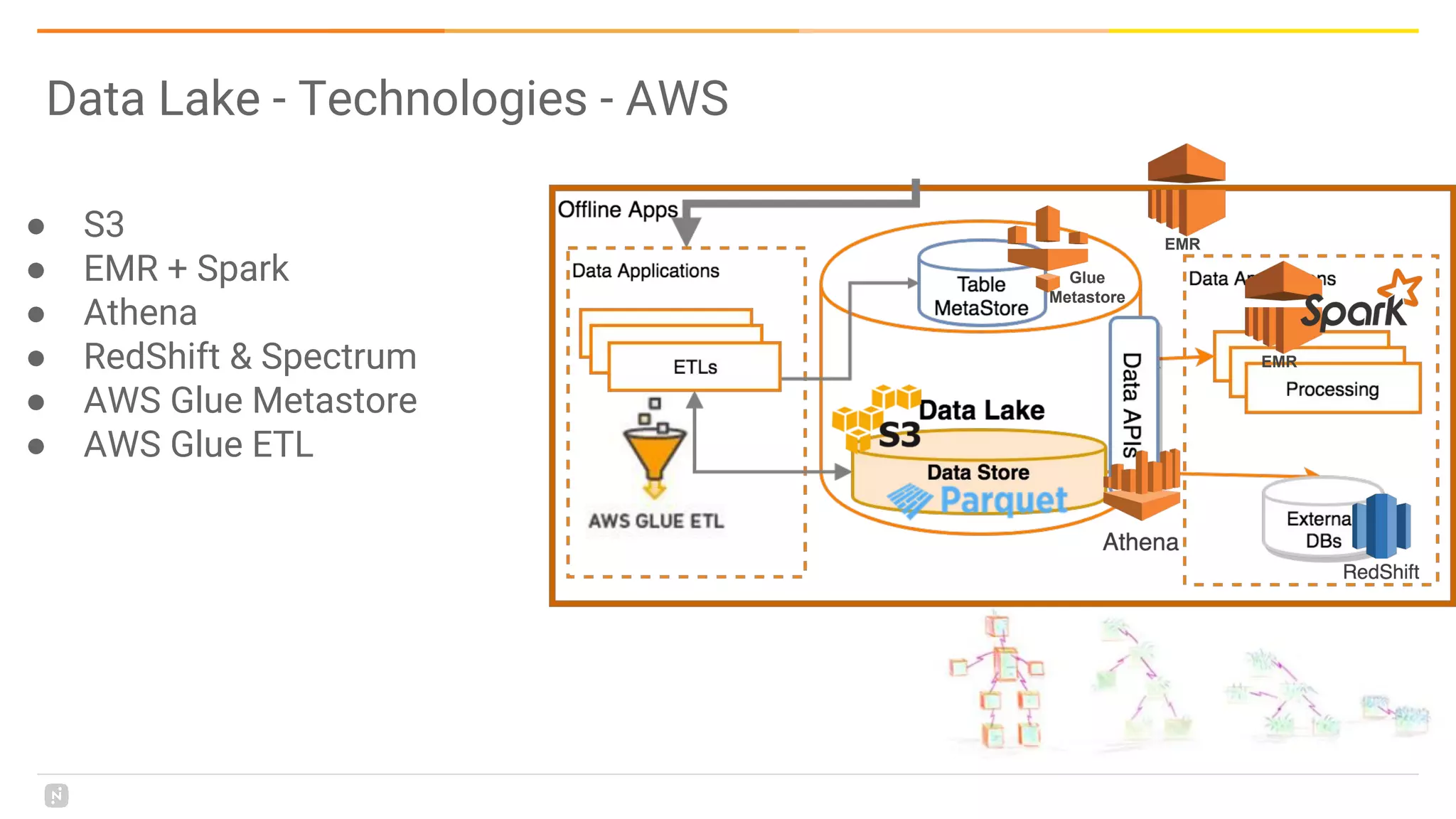
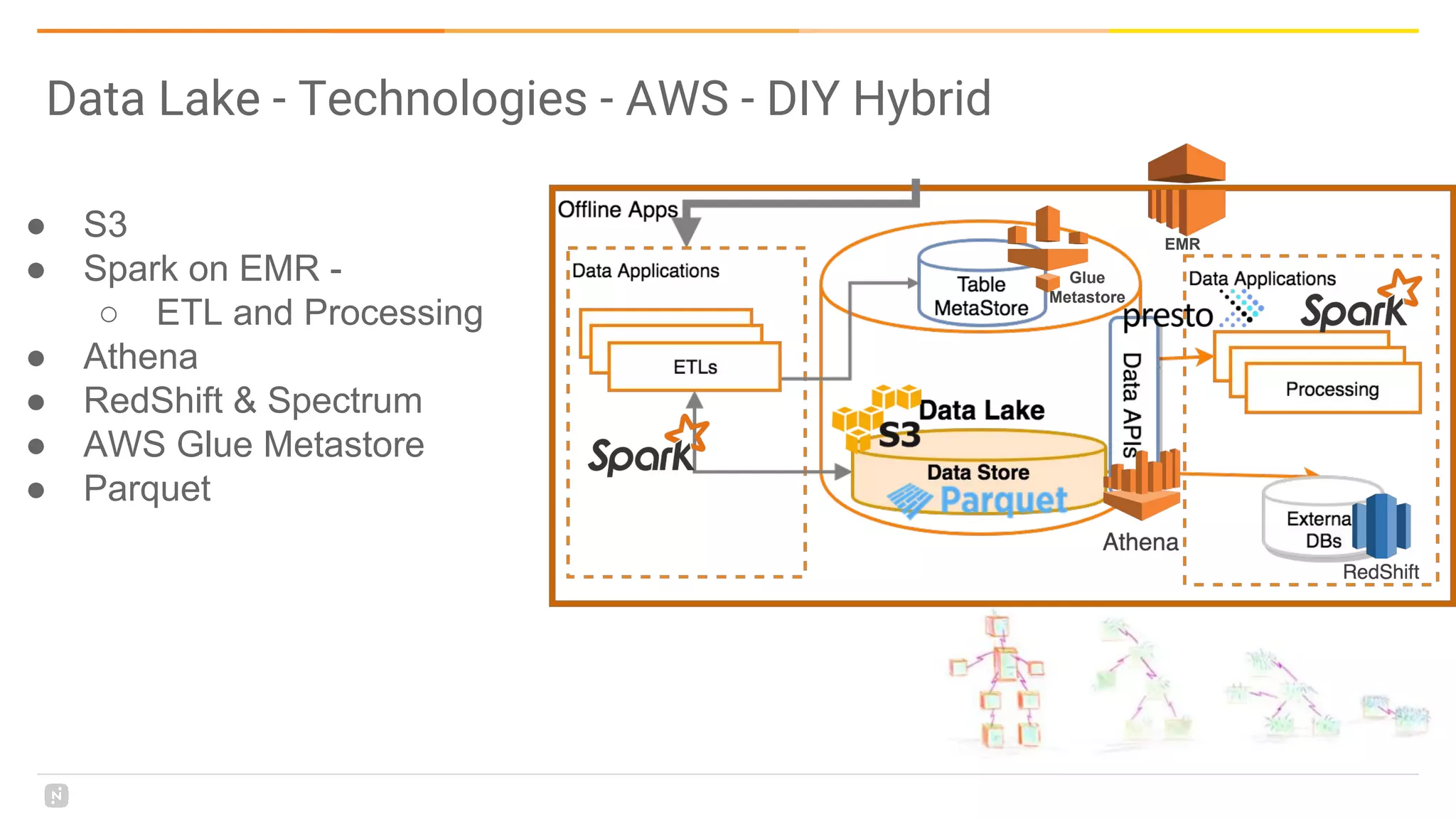
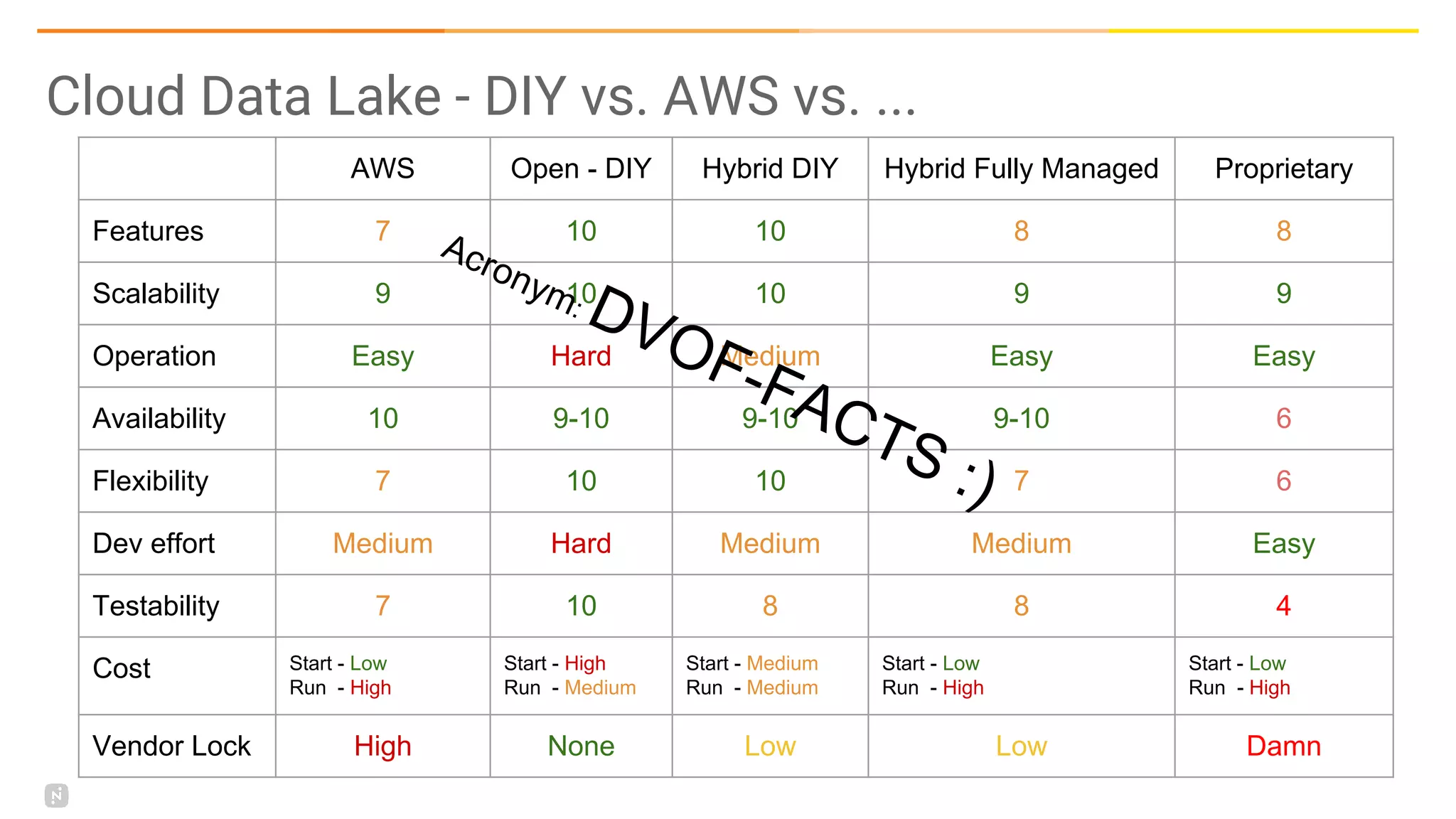
