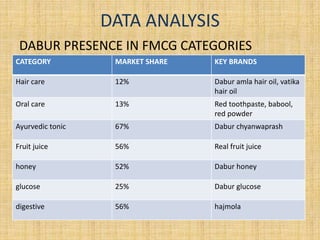
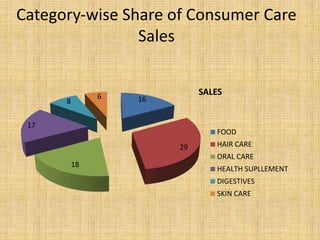
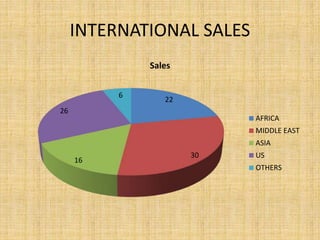
Dabur India Limited is India's leading FMCG company that was founded in 1884. It has grown to have a turnover of Rs. 7,073 crore in FY 2013-14. The company's vision is dedicated to the health and well-being of every household. It has a strong presence in India with over 5000 distributors and 2.8 million retail outlets, and also operates in over 60 countries worldwide with key international markets being Africa, the Middle East, and Asia. The presentation provides an overview of Dabur's business units, product categories, market share, sales performance and recommendations for future growth.