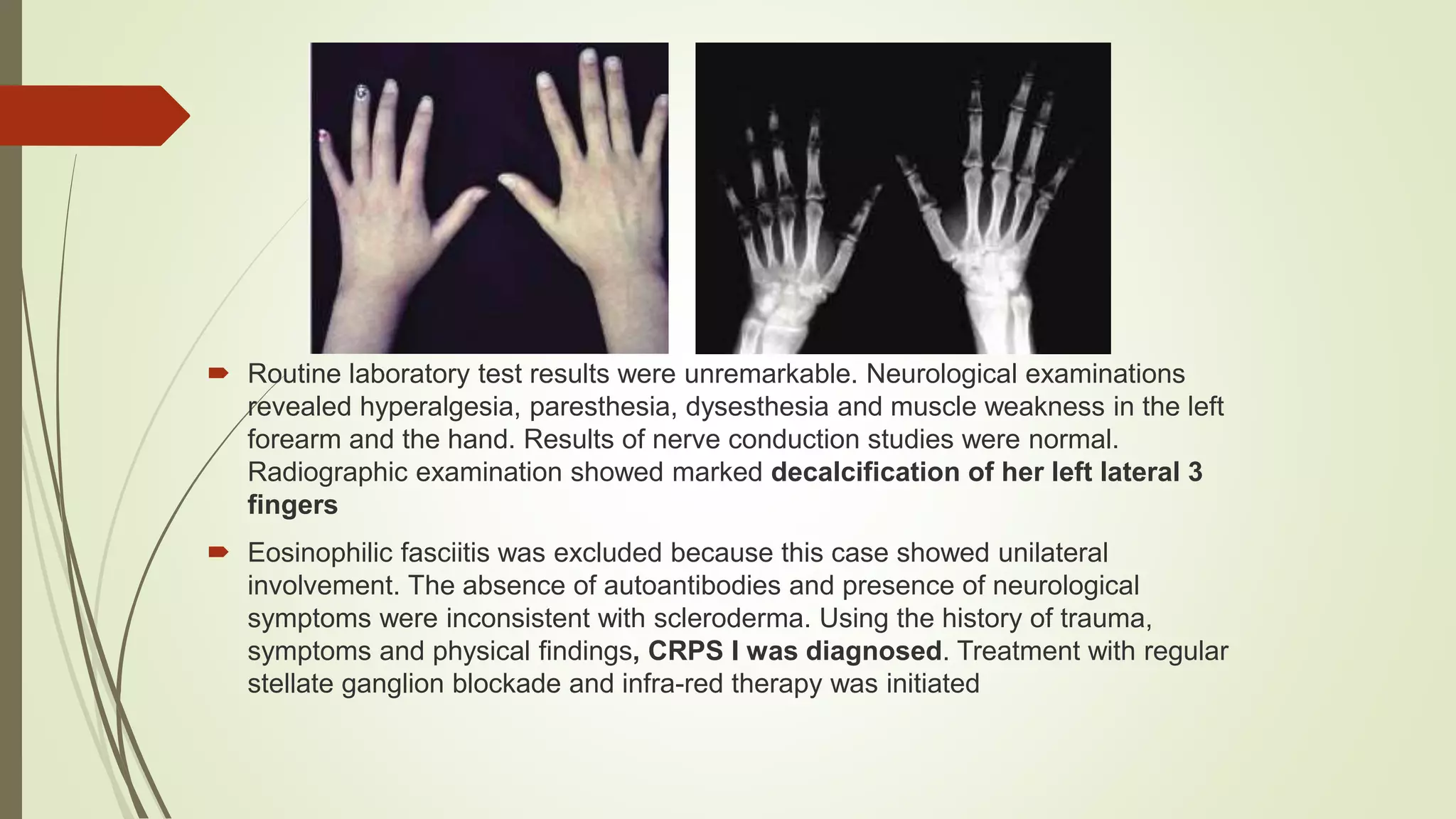
This document presents a case study of a 25-year-old woman diagnosed with Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS) type 1. She experienced persistent pain and skin changes in her left hand following a wrist sprain one year prior. Her symptoms met the diagnostic criteria for CRPS based on her history of trauma and symptoms including pain, skin changes, and neurological abnormalities. Treatment for her condition involved stellate ganglion blockade and infrared therapy.