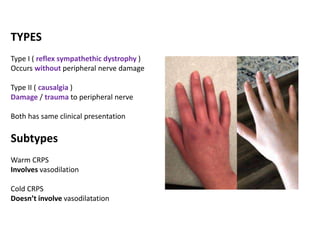
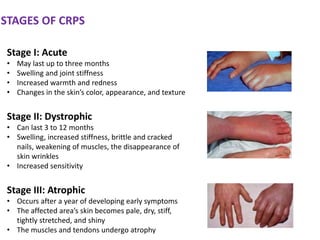
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS) is a neuropathic pain disorder characterized by long-lasting pain that exceeds the underlying injury, with potential genetic, inflammatory, and immunological factors involved. Symptoms include varying degrees of pain, hyperalgesia, functional impairment, and changes in skin appearance. Treatment options range from lifestyle changes and physiotherapy to pharmacotherapy and other therapies for symptom management.