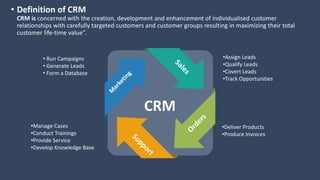
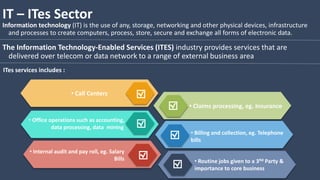
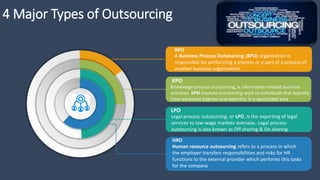
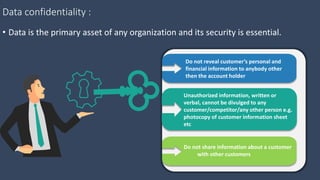
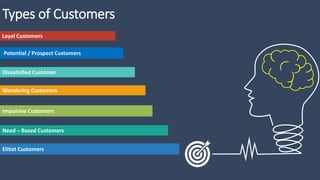
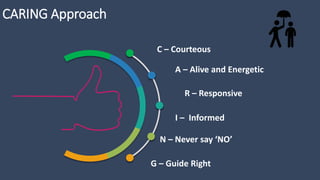
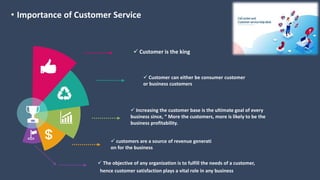
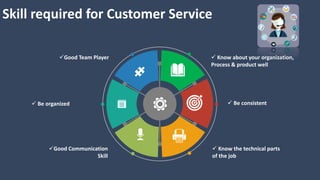
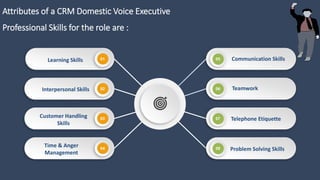
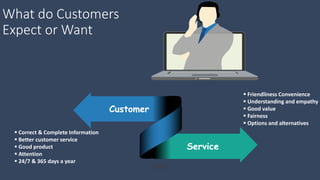
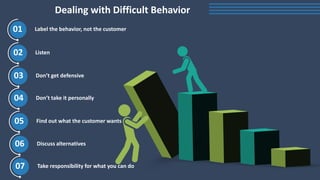
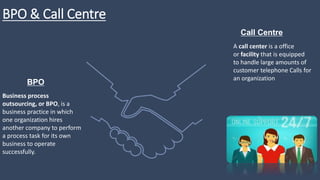
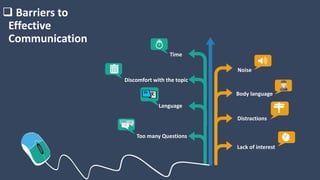
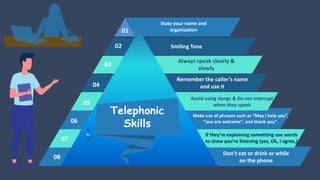
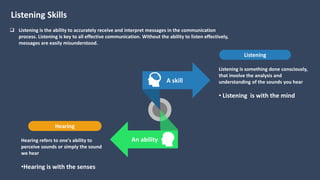
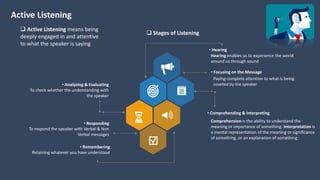
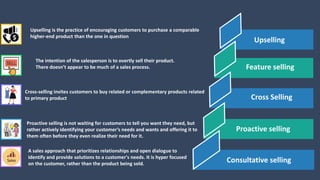
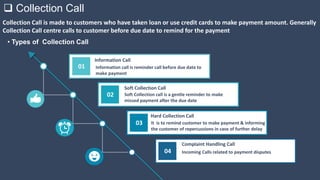
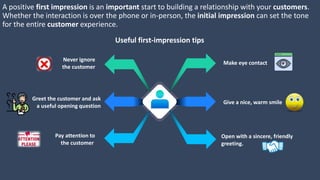
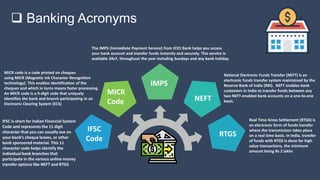
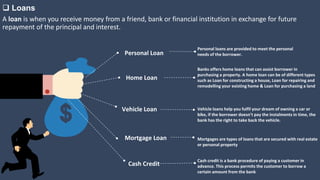
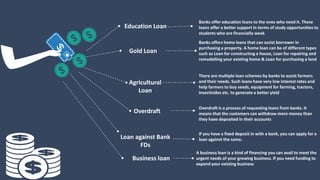
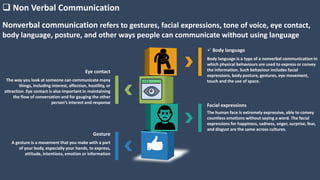
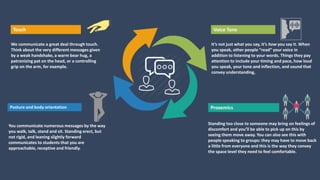
