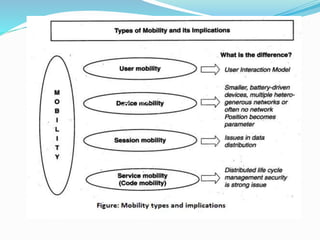
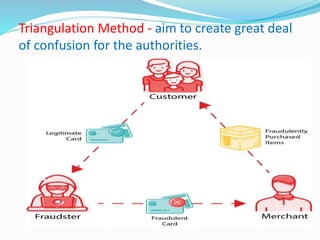
This document discusses security challenges posed by mobile devices. It begins by outlining three main types of threats: application-based threats like malware and spyware; web-based threats like phishing and drive-by downloads; and network-based threats when using public WiFi.
Application-based threats occur when malicious apps steal data or request unnecessary permissions. Web-based threats happen through compromised websites that download malware. Network-based threats risk intercepting unencrypted data on public WiFi networks.
The document provides examples for each threat type and recommends mitigation strategies like mobile application management, secure web browsing practices, and VPNs for public networks. Managing a variety of personal and company-owned devices poses additional challenges to