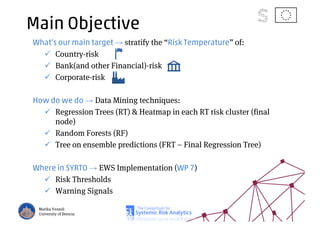
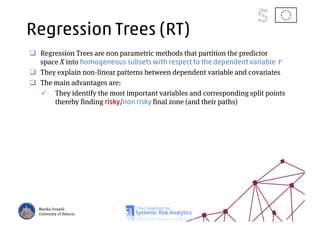
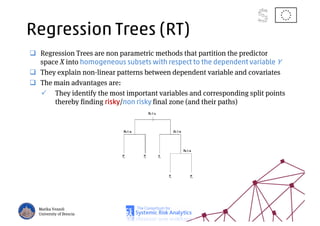
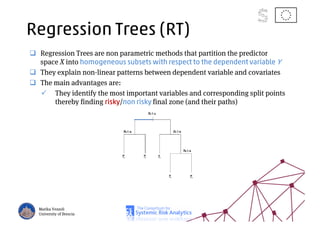
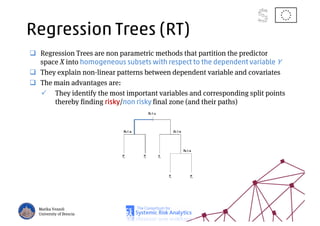
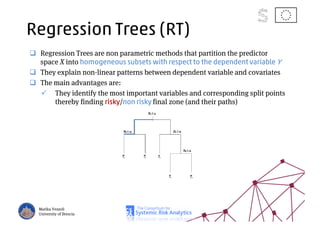
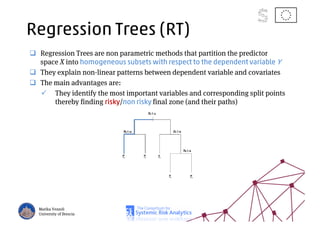
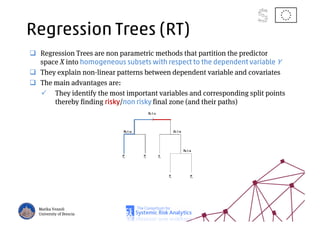
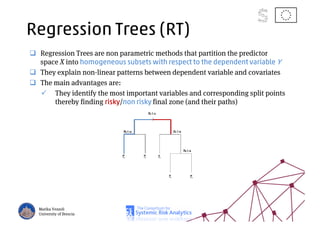
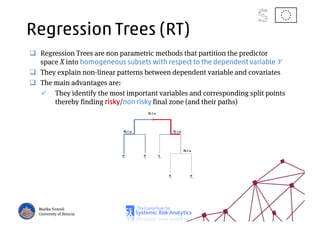
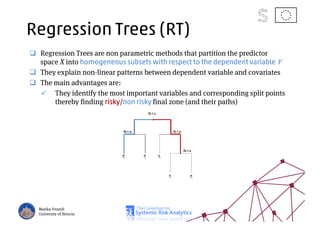
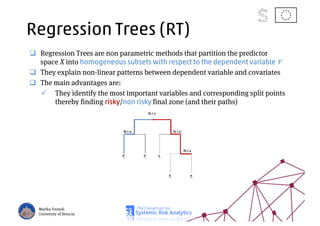
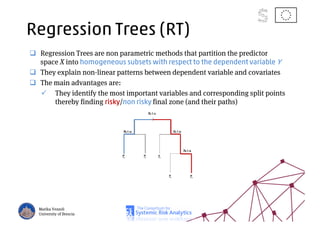
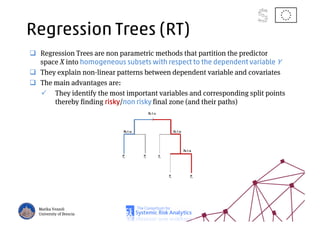
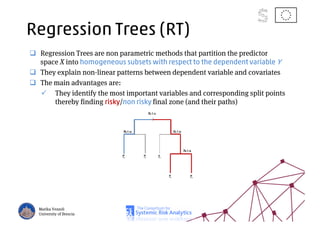
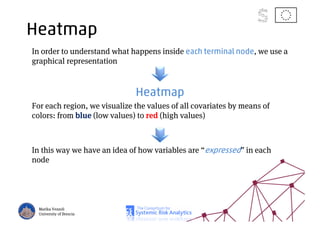
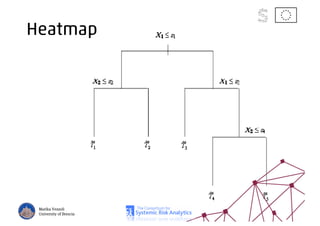
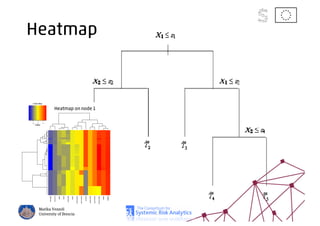
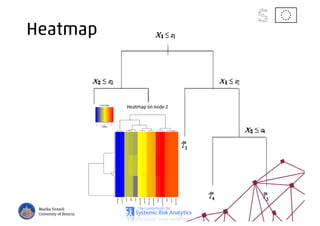
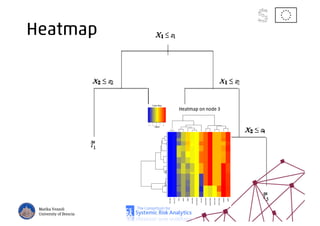
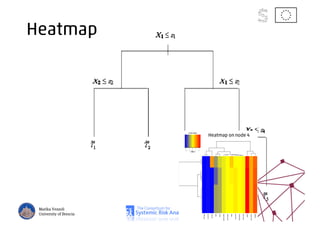
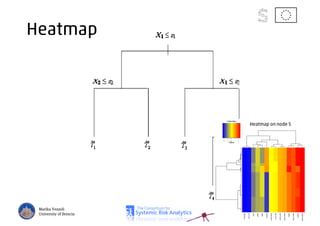
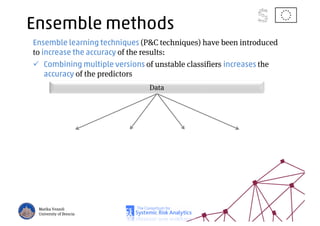
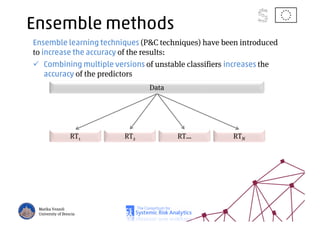
