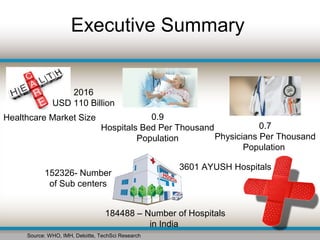
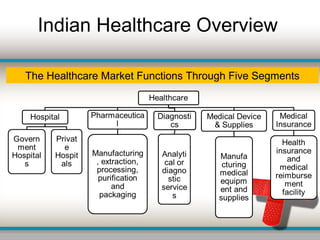
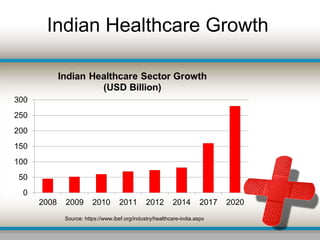
The document outlines the current challenges facing India's healthcare system, including a growing burden of disease, inadequate healthcare financing, and lack of universal access to services. Key issues include high maternal and under-5 mortality rates, poor health resource distribution, and a significant reliance on an unregulated private sector. It concludes that India's healthcare performance lags behind global standards due to poor governance, insufficient funding, and inequitable resource allocation.