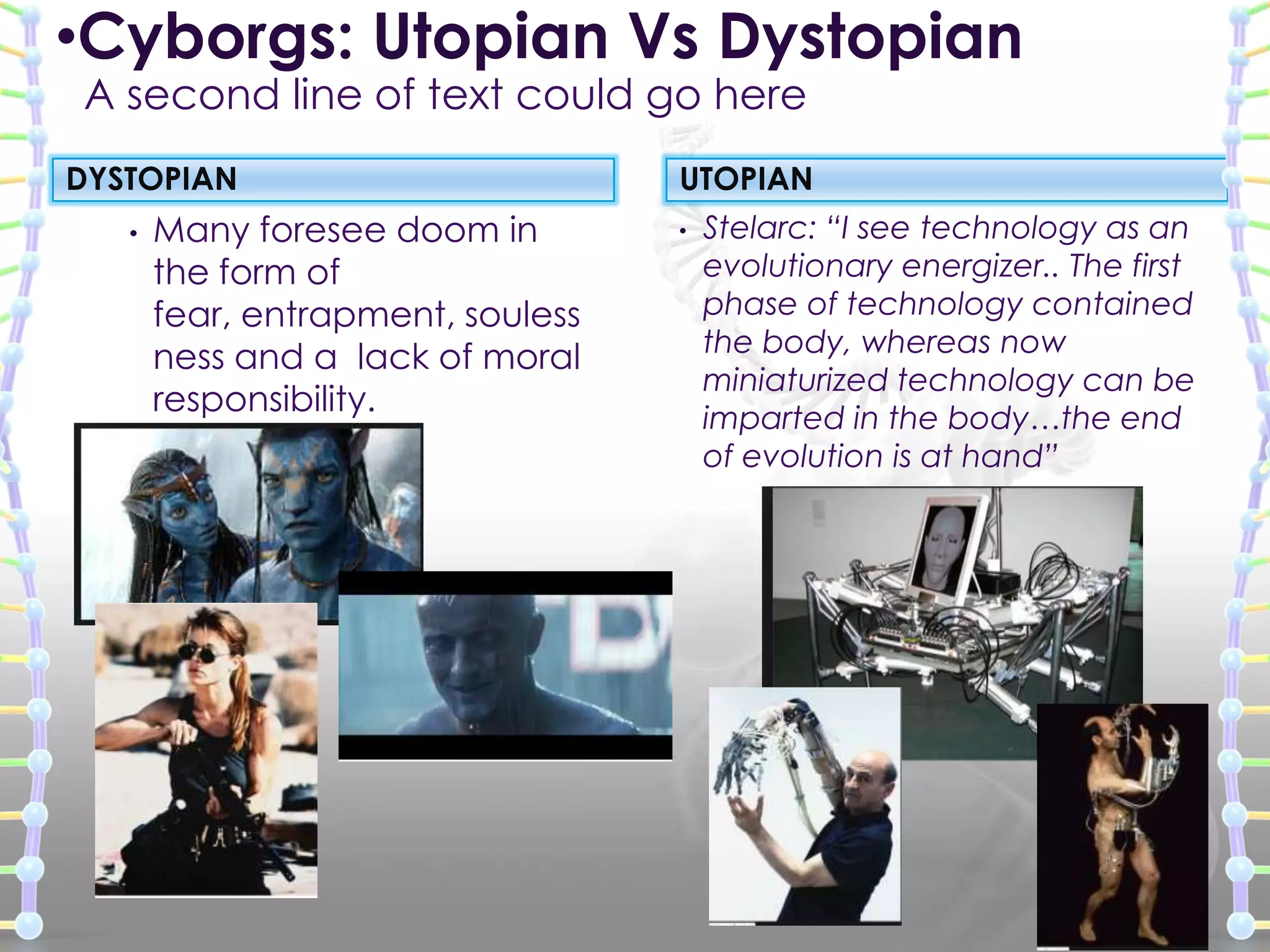
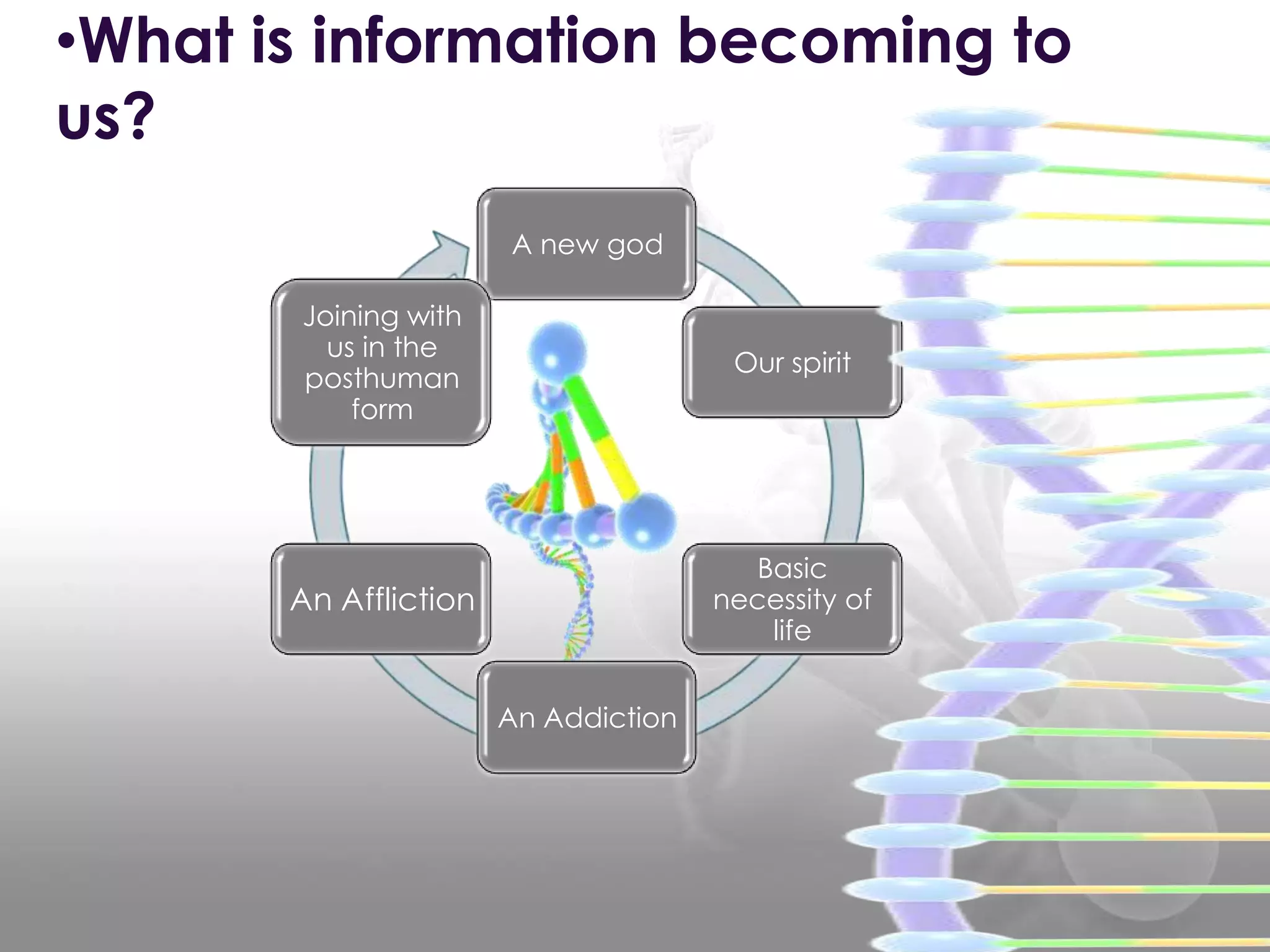
The document discusses the concept and definitions of cyborgs from various perspectives. It notes that the term originated from a merging of "cybernetic" and "organism" to refer to a person whose abilities are enhanced by technology. There is no single agreed upon definition of cyborgs, and the implications of integrating humans with machines are debated as having both utopian and dystopian consequences. The transition to becoming posthuman raises questions around who maintains control over the process and what it means for human identity and autonomy.

![Edgar Allen
Poe 1843
“a person whose physiological functioning is aided by or dependent up
a mechanical or electronic device”
“For the exogenously extended organizational complex
functioning as an integrated homeostatic system,
unconsciously we propose the term „Cyborg‟
•Cyborg – Indefinable?
”a fictional or hypothetical person whose physical abilities are
extended beyond normal human limitations by mechanical elements
built into the body.”
A cyborg essentially a man-made system in which the control
mechanisms of the human portion are modified externally by
drugs or regulatory devices so that the being can live in an
environment different from the normal one]
The concept of a man-machine mixture was widespread in
science fiction before World War II. As early as 1843 Edgar Allan
Described a man with extensive prostheses in the short story
The Man That Was Used Up".
Oxford
Definition
Other dictionary
definitions
Clynes and
Klyne 1960
New York
Times 1960](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cyborgsthebodytheinformationandthetechnology-130527024548-phpapp01/75/Cyborgs-the-body-the-information-and-the-technology-2-2048.jpg)