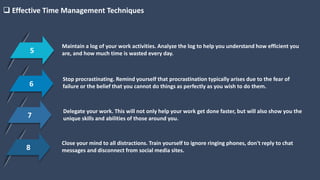
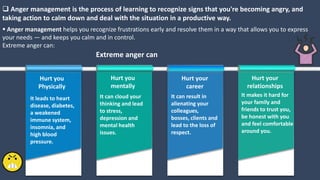
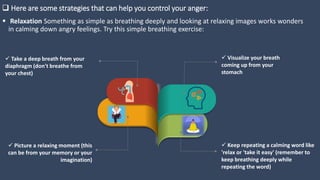
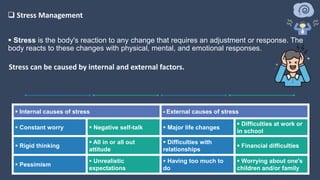
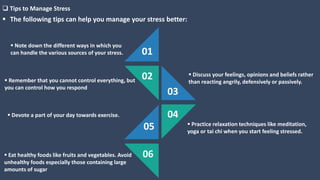
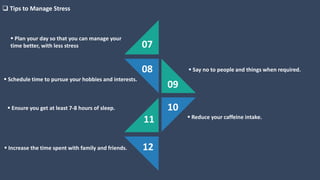
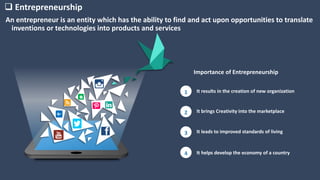
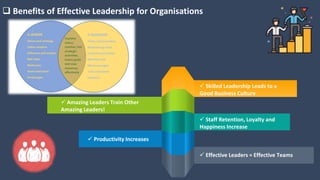
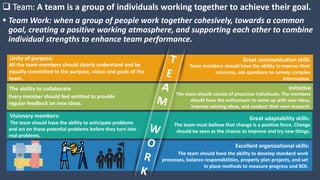
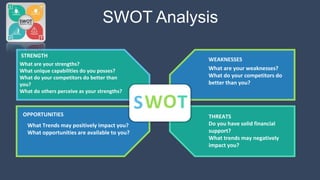
The document covers various aspects of call centers and business process outsourcing (BPO), detailing the significance of customer relationship management (CRM) in enhancing customer satisfaction and retention. It outlines key processes within BPO, types of outsourcing, and the roles of customer service executives, emphasizing effective communication, customer handling skills, and metrics for measuring performance. Additionally, it discusses the importance of data confidentiality and strategies to manage different types of customers effectively.