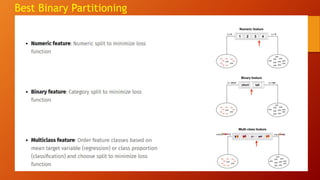
This document discusses decision trees and random forests. It begins with an example decision tree using retail data and defines decision tree terminology. It describes how to minimize overfitting in decision trees through early stopping and pruning. Random forests are then introduced as an ensemble method that averages predictions from decision trees trained on randomly sampled data. Random forests introduce additional randomness by selecting a random subset of features to consider for splits. They typically have lower prediction error than decision trees due to their diversity. The document contrasts bagging and random forests, and discusses tuning and out-of-bag error estimation for random forests.