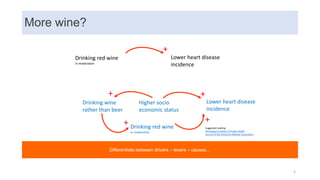
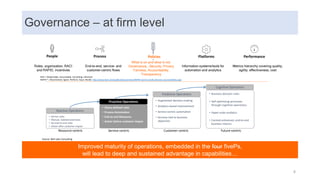
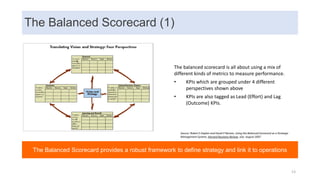
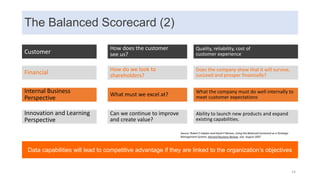
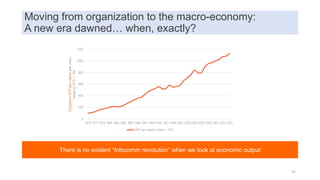
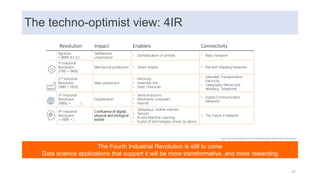
This document discusses data capabilities and competitive advantage, drawing from lessons from consulting and research. It provides several examples and case studies to illustrate key points. The examples show how differentiating between drivers, levers, and causes is important to avoid making incorrect assumptions. They also demonstrate how the direction of causality and errors in arithmetic can pose problems. The document advocates using multiple metrics and perspectives, such as through the balanced scorecard framework, to measure performance and link data capabilities to organizational objectives. It also discusses different views on the impacts and transformative nature of technological changes and digitalization.