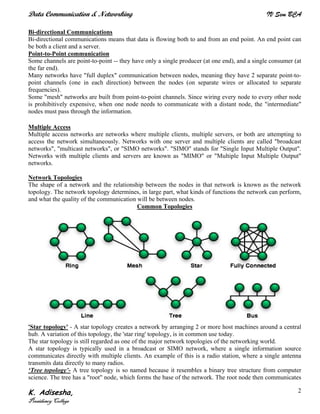
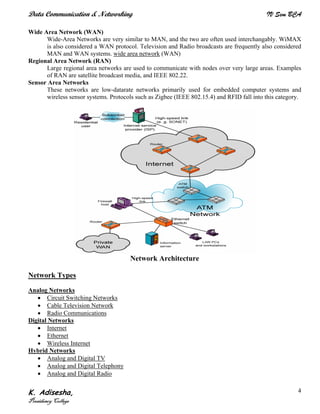
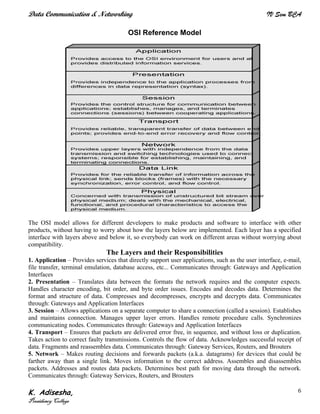
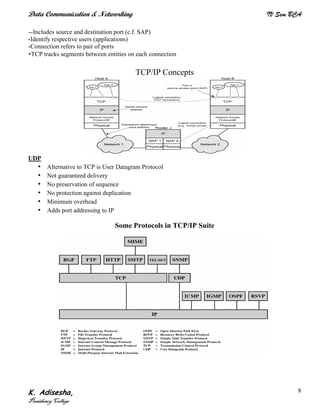
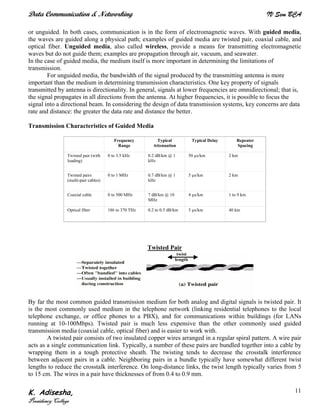
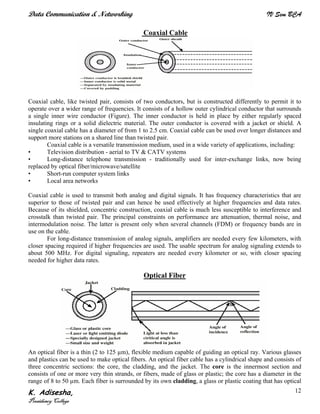
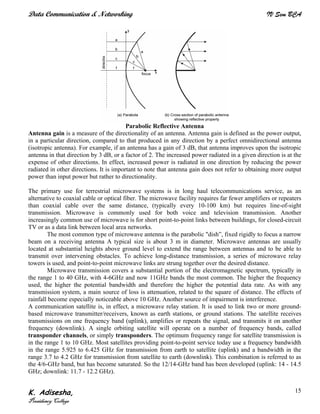
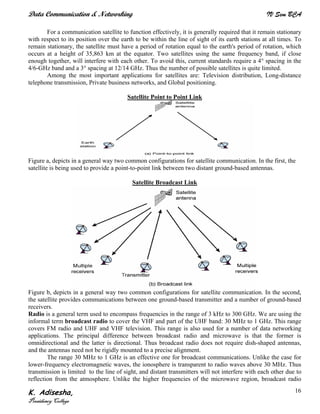
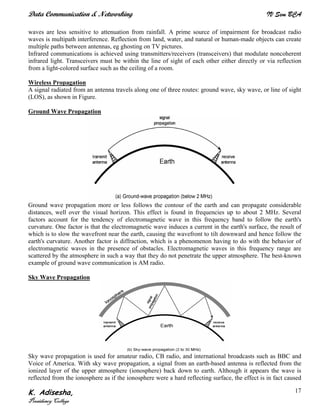
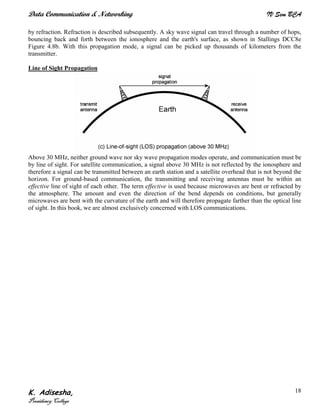
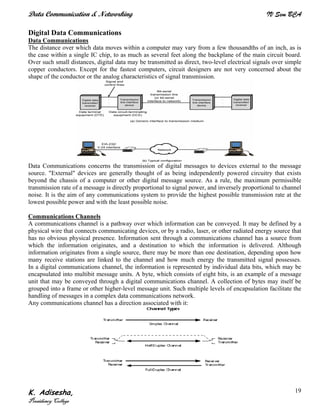
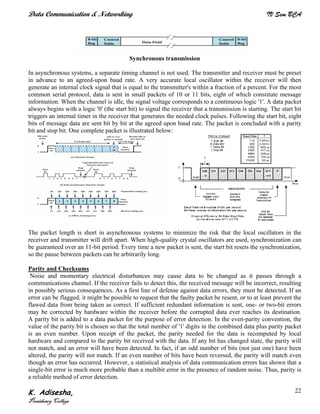
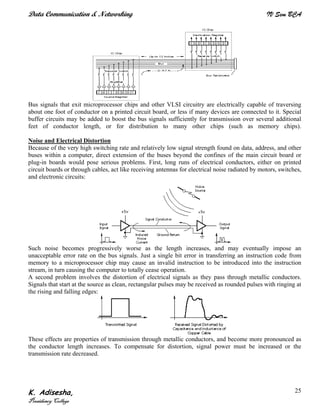
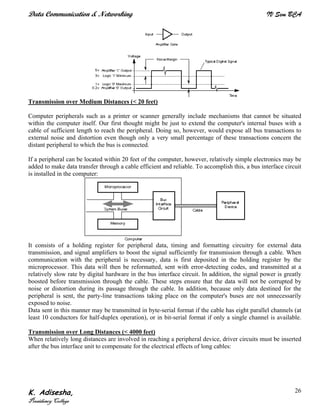
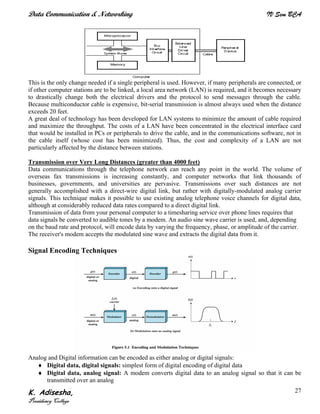
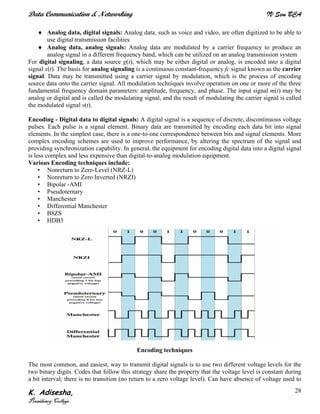
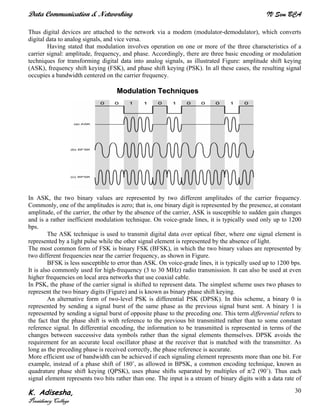
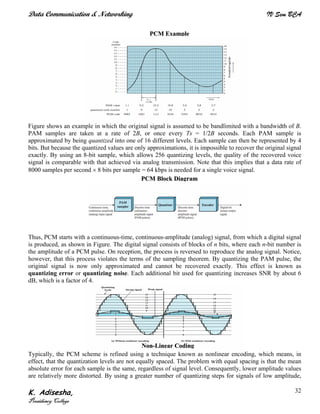
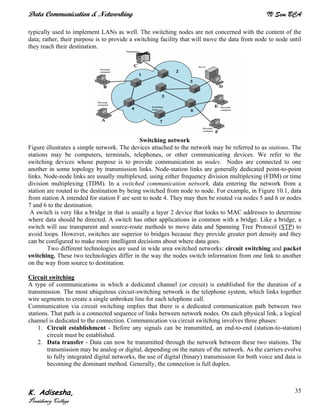
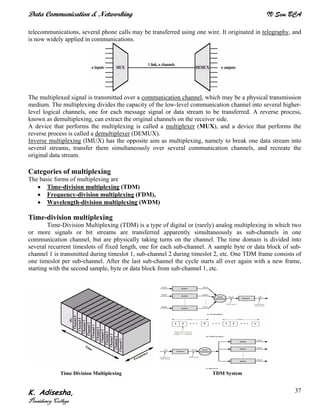
