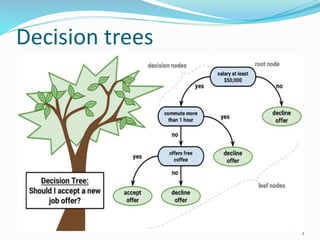
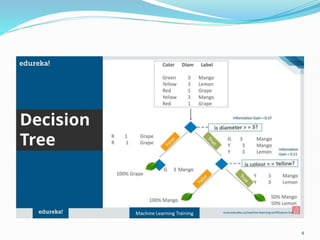
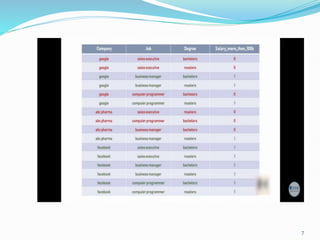
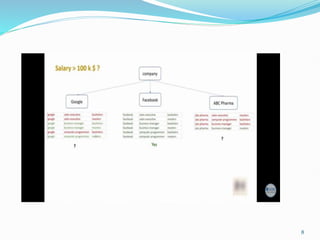
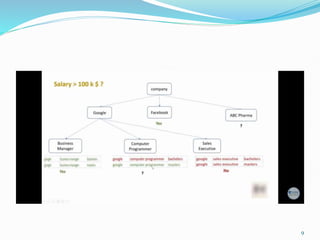
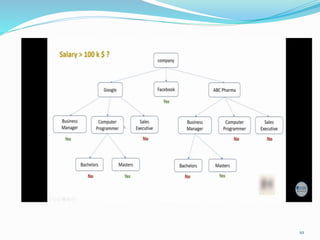
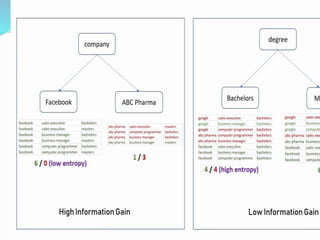
Decision trees utilize a tree structure to model relationships between features and outcomes. They work by recursively splitting the data into increasingly homogeneous subsets based on feature values, represented as branches in the tree. The C5.0 algorithm is an improved version of earlier algorithms and is widely used due to its strong out-of-the-box performance. It automatically learns the optimal structure of the tree and prunes branches to avoid overfitting, resulting in an accurate and interpretable model.