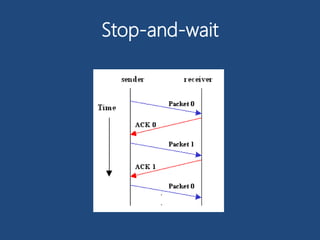
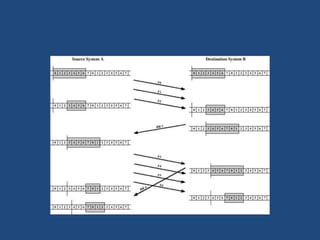
Flow control manages the rate of data transmission between nodes to prevent overwhelm. It ensures a receiving node is not overwhelmed by a fast sender. Flow control prevents degradation from overload, avoids deadlock, and provides fair resource allocation. There are two main types: stop-and-wait which provides reliable transfer but is inefficient for long transmissions, and sliding window which controls packets between computers for reliable sequential delivery and performs better with limited buffers. Flow control occurs at different levels including between individual nodes, switches, and transport between users.