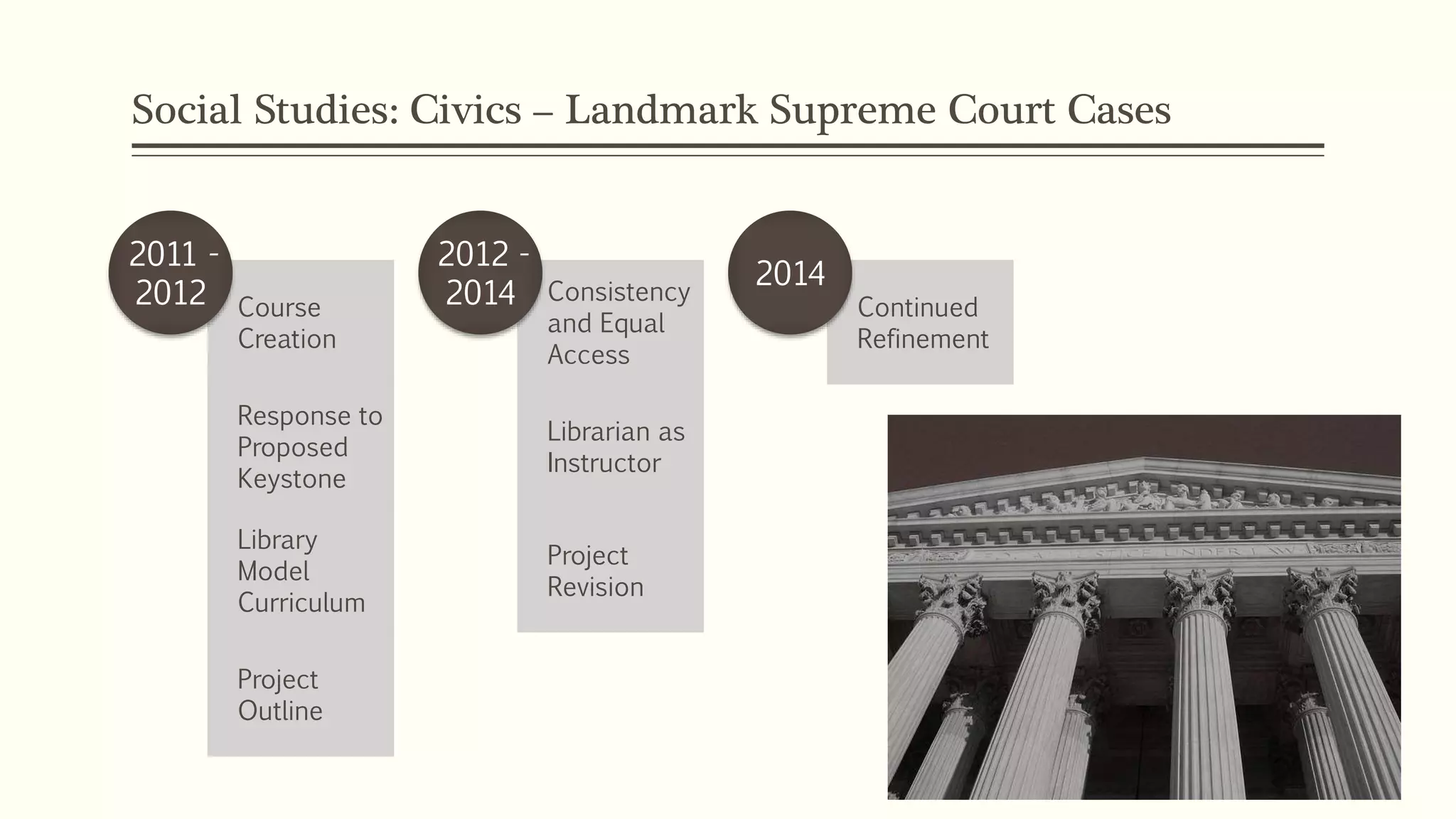
The document outlines a curriculum development plan by Allison Mackley at Hershey High School, focusing on building information literacy and integrating library resources with academic subjects. It details the process from 2007 to 2014, including collaboration with teachers, mapping standards, and evolving classroom practices to enhance students' critical thinking and research skills. The vision extends to future improvements in elementary and middle school curricula to empower students as effective problem solvers and lifelong learners.