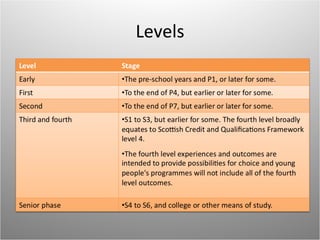
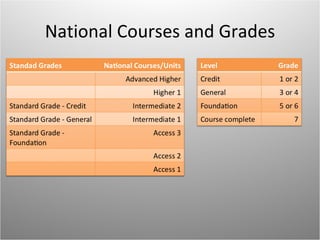
The Curriculum for Excellence in Scotland aims to provide a coherent and flexible education for children and young people aged 3 to 18, focusing on developing key capacities like successful learners and responsible citizens. It emphasizes a broad general education that enhances literacy, numeracy, and life skills while offering tailored support and options for personalization. The curriculum encompasses interdisciplinary learning and is structured around eight core areas to foster connections across subjects.