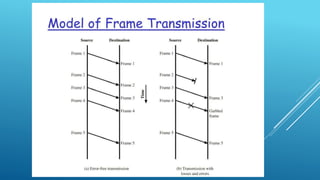
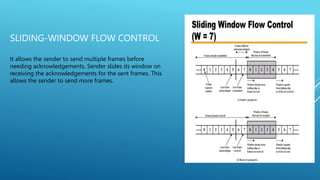
Data link control involves flow control, error detection, and error control mechanisms to manage data transmission between nodes. Flow control prevents fast senders from overwhelming slow receivers by regulating transmission rates. Stop-and-wait and sliding-window flow control break messages into frames and use acknowledgments to control transmission. Error detection uses redundancy to identify errors without an original copy, while error control detects and corrects errors in transmitted frames.