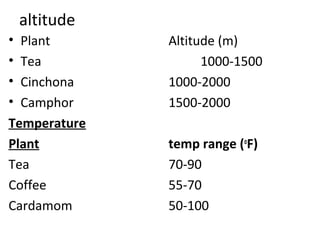
Cultivation of medicinal plants has several advantages including ensuring quality, purity, yield and regular supply. It also allows for modern technologies and industrialization. The main methods of cultivation are seed propagation and asexual propagation. Seed propagation uses seeds to grow seedlings, which are long-lived though variable, while asexual propagation uses vegetative parts for uniform plants that fruit earlier. Factors like altitude, temperature, rainfall, soil type and fertilizers must be considered for proper cultivation. Collection methods vary by plant part and drying can be natural or using equipment like tray or vacuum dryers.