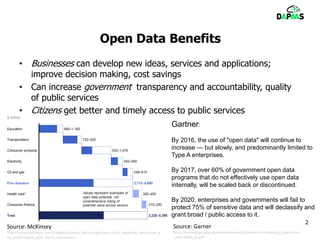
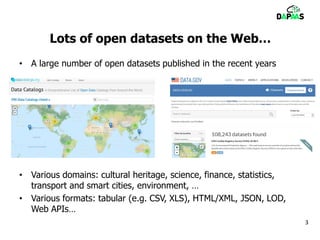
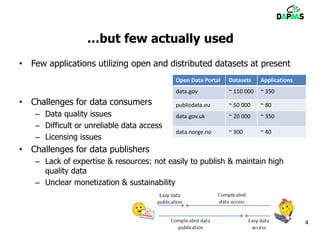
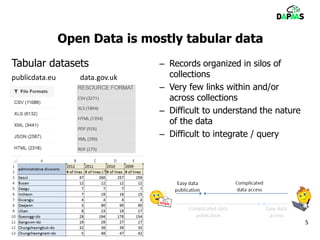
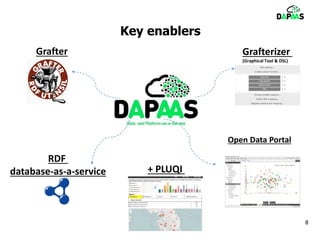
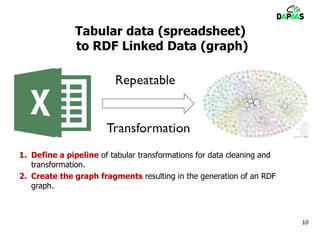
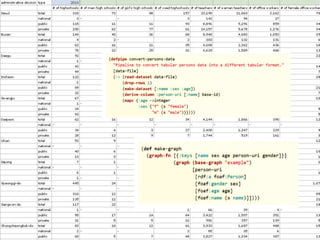
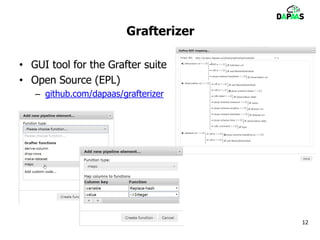
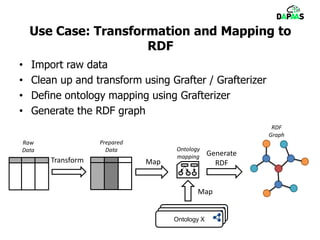
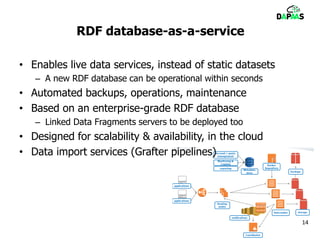
The document discusses the potential benefits of open data for businesses, governments, and citizens, highlighting its application in various domains and the current challenges in accessing and using open datasets. It presents DAPaaS as a solution for facilitating low-cost publishing and reuse of open (linked) data through a platform and set of tools designed to improve data accessibility and integration. Despite the availability of numerous datasets, the document emphasizes the need for better tools and resources to enhance the quality and usability of open data.