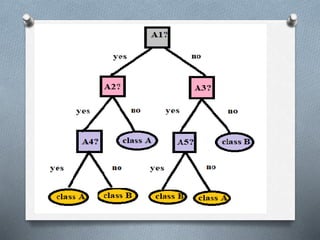
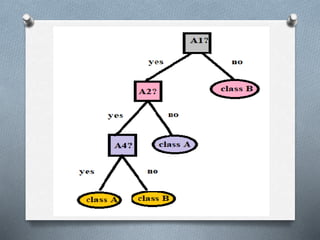
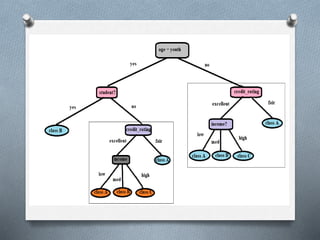
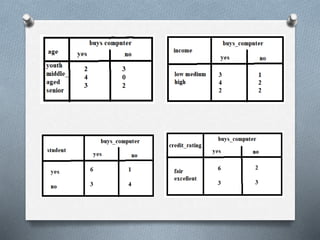
1. Decision tree induction is used for data mining but can result in overfitting due to noise in the training data. Tree pruning methods address this by removing the least reliable branches using statistical measures.
2. There are two tree pruning approaches - prepruning which halts tree construction early, and postpruning which removes subtrees from a fully grown tree. Cost complexity pruning removes subtrees if they increase encoding costs.
3. For large datasets, decision tree construction becomes inefficient due to memory swapping. More scalable algorithms like BOAT use bootstrapping statistics to construct trees from samples rather than requiring the full dataset to fit in memory.