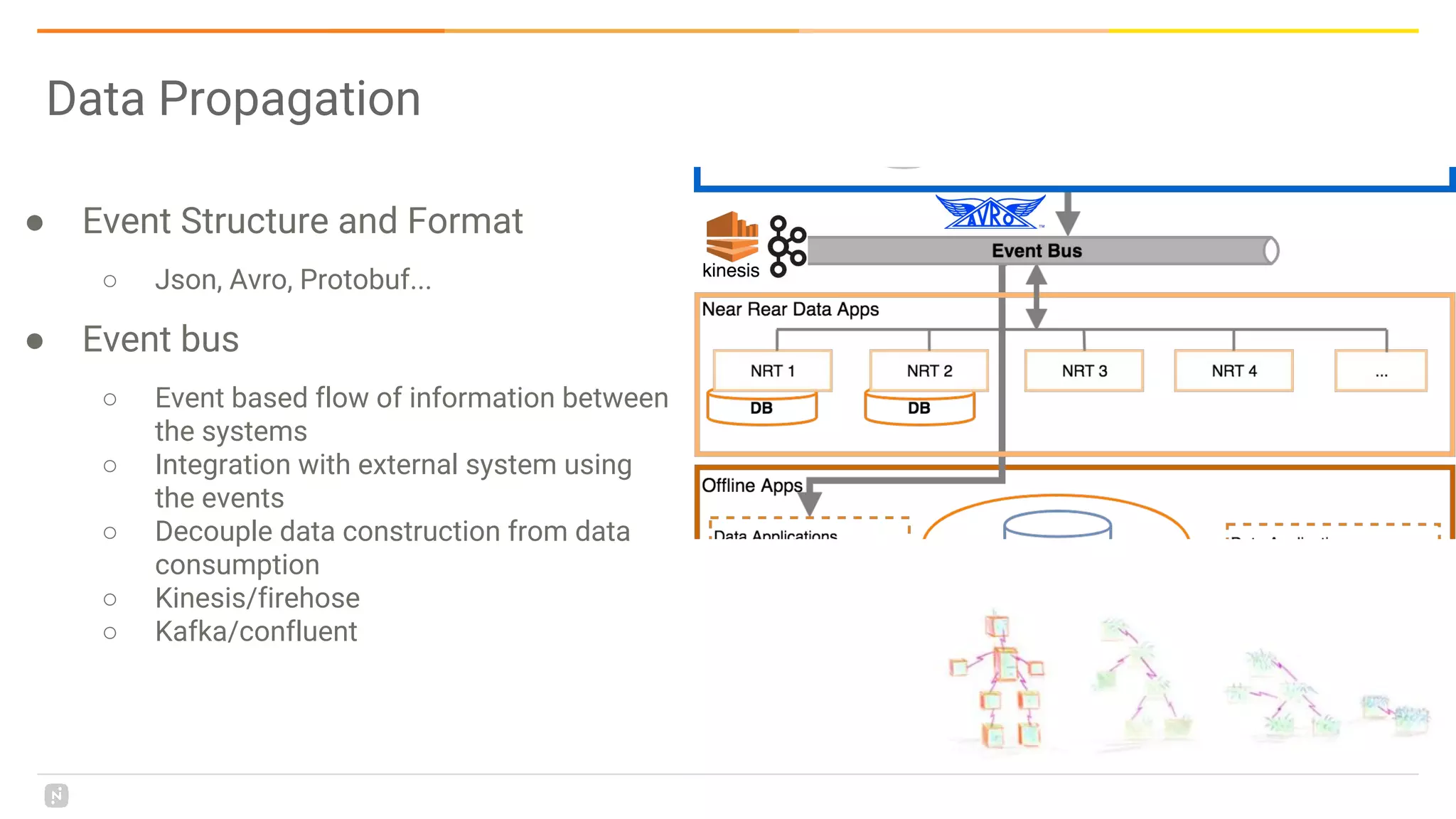
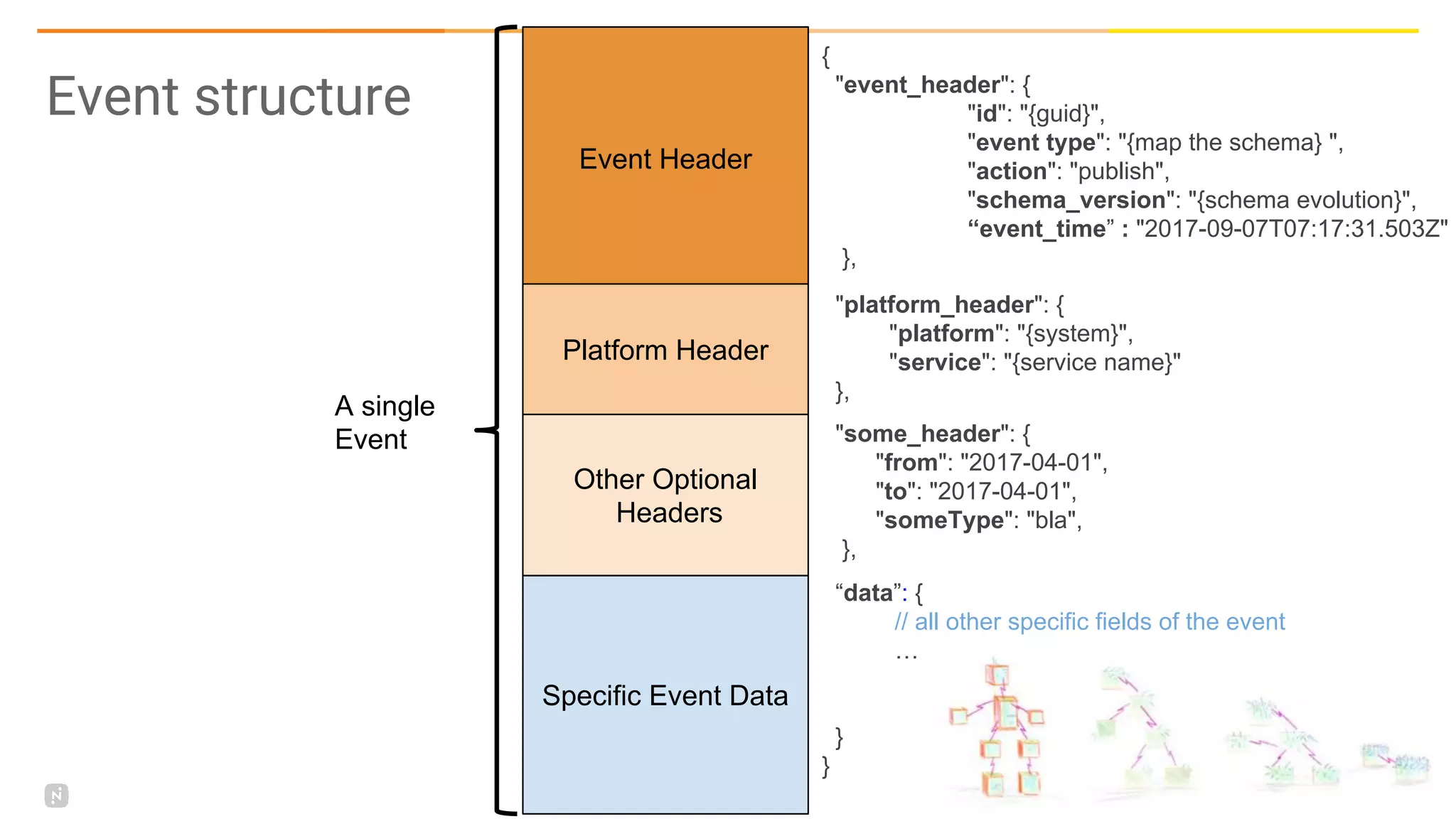
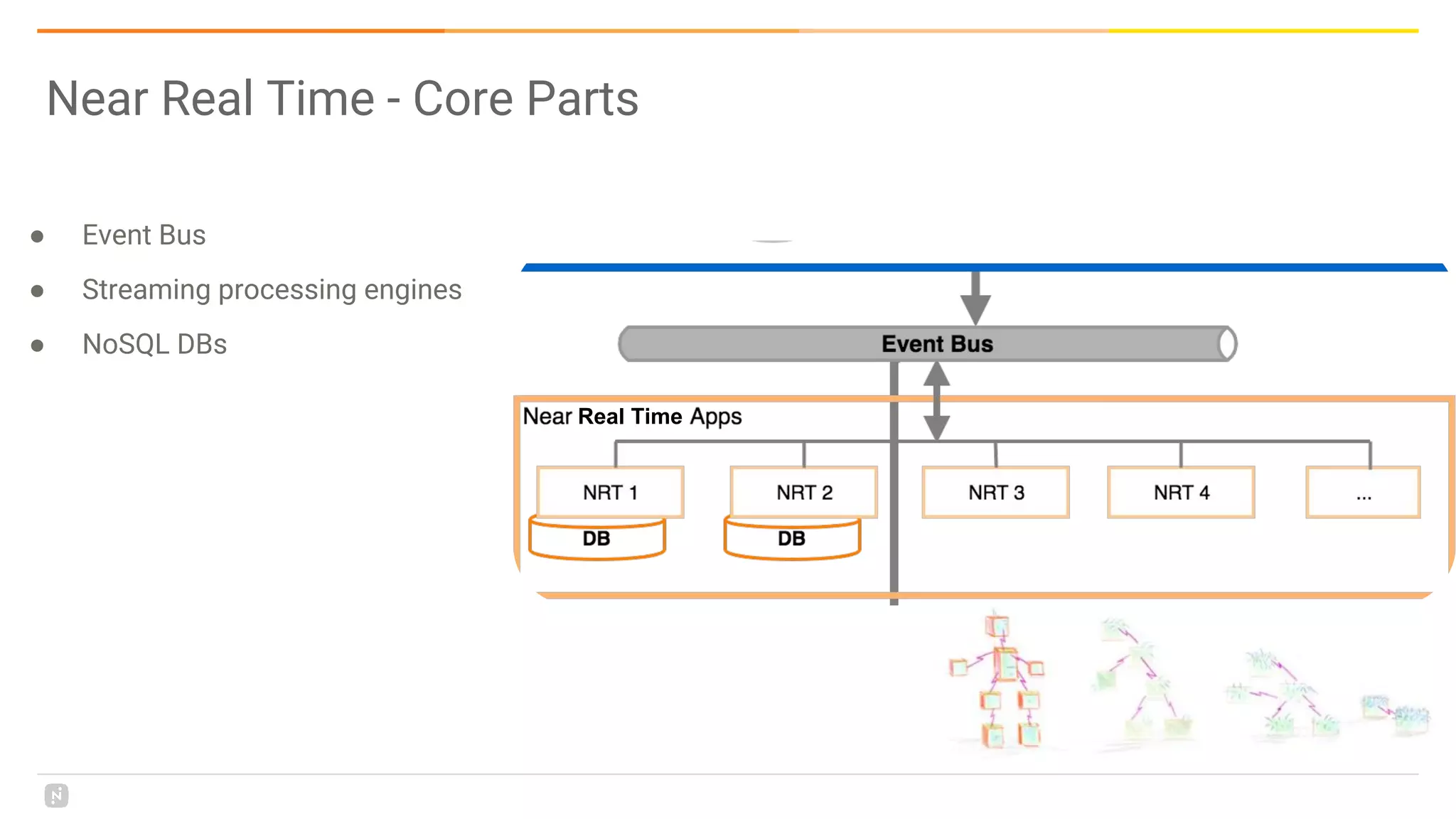