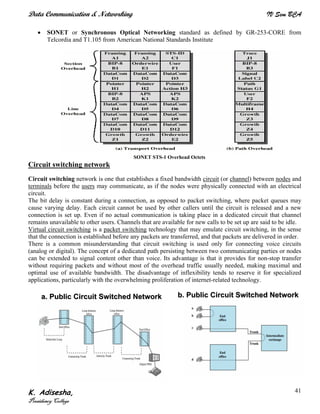
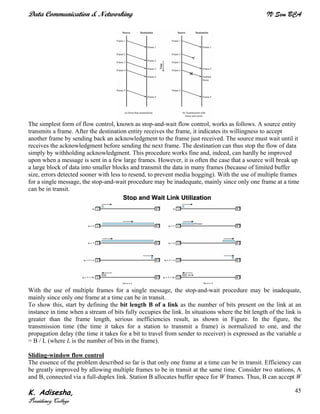
Networks connect devices using common protocols to exchange data. They allow information to be sent from one location to another through nodes and channels. The first wireless networks used analog signals for voice and music broadcasts (1G), while later generations introduced digital communications and increased data rates, with 3G networks combining voice and high-bandwidth data. Network topologies determine the shape of the network and the relationship between nodes, with common topologies including star, tree, ring, mesh, bus, and hybrid combinations of these. Networks are also classified by size from personal area networks (PANs) covering a single person up to regional area networks (RANs) spanning large regions.