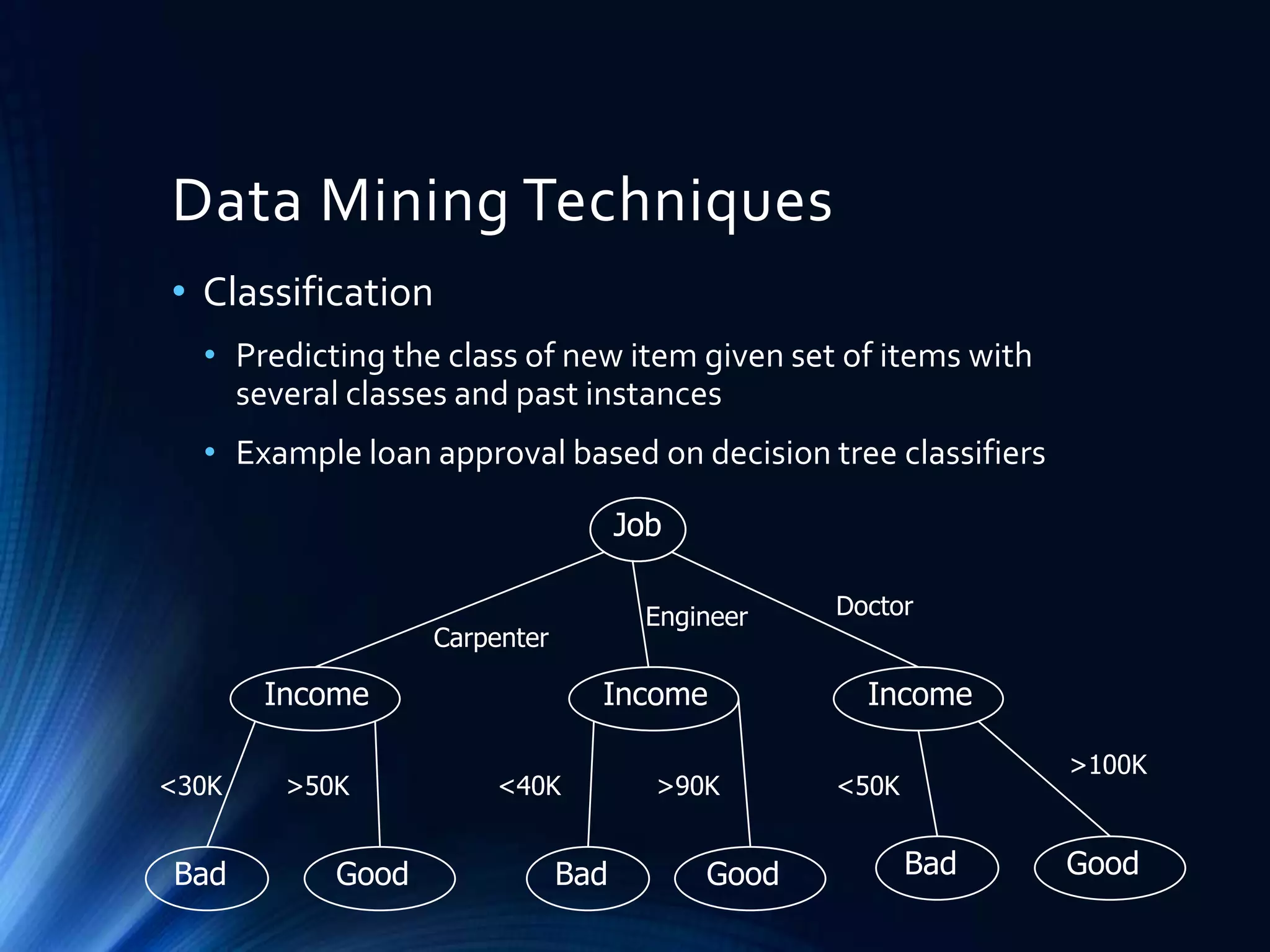
This document discusses data mining techniques and recommendation systems. It describes common data mining techniques like classification, clustering, regression, association rule mining and outlier analysis. It also discusses the knowledge discovery process and applications of data mining. The document then covers recommendation systems, describing content-based, collaborative filtering and hybrid recommendation approaches. It provides examples of these systems.