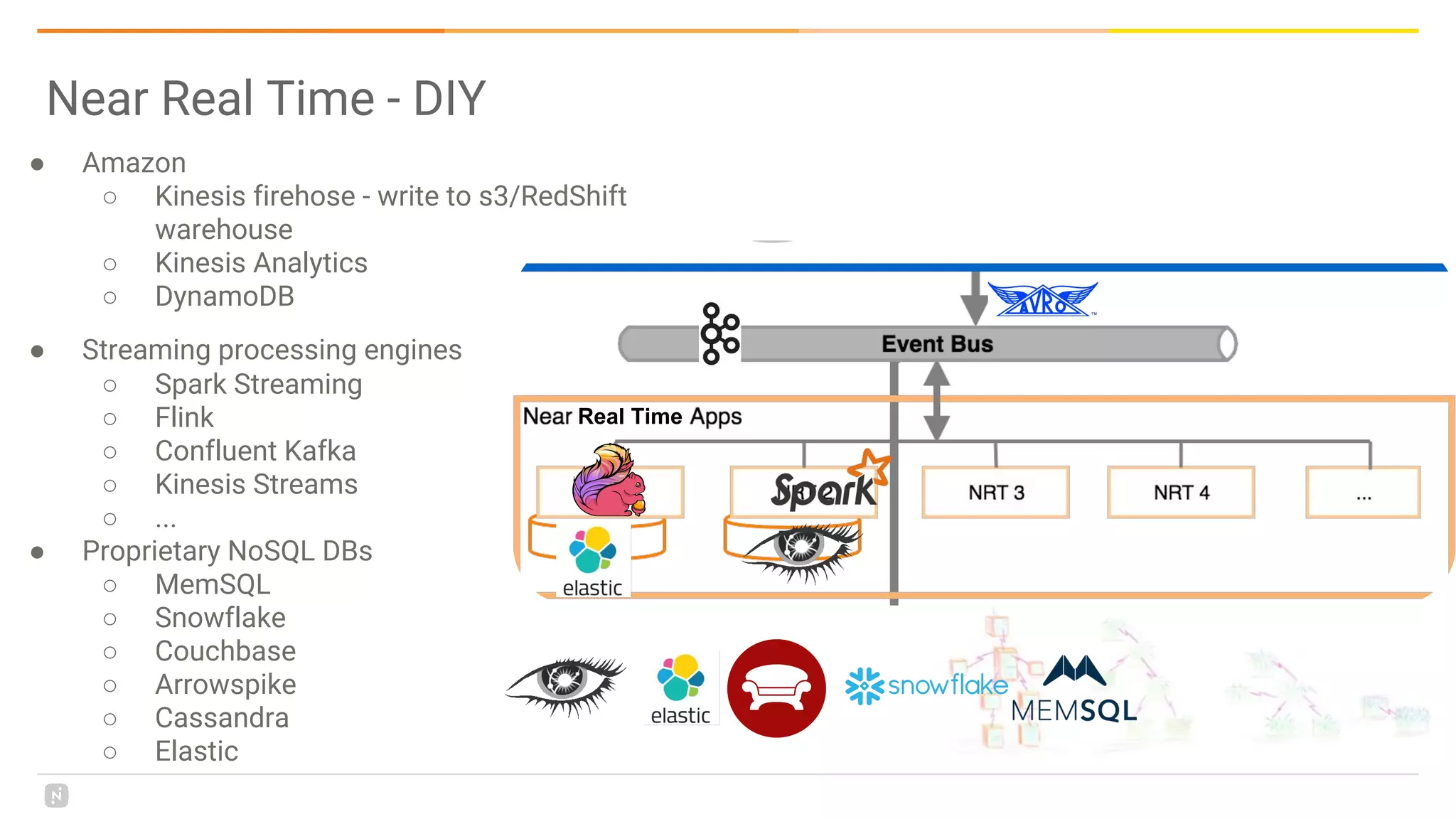
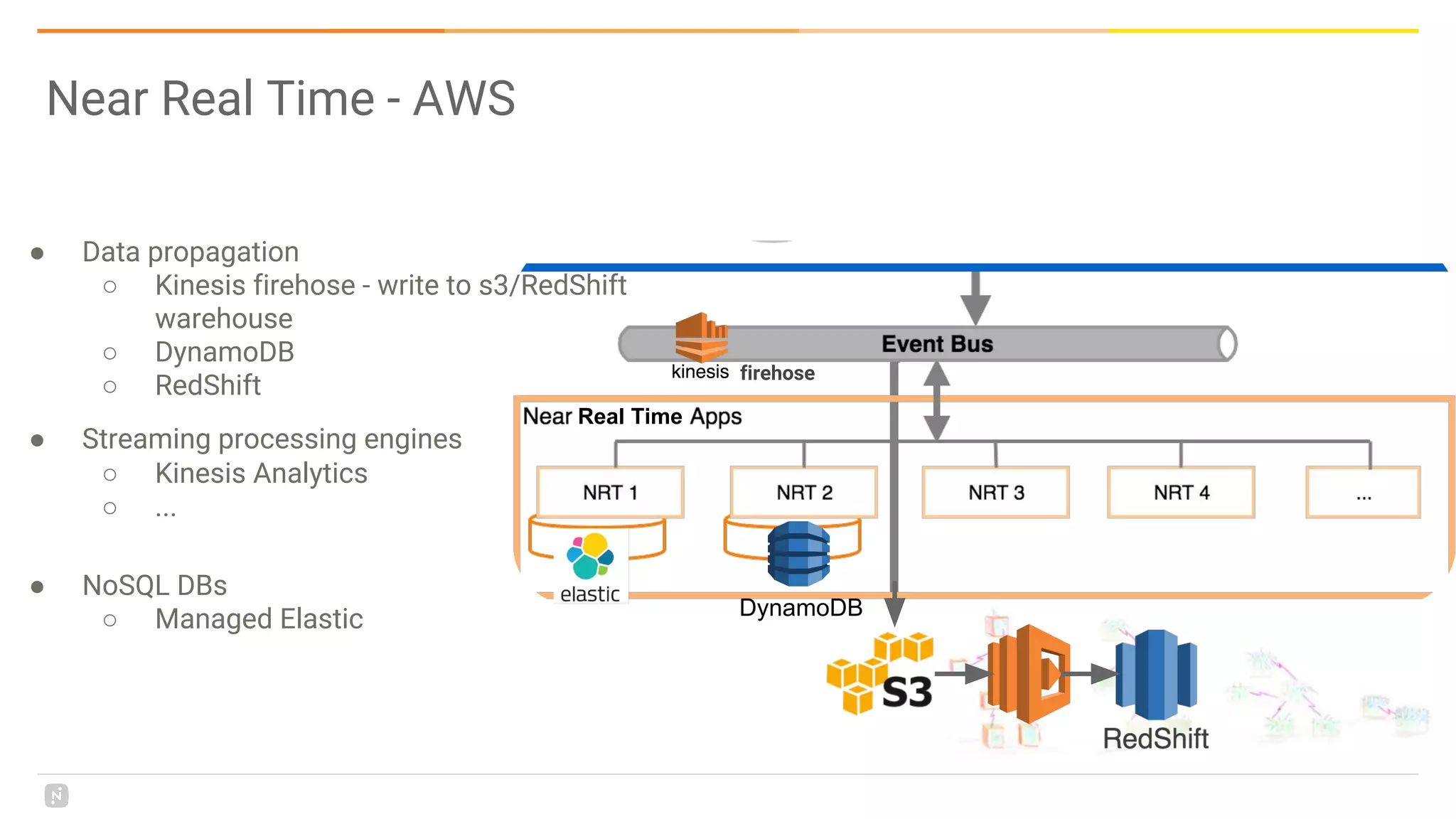
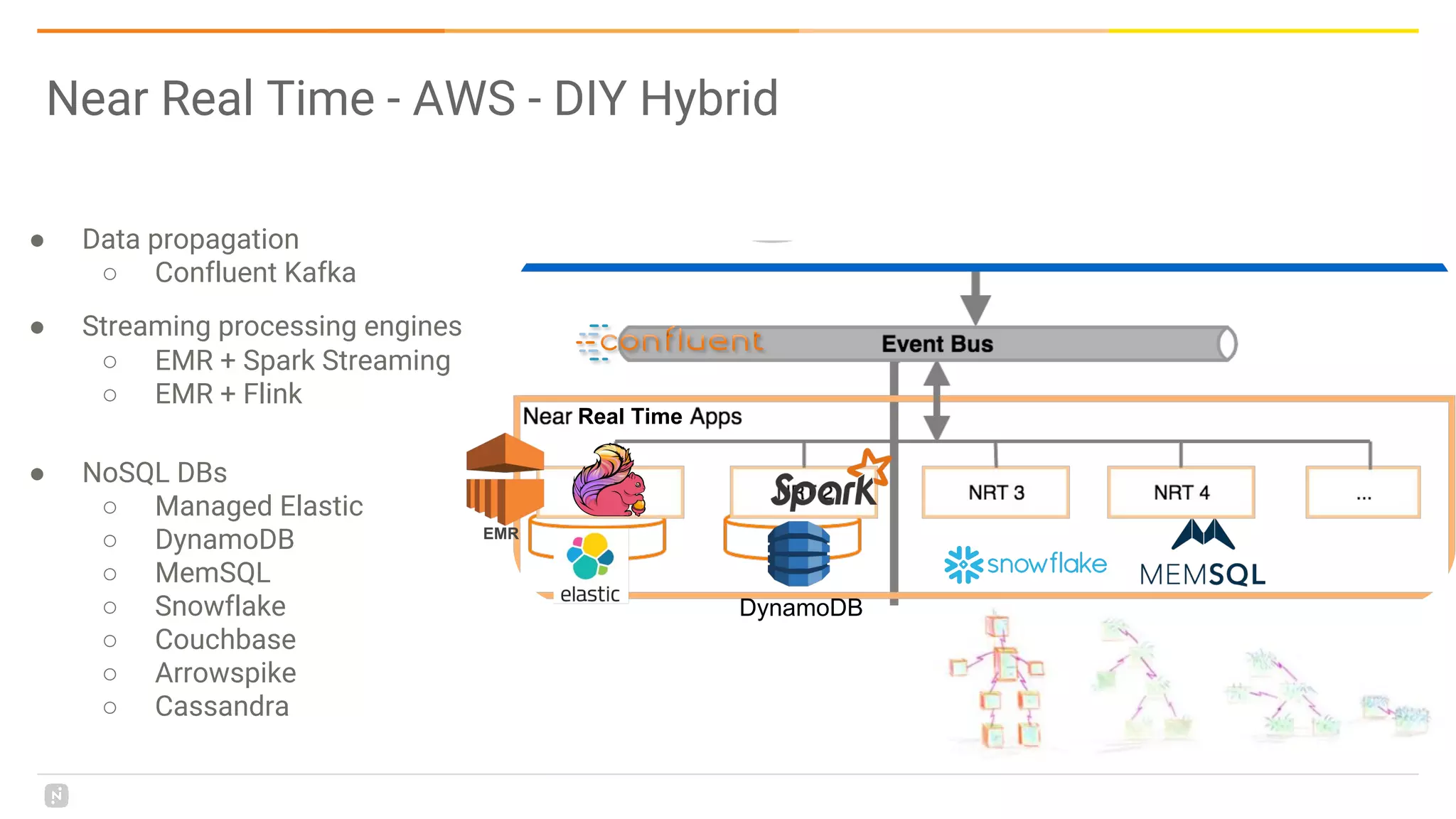