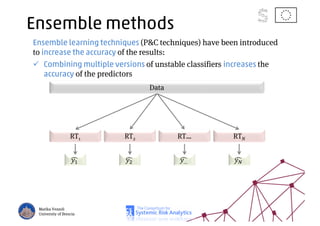
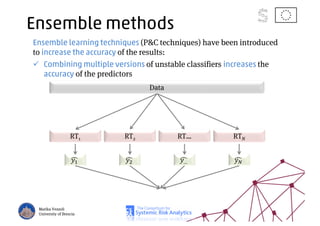
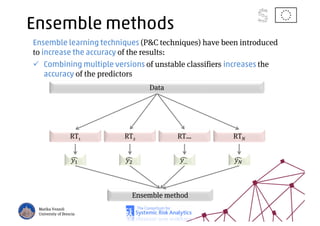
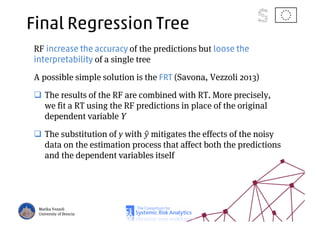
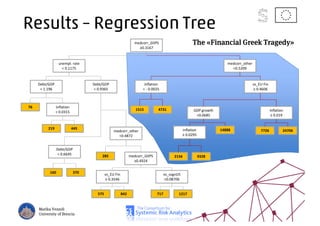
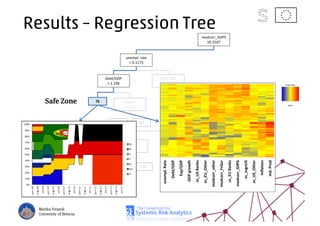
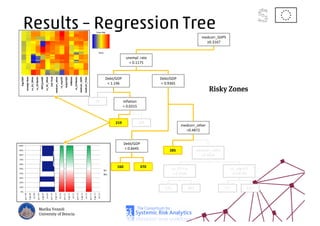
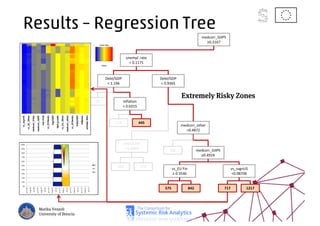
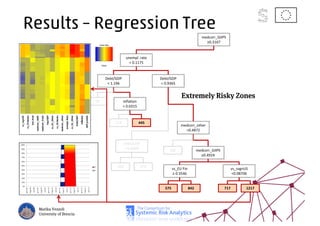
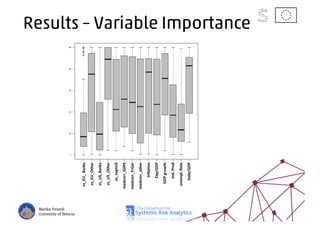
The document discusses using machine learning, particularly regression trees and ensemble methods, to detect financial risk zones across various sectors, including country, bank, and corporate risks. It highlights the methods' capabilities in identifying critical variables and risk thresholds, applying these techniques to analyze the financial instruments of different European countries, specifically during the euro crisis. Additionally, the project, funded by the EU, aims to enhance predictive accuracy while addressing the challenges posed by noisy data.