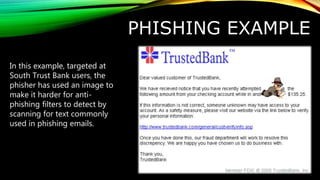
This document discusses phishing, which is a type of criminal activity where scammers try to acquire sensitive information like usernames, passwords, and credit card details by masquerading as a trustworthy entity. Phishing is dangerous because emails and websites can look very convincing. Statistics show that phishing attacks increased dramatically between 2005 and 2006, affecting millions of people and costing businesses billions. The document describes common phishing techniques like website forgery, voice phishing, and using images to evade detection. It concludes by providing tips to protect yourself such as using spam filters, anti-phishing browser tools, and not clicking links in emails.