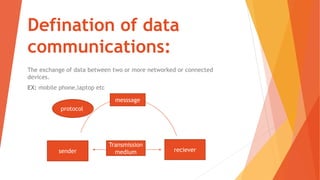
This document defines data communication and its components. It discusses protocols that establish communication rules between devices, including TCP, UDP, and IP. It also describes the three main data flow modes: simplex for one-way transmission; half duplex for two-way transmission but not simultaneously; and full duplex for simultaneous two-way transmission, giving examples for each. Key parts of data communication systems are identified as the sender, receiver, transmission medium, and protocols that govern message exchange.