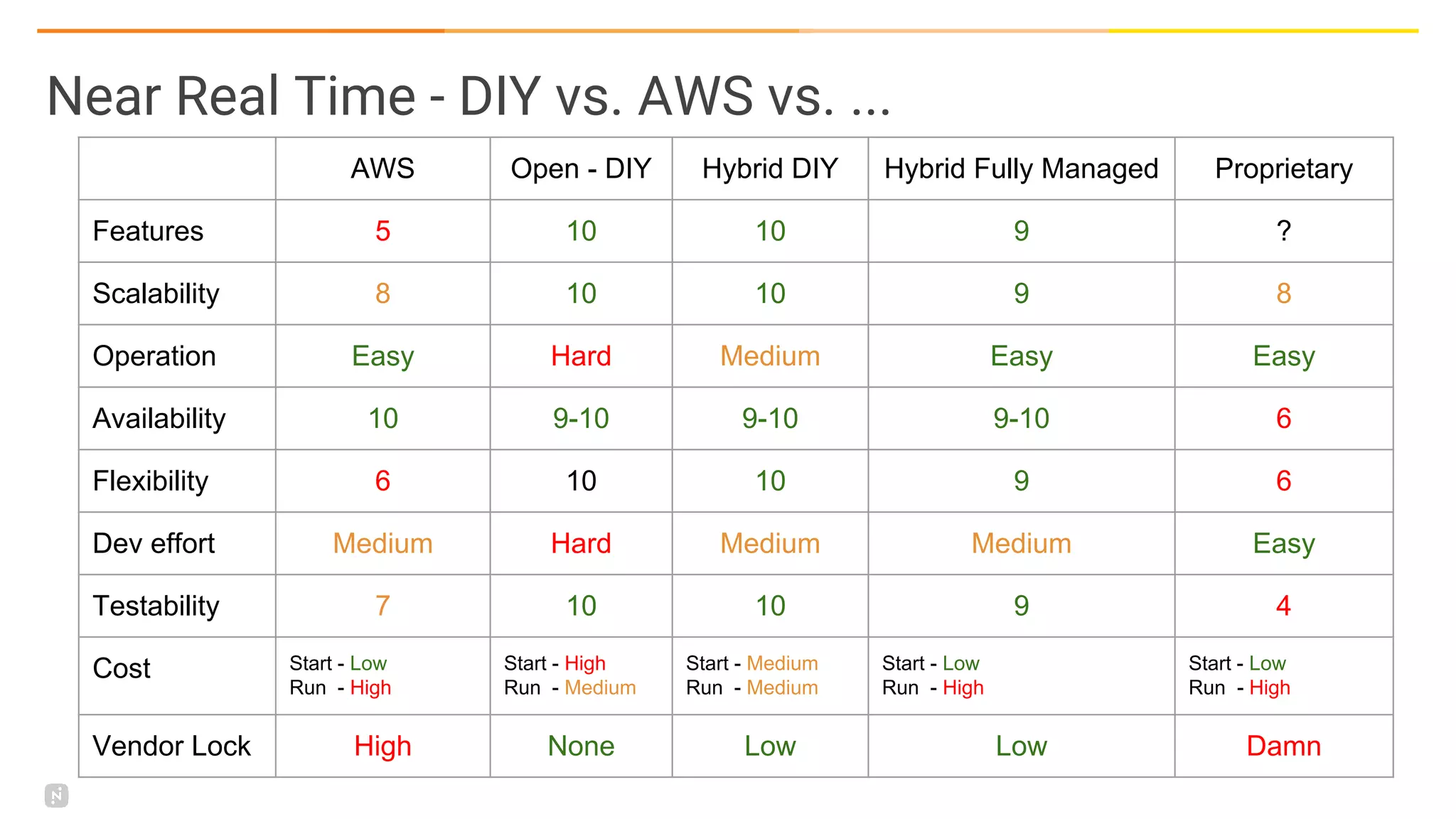
This document discusses building a data platform in the cloud. It covers the evolution of data platforms from monolithic architectures to distributed event-driven architectures using a data lake. Key aspects of a cloud data platform include collecting and persisting all data in a data lake for standardized access, near real-time processing using streaming technologies, and building the platform using either fully managed or DIY/hybrid approaches on AWS. Design principles focus on event-driven separation of data producers and consumers and choosing the right technology for the problem.