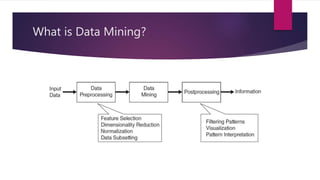
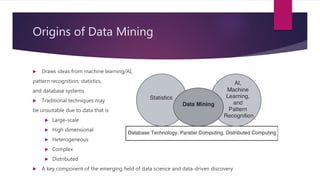
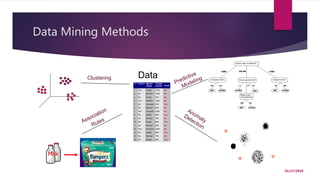
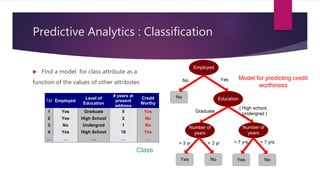
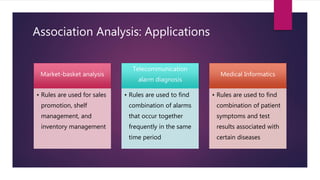
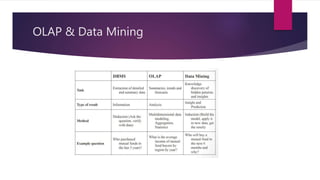
The document provides an introduction to data mining. It states that 40 zettabytes of data will be created in 2019 and 90% of existing data has been created in the last two years. It defines data, information, and knowledge and explains what data mining is and some of its applications. The document discusses different types of data and data analysis techniques like classification, clustering, regression, and association rule mining. It provides examples of how these techniques can be applied to problems in business, science, and other domains.